DNA Rekombinan - Pembuatan Insulin
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the process of recombinant DNA technology, focusing on gene cloning and insulin production. It explains the isolation and cutting of DNA using restriction enzymes, the recombination with vectors like E. coli plasmids, and the introduction of recombinant DNA into host organisms. The script highlights the production of insulin through bacteria as an example, as well as the potential for creating transgenic plants, such as tobacco, to produce proteins like insulin. The technology's significance in biotechnology, medicine, and agriculture is emphasized, showcasing its transformative impact on various industries.
Takeaways
- 😀 Recombinant DNA technology is used in gene cloning, where two different DNA strands are combined.
- 😀 Recombinant DNA is commonly used to produce products like insulin and other biotechnological applications.
- 😀 Insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar, is a common product made using recombinant DNA technology.
- 😀 To make recombinant DNA, DNA is extracted from humans (e.g., pancreatic cells for insulin) and cut using restriction enzymes.
- 😀 A vector, like the E. coli bacteria, is used to carry and insert the desired DNA (e.g., insulin gene) into the host organism.
- 😀 Plasmids, small DNA molecules within bacteria, are often used as vectors in recombinant DNA technology.
- 😀 After DNA is inserted into the vector, it is introduced into bacteria where it replicates and produces the desired product.
- 😀 The cloning process involves isolating the gene of interest, cutting it with restriction enzymes, and combining it with a vector.
- 😀 Bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) can also be used as vectors for gene insertion in recombinant DNA technology.
- 😀 Recombinant DNA technology can be applied to plants, such as tobacco, to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) capable of producing substances like insulin.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA technology?
-Recombinant DNA technology involves combining two different DNA strands to create recombinant DNA. This technique allows scientists to isolate specific genes from one organism and insert them into another organism to produce desired traits or products, such as insulin.
How is insulin produced using recombinant DNA technology?
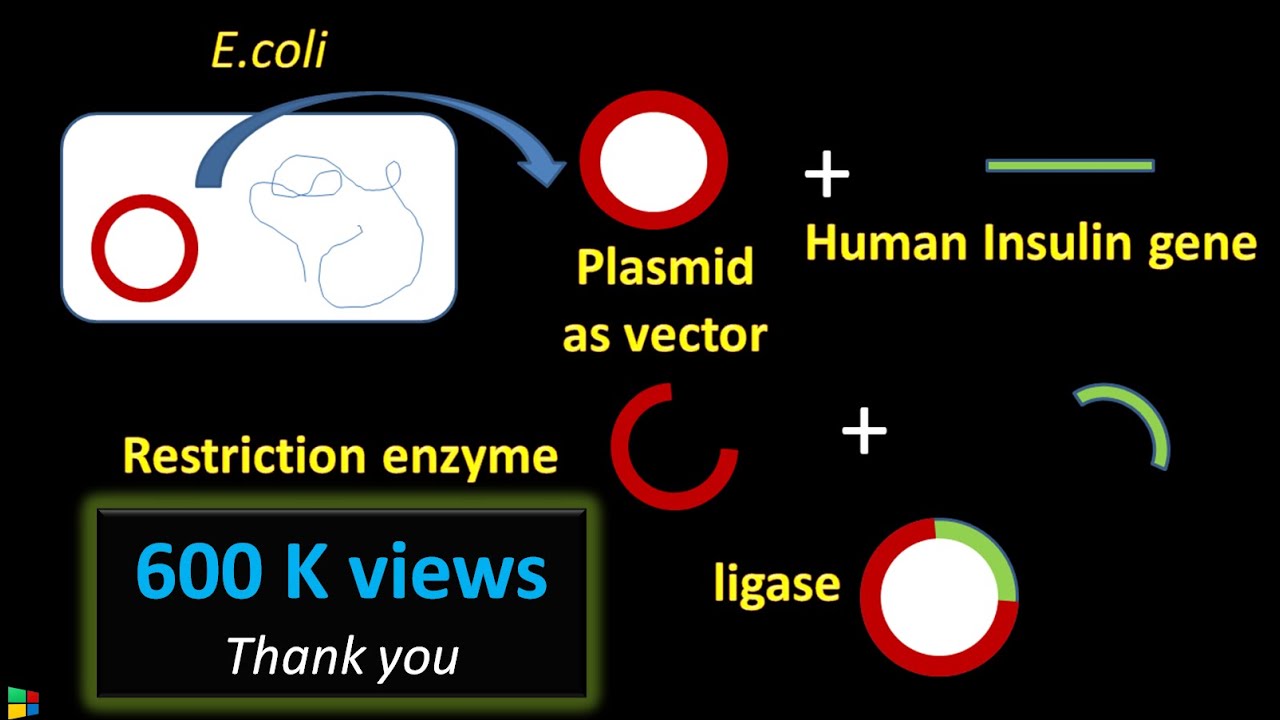
-Insulin is produced by isolating the insulin gene from human DNA, cutting it using restriction enzymes, and inserting it into a plasmid from a bacterium (such as *E. coli*). The recombinant plasmid is then introduced into the bacteria, which multiply and produce insulin.
What role do restriction enzymes play in recombinant DNA technology?
-Restriction enzymes, or endonucleases, are used to cut DNA at specific locations. In the case of insulin production, they are used to cut the human DNA to isolate the insulin gene, which can then be inserted into another DNA molecule, such as a plasmid.
What is a plasmid and how is it used in recombinant DNA technology?
-A plasmid is a small, circular piece of DNA found in bacteria. It is often used as a vector in recombinant DNA technology to carry foreign genes, like the insulin gene, into bacterial cells, where the genes can be replicated and expressed.
What is the purpose of using *E. coli* in the recombinant DNA process?
-*E. coli* is used in recombinant DNA technology because it is a fast-growing bacterium. Once the recombinant DNA is introduced into *E. coli*, the bacteria can rapidly multiply and produce the desired product, such as insulin.
What is the significance of gene cloning in biotechnology?
-Gene cloning allows scientists to produce specific genes in large quantities, which can be used for various applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals (e.g., insulin), genetic research, and the development of genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
Can recombinant DNA technology be applied to plants?
-Yes, recombinant DNA technology can be used in plants to create transgenic plants. These plants contain genes from other species. For example, plants like tobacco can be engineered to produce human insulin, making them a potential source for insulin production.
What are transgenic plants and how are they related to recombinant DNA technology?
-Transgenic plants are plants that contain genes from other species, achieved through recombinant DNA technology. This allows for the introduction of new traits, such as the ability to produce human proteins like insulin.
What is the process of isolating and cutting DNA in recombinant DNA technology?
-The process involves isolating the desired DNA (e.g., the insulin gene) from the organism's genome. The DNA is then cut at specific locations using restriction enzymes to isolate the gene, which can be inserted into another DNA molecule for further manipulation.
What is the role of bacterial transformation in recombinant DNA technology?
-Bacterial transformation involves introducing recombinant DNA into bacterial cells. Once the DNA is inside, the bacteria can replicate and express the foreign genes, producing proteins like insulin or other desired products.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Steps in Recombinant DNA Technology or rDNA technology | Biotechnology

CBSE Class 12 Biology || Biotechnology Principles And Processes || Full Chapter || By Shiksha House
Bioteknologi: Rekayasa Genetika | Biologi SMA | Alternatifa

Animation E4, 1.1 Production of human insulin

Cloning Vectors | Plasmid | Insertional Inactivation |Cosmid|Artificial Chromosome|Class 11 Biology

Ch. 20 - Part 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)