Giardiasis - Giardia Lamblia
Summary
TLDRGiardiasis is a parasitic infection caused by *Gardia lamblia*, commonly found in developing countries due to poor sanitation. The infection is spread through contaminated water, leading to symptoms like diarrhea, abdominal pain, and nausea. The parasite has two forms: cysts, which are infective, and trophozoites, which attach to the intestines. Diagnosis involves stool examination and the string test, while Metronidazole is the main treatment. Chronic infections can result in malabsorption of nutrients, highlighting the importance of proper diagnosis and treatment for those affected.
Takeaways
- 😀 Giardiasis is caused by the protozoan *Giardia intestinalis* (also known as *Giardia lamblia*), primarily affecting people in developing countries.
- 😀 The infection is a major cause of diarrhea-like symptoms, abdominal pain, and nausea, especially in children.
- 😀 Giardia exists in two forms: cysts (infective) and trophozoites (active form that causes infection).
- 😀 Giardia cysts are ovoid, 10 micrometers in diameter, and contain four nuclei, making them the infective form.
- 😀 Trophozoites are pear-shaped and have eight flagella and two suction discs, which help them attach to the small intestine's mucosal surface.
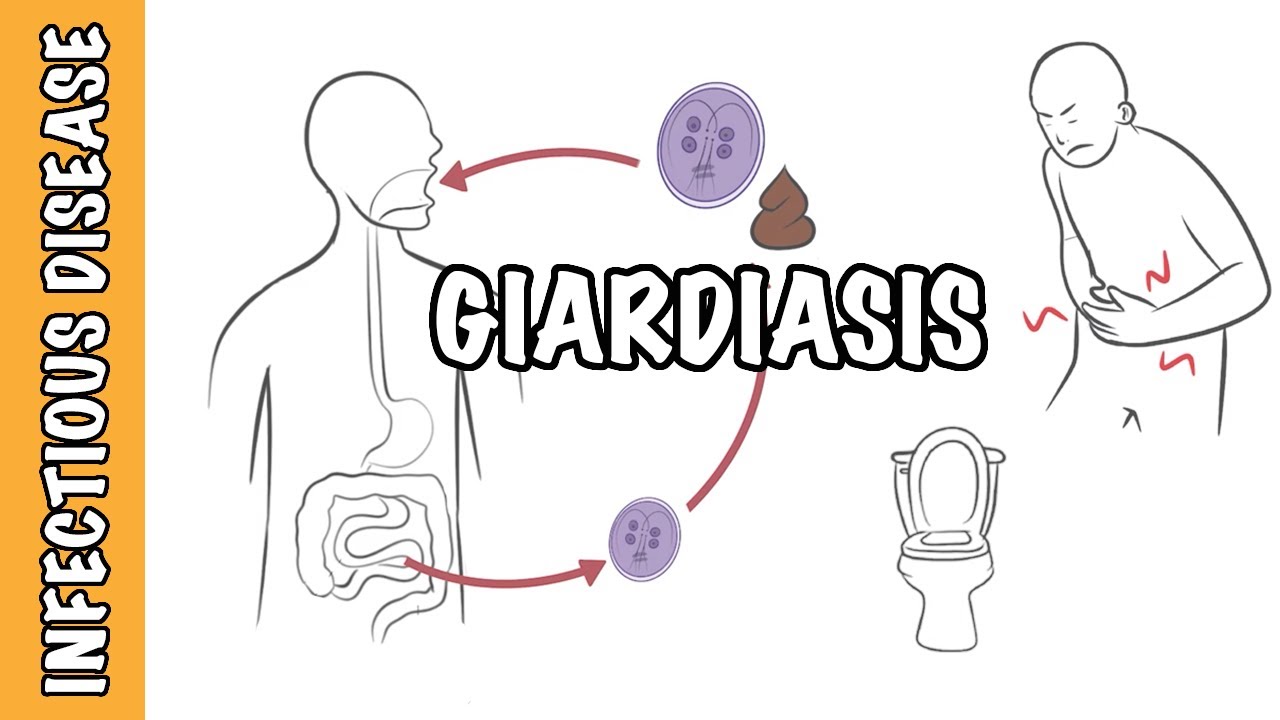
- 😀 Infection begins when a person ingests Giardia cysts from contaminated water or food.
- 😀 After ingestion, cysts transform into trophozoites in the small intestine through excystation, where they multiply and damage the intestinal lining.
- 😀 Some trophozoites encyst in the colon, and the cysts are passed out in the feces, completing the infection cycle.
- 😀 Symptoms of giardiasis include abdominal pain, nausea, and diarrhea. Chronic infections can lead to vitamin B12 malabsorption and lactose intolerance.
- 😀 Diagnosis of giardiasis can be done through microscopic examination of stool samples or by using the string test if stool samples are negative.
- 😀 Metronidazole is the main treatment for giardiasis, commonly used for other protozoan infections as well.
Q & A
What is giardiasis?
-Giardiasis is an infection caused by the protozoan *Giardia lamblia* (also known as *Giardia intestinalis*), which primarily affects the gastrointestinal tract.
Why is giardiasis particularly problematic in developing countries?
-Giardiasis is a major issue in developing countries due to factors like overcrowding, unhygienic environments, and poor water quality control, making the transmission of *Giardia* more likely.
How is giardiasis transmitted?
-Giardiasis is transmitted through the ingestion of *Giardia* cysts, typically found in contaminated water or food.
What are the symptoms of giardiasis?
-Symptoms of giardiasis include abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, and occasionally, blood and mucus in stool. Chronic infections can lead to issues like vitamin B12 malabsorption and lactose intolerance.
What are the two forms of *Giardia lamblia*?
-The two forms of *Giardia lamblia* are the cyst (the infective form) and the trophozoite (the active, mobile form).
How does the *Giardia* cyst cause infection in the human body?
-After being ingested, the *Giardia* cyst travels through the digestive tract and reaches the small intestine. There, it transforms into trophozoites that attach to the intestinal wall, causing symptoms.
What is the role of trophozoites in giardiasis?
-Trophozoites are the active form of *Giardia* that attach to the mucosal surface of the small intestine, causing abdominal pain, cramps, and diarrhea. They can also move to the colon and form cysts.
What is the significance of cyst formation in *Giardia* infection?
-Cyst formation in the colon helps *Giardia* survive outside the body. Cysts are highly resistant and can persist in the environment, making it easier for the infection to spread.
How is giardiasis diagnosed?
-Giardiasis can be diagnosed by examining stool samples under a microscope to detect cysts or trophozoites. If this test is negative but giardiasis is still suspected, a string test can be used to collect samples from the small intestine.
What treatment is typically used for giardiasis?
-The standard treatment for giardiasis is metronidazole, an antibiotic used to target protozoan infections like giardiasis.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

AMEBÍASE - ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA - PARASITOLOGIA| INFECTOLOGIA
Giardiasis - Giardia Lamblia (Giardia intestinalis, Giardia duodenalis) infection

PATOFISIOLOGI GIS CASE 4 "STUNTING, INFEKSI CACING, DAN ANEMIA DEFISIENSI BESI" - ray

Introduction to Protozoa - the unicellular parasites (amoeba, giardia, leishaniasia, plasmodium)

Schistosomiasis (Bilharzia)– an overview

ANCILOSTOMÍASE: A. duodenales e N. americanus | PARASITOLOGIA #16
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)