Ch. 20 - Part 1
Summary
TLDRThis recording covers the fundamentals of recombinant DNA technology, focusing on isolating and manipulating DNA fragments to create new arrangements. It explains the processes of gene cloning, including the use of chromosomal and vector DNA, restriction enzymes, and plasmids. The steps for gene cloning, the importance of sticky ends, and the role of DNA ligase are detailed. Additionally, it discusses complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis, the creation of genomic and cDNA libraries, and their applications in gene cloning and research.
Takeaways
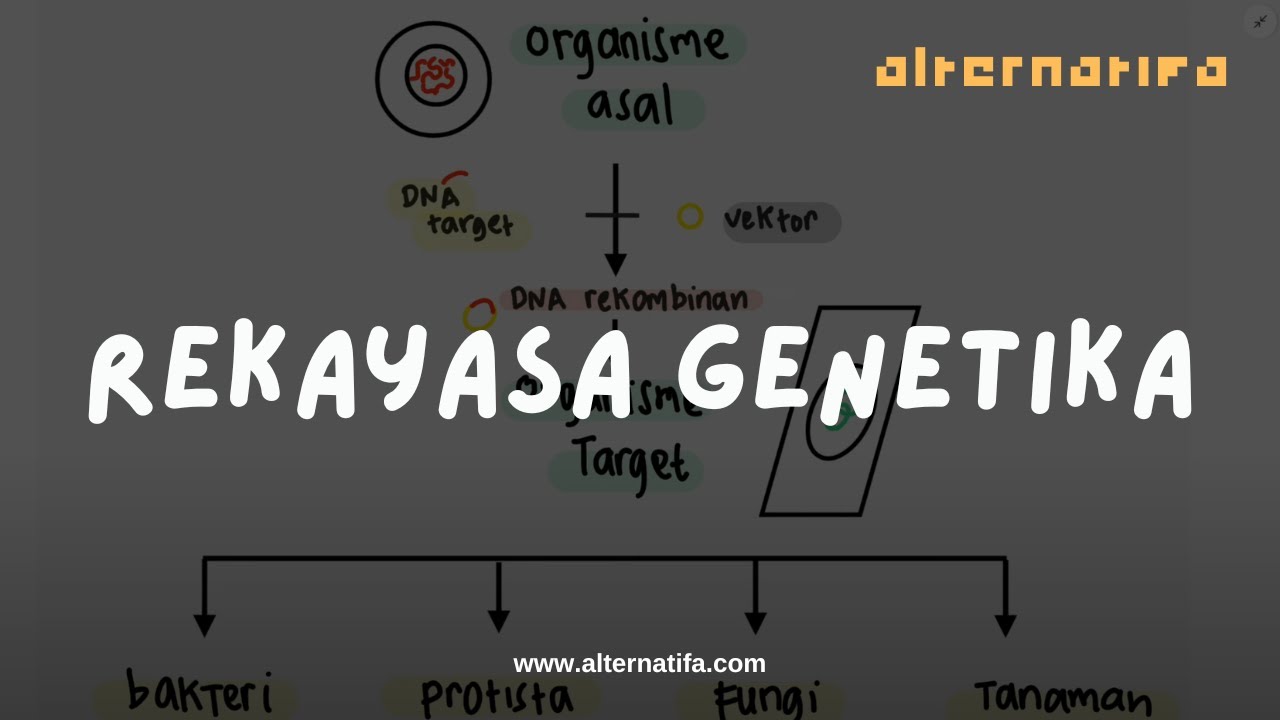
- 🧬 Recombinant DNA technology is used to isolate and manipulate DNA fragments to create new arrangements for various applications like research and gene therapy.
- 🔬 Gene cloning involves making multiple copies of a gene and is utilized in areas such as DNA sequencing, gene editing, and biotech research.
- 🌟 There are two types of DNA fragments in cloning: chromosomal DNA, which contains the gene of interest, and vector DNA, which integrates into the host cell and replicates independently.
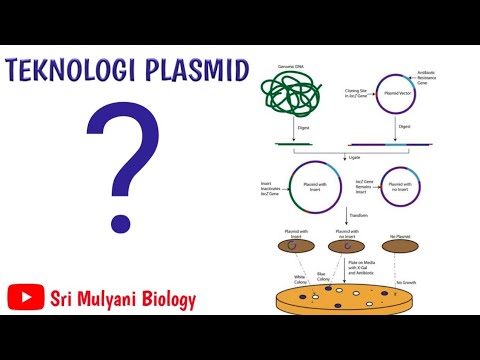
- 🔄 Plasmids are the most common vector DNA, naturally occurring in bacteria, with features like an origin of replication and unique restriction sites for DNA insertion.
- 📌 Plasmids also have selectable markers, often antibiotic resistance genes, which help in selecting bacterial colonies that contain the plasmids with the gene of interest.
- ✂️ Restriction enzymes, also known as endonucleases, are specific enzymes that recognize and cut DNA at particular sequences, creating sticky ends crucial for cloning.
- 🔄 Most restriction enzymes generate palindromic sequences that read the same forwards and backwards, facilitating the formation of sticky ends for DNA fragment combination.
- 🔬 DNA ligase is essential in cloning experiments, as it seals the gaps in the DNA backbone, creating stable recombinant DNA.
- 🛠️ The gene cloning process involves several steps: purification of chromosomal DNA, use of the same restriction enzyme on vector DNA, mixing and ligation, transformation, and selection of transformed cells.
- 🔵 The Lac Z gene and its interaction with beta-galactosidase are used to differentiate between successful cloning and the presence of the gene of interest through color change assays.
- 📚 cDNA, or complementary DNA, is synthesized from eukaryotic mRNA and is used to study genes without introns, avoiding complications from non-coding regions in the DNA.
- 🗂️ DNA libraries, both genomic and cDNA, are collections of bacterial colonies containing different pieces of DNA, created through similar cloning steps for various research purposes.
Q & A
What is recombinant DNA technology?
-Recombinant DNA technology is a method used to isolate and manipulate DNA fragments to produce new arrangements. It is utilized for various purposes such as researching the relationship between DNA sequence and phenotype, studying gene structure and expression, and for applications like gene therapy.
What does gene cloning involve?
-Gene cloning involves making more copies of a gene. It is widely used in areas such as DNA sequencing, gene editing, producing probes for hybridization, Southern blotting, and for the expression of cloned genes in research and biotechnology.
What are the two types of DNA fragments involved in cloning experiments?
-The two types of DNA fragments involved in cloning experiments are chromosomal DNA, which contains the gene of interest, and vector DNA, which will be integrated into the host cell and replicate independently.
Why is chromosomal DNA purified from tissues and cells?
-Chromosomal DNA is purified from tissues and cells to isolate the gene of interest for cloning or other techniques, ensuring that the specific gene can be studied or manipulated separately from the rest of the genome.
What is the role of vector DNA in cloning?
-Vector DNA serves as the carrier for the gene of interest to be cloned. It integrates into the host cell and replicates independently, allowing for the production of multiple copies of the gene within the host.
Why are plasmids the most common type of vector DNA used in cloning?
-Plasmids are the most common type of vector DNA used in cloning because they naturally occur in bacteria, are separate from the bacterial chromosome, have an origin of replication allowing for replication within the host cell, and possess unique restriction sites for inserting DNA fragments.
What is a selectable marker and why is it important in cloning?
-A selectable marker is a gene that allows for the selection of bacterial colonies that contain the plasmids with the gene of interest. Typically, it consists of a gene for antibiotic resistance, enabling the selection for the growth of host cells that carry the plasmid.
What are restriction enzymes and what is their role in gene cloning?
-Restriction enzymes, also known as endonucleases, are enzymes that break down nucleic acids by cutting DNA at specific sequences. They are essential in gene cloning for generating sticky ends, which facilitate the joining of different DNA fragments to form recombinant DNA.
Why are sticky ends important in cloning experiments?
-Sticky ends are important in cloning experiments because they allow different DNA fragments from various sources to anneal through hydrogen bonding interactions, creating new combinations of DNA fragments that can be sealed and integrated into the host cell.
What is the purpose of DNA ligase in gene cloning?
-DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to seal the gaps in the backbone of the DNA, effectively joining the DNA fragments together to form a stable recombinant DNA molecule within the host cell.
How are cDNA libraries different from genomic DNA libraries?
-cDNA libraries are created from complementary DNA synthesized from messenger RNA, bypassing introns and focusing on the exons that code for proteins. Genomic DNA libraries, on the other hand, contain all the DNA from an organism, including introns and exons, and are used to study the entire genome.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)