Basic fracture mechanics
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to fracture mechanics, explaining key concepts such as stress intensity factor (K), critical stress intensity factor (K_IC), and the difference between toughness and fracture toughness. It covers the importance of understanding when cracks in materials become critical, transitioning from stable to unstable growth. The video also highlights the relationship between stress, crack size, and material properties, as well as the modes of crack displacement. With a focus on engineering applications, the content aims to equip viewers with the foundational knowledge needed to prevent material failure through careful design and testing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fracture mechanics focuses on understanding when a crack becomes critical, leading to uncontrollable propagation.
- 😀 The stress intensity factor (K) relates the applied stress and crack size, determining crack growth stability.
- 😀 When the stress intensity factor reaches a critical value, the crack growth shifts from stable to unstable.
- 😀 Fracture toughness (K_IC) is the critical value of stress intensity factor that causes a crack to become unstable.
- 😀 K_IC is a material property that characterizes resistance to crack propagation under stress, specifically under Mode I (opening) crack displacement.
- 😀 The stress concentration factor (K_t) quantifies how stress is concentrated at the crack tip compared to the applied stress.
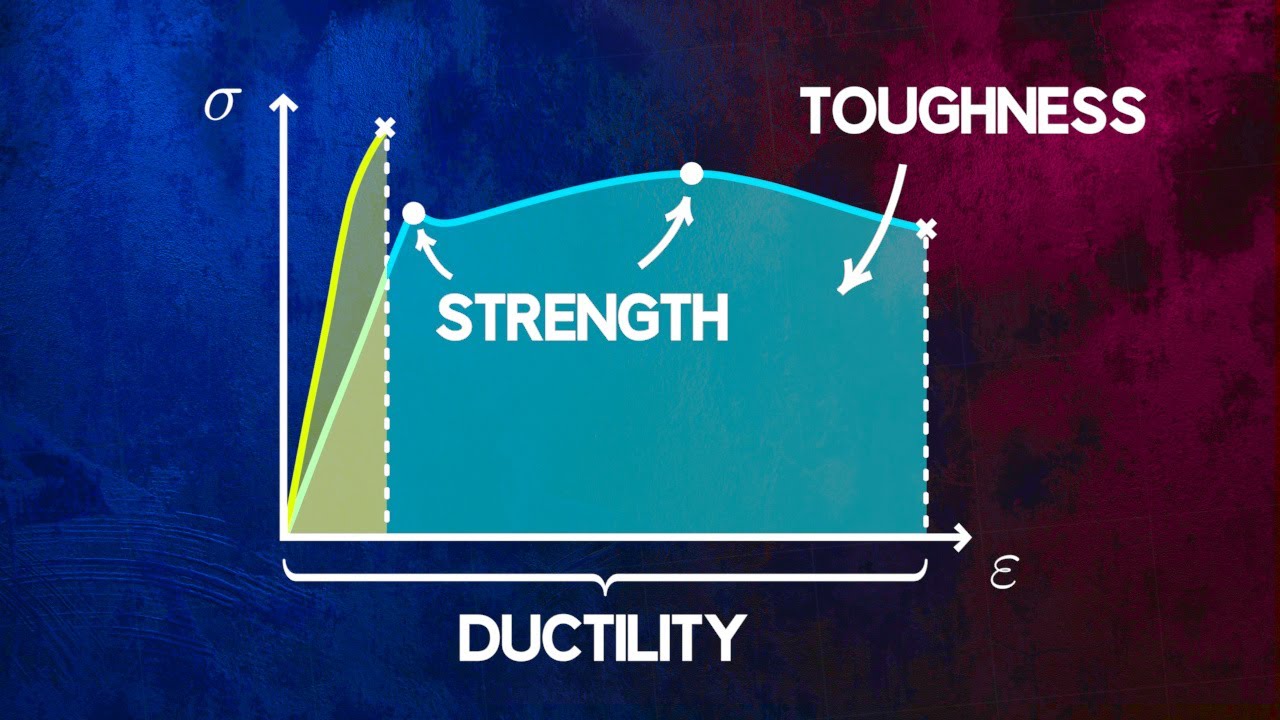
- 😀 Toughness refers to the total energy a material can absorb before it fractures, distinct from fracture toughness (K_IC).
- 😀 The fracture toughness (K_IC) is a material-specific property, while the toughness (area under the stress-strain curve) is a more general measure of energy absorption.
- 😀 The most common mode of crack displacement is Mode I (opening), which is primarily concerned in fracture mechanics.
- 😀 Stress, crack size, and material properties are interconnected in fracture mechanics to predict material failure in structural designs.
Q & A
What is the main focus of fracture mechanics?
-Fracture mechanics focuses on understanding when a crack in a material becomes critical, meaning when its propagation shifts from stable to unstable due to stress.
What does the stress intensity factor (K) represent in fracture mechanics?
-The stress intensity factor (K) relates the applied stress and crack length, with a geometric factor that accounts for the sample's size and the crack's dimensions. It helps quantify the behavior of cracks under stress.
How does the stress intensity factor (K) change as the crack length increases?
-As the crack length increases, the stress intensity factor (K) also increases, which ultimately determines when the crack will become critical and start propagating unstably.
What is the significance of the fracture toughness (K_IC) in fracture mechanics?
-Fracture toughness (K_IC) is the critical value of the stress intensity factor at which a crack becomes unstable and begins to propagate uncontrollably. It represents a material's resistance to crack growth under stress.
Why is Mode I crack displacement most commonly studied in fracture mechanics?
-Mode I crack displacement, also known as crack opening, is the most common form of crack behavior encountered in practice. It involves the crack faces moving apart under stress, and is the primary mode of crack propagation in many materials.
What is the difference between toughness and fracture toughness?
-Toughness refers to the material's ability to absorb energy before fracture, represented by the area under the stress-strain curve. Fracture toughness (K_IC), on the other hand, refers specifically to the material's resistance to crack propagation under stress.
What is the role of the stress concentration factor (K_t) in fracture mechanics?
-The stress concentration factor (K_t) describes how much stress is amplified at the crack tip. It is crucial for understanding how local stresses affect crack propagation and the material's susceptibility to fracture.
How does fracture toughness (K_IC) differ from toughness and stress concentration factor?
-Fracture toughness (K_IC) is a material property that quantifies resistance to crack growth under stress, while toughness is the energy absorbed before fracture. The stress concentration factor (K_t) specifically measures stress amplification at the crack tip.
What does it mean when the stress intensity factor reaches the critical value?
-When the stress intensity factor reaches its critical value (K_IC), the crack has grown to a length where its propagation becomes unstable, leading to rapid and uncontrollable crack growth, which can result in material failure.
Why is fracture mechanics important in engineering and material science?
-Fracture mechanics is essential in engineering and material science because it helps predict when and how cracks will propagate in materials, enabling better design of safer and more durable structures and components.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pitch sobre Fratura (comportamento dúctil e frágil)
Understanding Material Strength, Ductility and Toughness

Physics of sound 6 - Intensity and decibels
Basic Geomechanics for Hydraulic Fracturing

What Are the Hidden Properties of Stuff?

Presentasi Tentang Cara Membaca Grafik Data Hasil Pengujian Uji Tarik
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)