SEGITIGA ISTIMEWA SUDUT 30,60,90 DAN SUDUT 45,45,90
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, Ibu Rita explains the concept of special right-angled triangles, specifically the 30°-60°-90° and 45°-45°-90° triangles, and how to use side ratios to calculate unknown side lengths. Through clear examples, she demonstrates the process of solving for sides using known ratios, making it easy for students to understand and apply the Pythagorean theorem. The video emphasizes the importance of memorizing the side ratios for these triangles to quickly solve geometry problems. Overall, it provides practical insight into understanding and applying special triangle properties in mathematics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Special triangles are right-angled triangles where only one side length is known, unlike the Pythagorean theorem where two sides are provided.
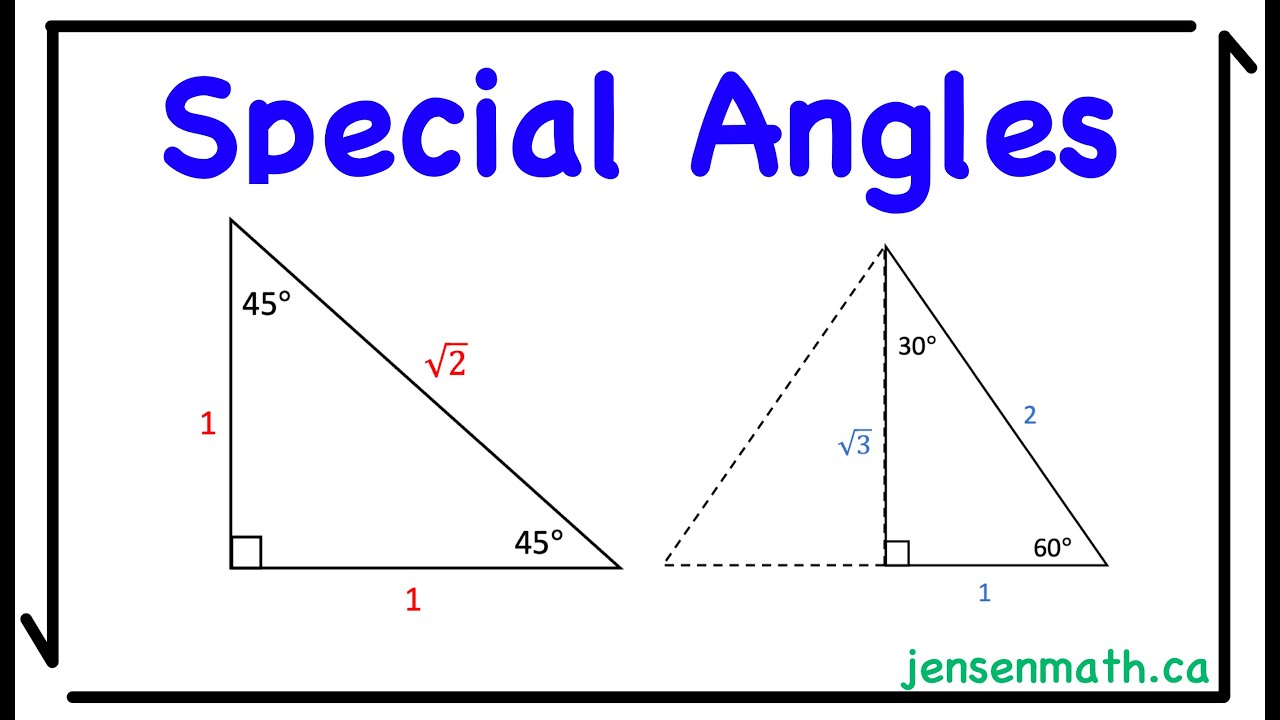
- 😀 A 30°-60°-90° triangle has a side ratio of 1:√3:2 (opposite 30°: opposite 60°: hypotenuse).
- 😀 In a 45°-45°-90° triangle, the legs are equal, and the ratio of the sides is 1:1:√2 (legs: hypotenuse).
- 😀 The main difference between special triangles and the Pythagorean theorem is that only one side is given in special triangles.
- 😀 To solve problems involving 30°-60°-90° triangles, you multiply the known side by the appropriate ratio (1, √3, or 2).
- 😀 For 30°-60°-90° triangles, if the hypotenuse is known, the legs can be calculated by halving the hypotenuse or multiplying it by √3/2.
- 😀 For 45°-45°-90° triangles, if the legs are known, the hypotenuse is calculated by multiplying the leg by √2.
- 😀 Special triangle problems involve using specific ratios to find unknown side lengths based on given angles.
- 😀 The instructor demonstrates using examples of both triangle types to find missing sides, showcasing the simplicity of the method once the ratios are known.
- 😀 Memorizing the ratios for each type of special triangle is essential for quick and efficient problem-solving in trigonometry.
Q & A
What is a special triangle (segitiga istimewa)?
-A special triangle is a method used to calculate the length of one side of a right triangle when only one side length is known. It is different from the Pythagorean Theorem, where two side lengths are known.
How is a special triangle different from the Pythagorean theorem?
-In the Pythagorean theorem, two side lengths are given, and the third is calculated. In a special triangle, only one side length is known, and the sides are determined using specific ratios.
What is the specific angle configuration of a special triangle in this script?
-The special triangle discussed in this script has angles of 30°, 60°, and 90°.
What is the relationship between the sides of a 30°-60°-90° triangle?
-For a 30°-60°-90° triangle, the sides are in the ratio 1 : √3 : 2. The side opposite the 30° angle is 1, opposite the 60° angle is √3, and the hypotenuse is 2.
What is the formula for the sides of an isosceles right triangle (45°-45°-90°)?
-In a 45°-45°-90° isosceles right triangle, the two legs are equal in length, and the ratio of the legs to the hypotenuse is 1 : 1 : √2.
How do you calculate the length of side PQ in a 30°-60°-90° triangle, given the hypotenuse is 20 cm?
-For a 30°-60°-90° triangle with the hypotenuse of 20 cm, the side opposite the 30° angle (PQ) is calculated by dividing the hypotenuse by 2, resulting in PQ = 10 cm.
How is the length of PR determined in the 30°-60°-90° triangle in the example?
-The length of PR, which is opposite the 60° angle, is found by multiplying the hypotenuse by √3/2. In this case, PR = 10√3 cm.
What is the method for finding the side length of an isosceles right triangle (45°-45°-90°)?
-In an isosceles right triangle (45°-45°-90°), if one leg is known (8 cm), the other leg is the same, and the hypotenuse is found by multiplying the leg length by √2, so the hypotenuse is 8√2 cm.
What is the process to calculate side ML in the isosceles right triangle with legs of 8 cm?
-To find ML in the 45°-45°-90° triangle, multiply the leg length (8 cm) by √2. The result is ML = 8√2 cm.
What is the importance of knowing the ratios in special triangles when solving for side lengths?
-Knowing the ratios of side lengths in special triangles (like 1 : √3 : 2 for a 30°-60°-90° triangle) simplifies the process of finding missing side lengths, as it eliminates the need for complicated calculations and allows for straightforward multiplication or division.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Teorema Pythagoras [Part 4] - Menentukan Perbandingan Sisi Segitiga Siku-siku

Matematika kelas 8 | cara menghitung panjang sisi segitiga siku-siku yang memiliki sudut 30° dan 60°

TRIGONOMETRI SUDUT ISTIMEWA
Special Triangles (full lesson) | jensenmath.ca

TEOREMA PYTHAGORAS : MATEMATIKA KELAS 8 SMP

Geometry 8-3: The Law of Sines
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)