Animation E4, 1.1 Production of human insulin
Summary
TLDRThis script outlines the process of producing human insulin using recombinant DNA technology. It starts with obtaining DNA encoding insulin from human pancreatic cells and cutting it with a restriction enzyme. A plasmid with antibiotic resistance genes is similarly treated. Recombinant plasmids are formed by joining the DNA fragments with the plasmids using DNA ligase. These are introduced into E. coli bacteria, with only some taking up the plasmids, leading to transformed bacteria. A selection process using agar plates with antibiotics identifies colonies with recombinant plasmids. These bacteria are cultured in fermenters, where the plasmid replicates, leading to the production of insulin-encoding DNA. Finally, gene expression is induced to produce polypeptides, which are processed into human insulin.
Takeaways
- 🧬 **DNA Extraction**: DNA encoding human insulin is obtained from human pancreatic cells.
- 🔪 **Restriction Enzyme**: A restriction enzyme is used to cut the DNA and a plasmid from bacteria.
- 🤝 **DNA Ligation**: Recombinant plasmids are formed by joining DNA fragments with plasmids using DNA ligase.
- 🚫 **Non-recombinant Plasmids**: Some plasmids bind without DNA fragments, forming non-recombinant plasmids.
- 🦠 **Bacterial Transformation**: Plasmids are introduced into E. coli bacteria, some of which become transformed.
- 💊 **Antibiotic Selection**: Transformed bacteria with recombinant plasmids are selected using ampicillin resistance.
- 🌿 **Colony Formation**: Surviving bacteria form colonies on agar plates, indicating successful transformation.
- 🔄 **Secondary Selection**: A second antibiotic, tetracycline, is used to differentiate recombinant from non-recombinant bacteria.
- 📈 **Fermentation Process**: Selected bacteria are cultured in fermenters to replicate and produce insulin-encoding DNA.
- 🔬 **Gene Expression**: Insulin production is induced in bacteria, and the polypeptides are extracted and processed.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA technology?
-Recombinant DNA technology is a method used to create new combinations of genetic material by cutting and joining together DNA fragments from different sources, which can be used for various applications such as producing human insulin.
How is human insulin DNA obtained?
-Human insulin DNA is obtained from a human pancreatic cell.
What is the role of a restriction enzyme in the production process?
-A restriction enzyme is used to cut the DNA encoding human insulin and also to open up a plasmid to allow the insertion of the insulin DNA.
What is a plasmid and where is it obtained from?
-A plasmid is a small circular DNA molecule found in bacteria that can replicate independently of the chromosomal DNA. It is obtained from a bacterium and used as a vehicle to carry the insulin DNA into E. coli.
What is the purpose of antibiotic resistance genes in the plasmid?
-Antibiotic resistance genes in the plasmid serve as a selectable marker to identify bacteria that have been successfully transformed with the plasmid.
How are recombinant plasmids formed?
-Recombinant plasmids are formed when the cut DNA encoding human insulin binds to the opened plasmid and is joined together with the help of DNA ligase.
What are non-recombinant plasmids?
-Non-recombinant plasmids are those that have not picked up any DNA fragments and have joined by themselves.
How are plasmids introduced into E. coli bacteria?
-Plasmids are mixed with E. coli bacteria to introduce them into the host cells.
How are transformed bacteria selected using agar plates?
-Transformed bacteria are selected by culturing them on agar plates containing antibiotics. Only bacteria with the plasmid's resistance gene can survive and form colonies.
Why are two different antibiotics used in the selection process?
-Two different antibiotics, ampicillin and tetracycline, are used to distinguish between bacteria with recombinant and non-recombinant plasmids. Bacteria with recombinant plasmids cannot survive on tetracycline because the inserted DNA fragment makes the tetracycline resistance gene non-functional.
How is human insulin produced from the transformed bacteria?
-Human insulin is produced by inducing gene expression in the transformed bacteria to produce polypeptides, which are then extracted and processed into functional human insulin.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How synthetic Insulin is made using Recombinant DNA Technology From Bacteria

Animation 27.1 Basic principle of recombinant DNA technology

Genetic engineering | Genetics | Biology | FuseSchool

Genetic Modification Explained || Insulin-Producing Bacteria
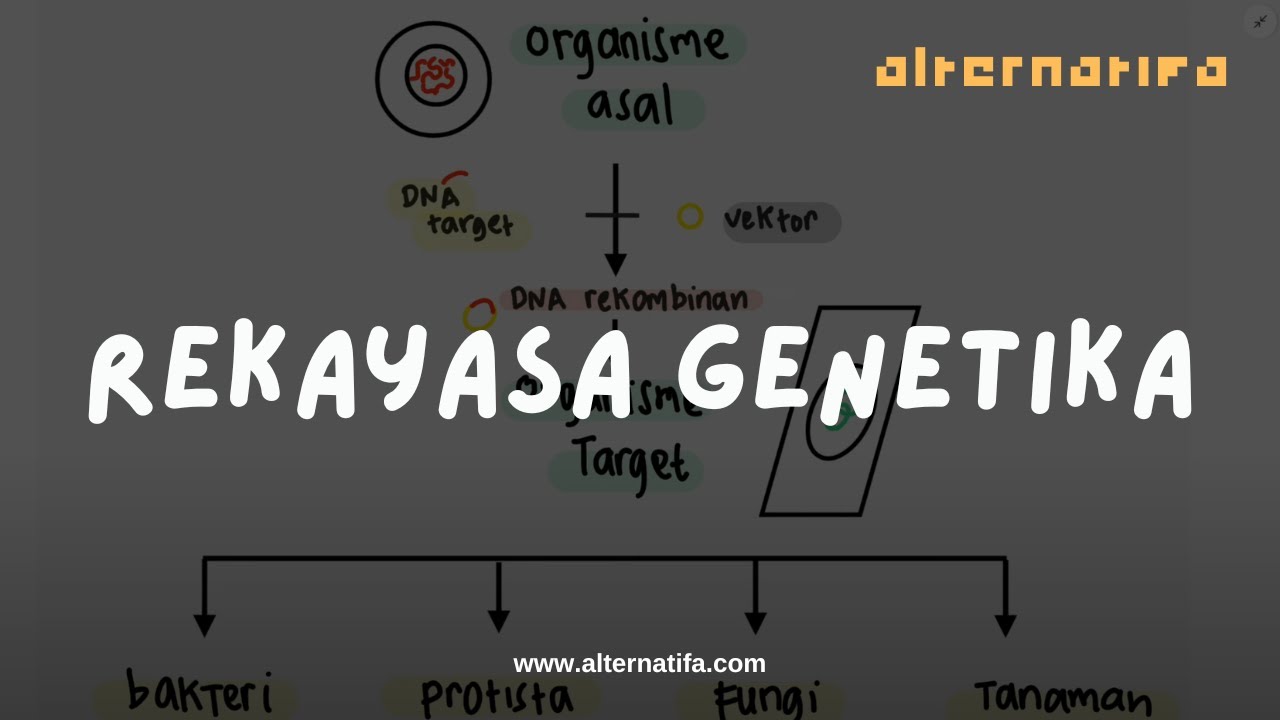
Bioteknologi: Rekayasa Genetika | Biologi SMA | Alternatifa

Genetic Engineering
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)