26 Model-model Komunikasi
Summary
TLDRThe script discusses various communication models, starting with the stimulus-response model, where reactions are formed based on messages received. It explores Aristotle’s rhetorical model, Lasswell’s five components of communication, and Shannon-Weaver’s mathematical model, highlighting the roles of communicator, message, medium, and receiver. It also touches on models like Helix, which portrays the growth of communication skills over time, and the two-step flow model, which emphasizes the influence of opinion leaders. Additionally, it delves into the complexities of communication, including cultural, psychological, and contextual factors that shape the exchange of messages.
Takeaways
- 😀 Models are representations of real or abstract phenomena, used to display important elements of those phenomena.
- 😀 Communication models describe the ideal process of communication, and their effectiveness depends on their simplicity, explanatory power, and general applicability.
- 😀 The stimulus-response model suggests that individuals react to a message they receive, like stopping at a red traffic light to avoid punishment.
- 😀 The Aristotelian model, known as the rhetorical model, involves a communicator delivering a message to an audience to persuade them, like a professor motivating students to study.
- 😀 Lasswell's model outlines five key components of communication: who, says what, in which channel, to whom, and with what effect.
- 😀 The SMCA model emphasizes the importance of four components: communicator, message, medium, and communicator skills in encoding and decoding messages.
- 😀 Shannon-Weaver's mathematical model illustrates how communication works through mediums like radio, involving encoding, transmission, and decoding of messages.
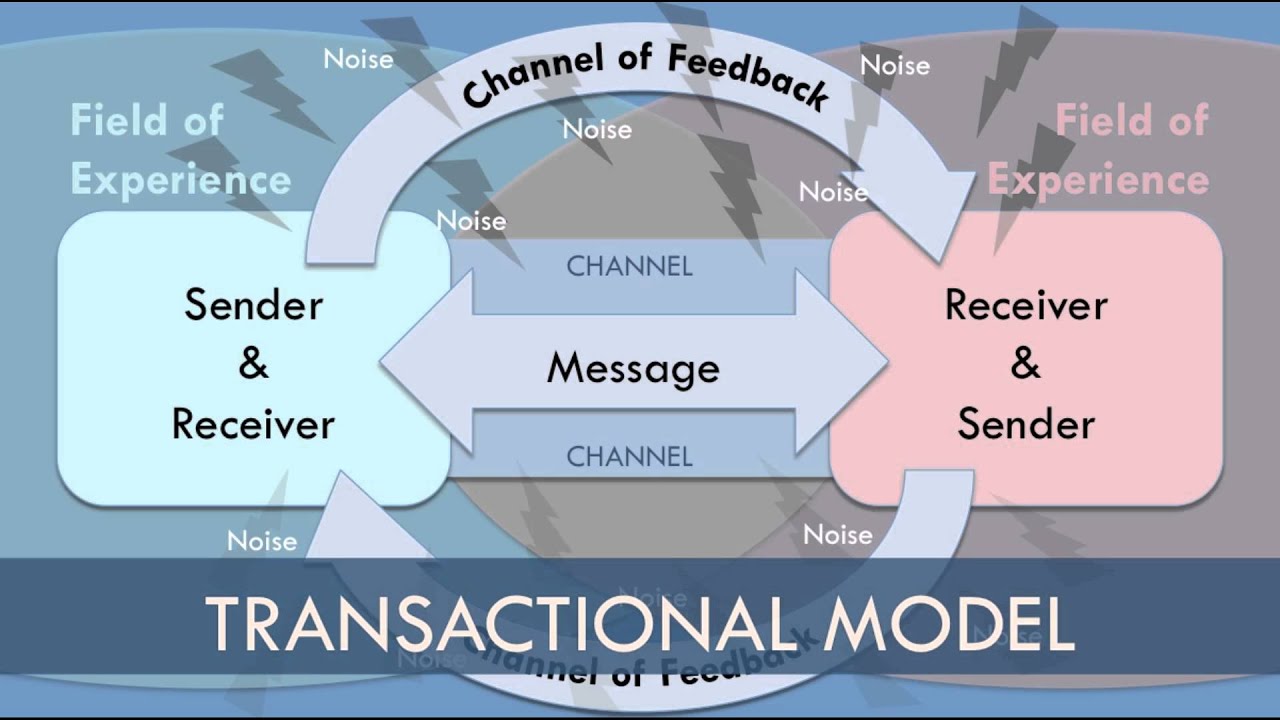
- 😀 The transactional model suggests communication is reciprocal, with both participants encoding and decoding messages, thus shaping ideas and perceptions.
- 😀 The two-step flow model posits that mass media influence is mediated by opinion leaders, who interpret messages for the audience.
- 😀 Helix's spiral model suggests that communication grows and evolves over time, improving with experience, starting from birth and developing as individuals age.
- 😀 Contexts such as physical, time, cultural, and social-psychological factors impact communication, shaping how messages are perceived and understood.
Q & A
What is a model, and what purpose does it serve?
-A model is a simplified representation of a real or abstract phenomenon, displaying its essential elements. Models help understand phenomena and can be in verbal, visual, or 3D formats, such as architectural models or airplane designs.
How does the Stimulus-Response (SR) model of communication work?
-The SR model explains that people react to messages they receive. For example, drivers stop when the traffic light turns red. This behavior, initially learned through punishment or fines, becomes a habit over time.
What is the Aristotelian model of communication?
-The Aristotelian model, also known as the rhetorical model, involves a communicator delivering a message to an audience in a specific context, with the aim of persuading them to act, such as a professor delivering a lecture to motivate students.
What are the five components in the Lasswell model of communication?
-The Lasswell model breaks down communication into five components: Who (communicator), says What (message), in Which channel (medium), to Whom (audience), and with What effect.
How does the SMCA model explain communication?
-The SMCA model focuses on four components: the communicator (source), the message, the medium (channel), and the communicator's skill in encoding and decoding the message, as well as their attitude and knowledge about the subject.
What role does noise play in the Shannon-Weaver model of communication?
-In the Shannon-Weaver model, noise refers to any interference, such as weather conditions or technical disruptions, that can distort the message during transmission, affecting the accuracy of the communication process.
What is the two-step flow of communication theory?
-The two-step flow of communication theory suggests that mass media influences the audience indirectly through opinion leaders, who interpret and transmit the messages to the larger audience, rather than directly influencing them.
What is the Helix model of communication, and how does it relate to human experience?
-The Helix model describes communication as a continuous, evolving process, where a person’s ability to communicate expands with age and experience. The model illustrates that communication grows and becomes more sophisticated over time.
What factors affect the context of communication according to Devito's model?
-Devito's model identifies several contexts that affect communication, such as physical context (environmental factors), time context (e.g., morning vs. evening), cultural context (values, language), and social-psychological context (mood or emotional state).
How does Kim's model of intercultural communication differ from other models?
-Kim's model emphasizes two-way communication between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, highlighting how differences in culture, values, language, and perceptions affect the communication process, where both communicators act as encoders and decoders of messages.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)