Basic Geomechanics for Hydraulic Fracturing
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the mechanics of geological materials, particularly focusing on the behavior of reservoir rocks under stress. It discusses the concepts of stress, strain, and the Poisson ratio, which are crucial for understanding material deformation and fracture in reservoir engineering. The talk highlights the importance of the modulus of elasticity and the three principal stresses in determining the direction and growth of hydraulic fractures, emphasizing the significance of overburden stress and its impact on fracture orientation in reservoir stimulation.
Takeaways
- 📘 Material in the context of reservoir geomechanics is considered to be starting from the basics, acknowledging the use of Excel for stress calculations.
- 🔨 Stress and strain are fundamental concepts, where stress is force per unit area, and materials like rock and metal can deform under stress.
- 📏 The Poisson's ratio is introduced as an important parameter in geomechanics, relating the ratio of lateral strain to axial strain under load.
- 📊 Poisson's ratio values for various rocks such as sandstone, limestone, and shale are generally around 0.20 to 0.30.
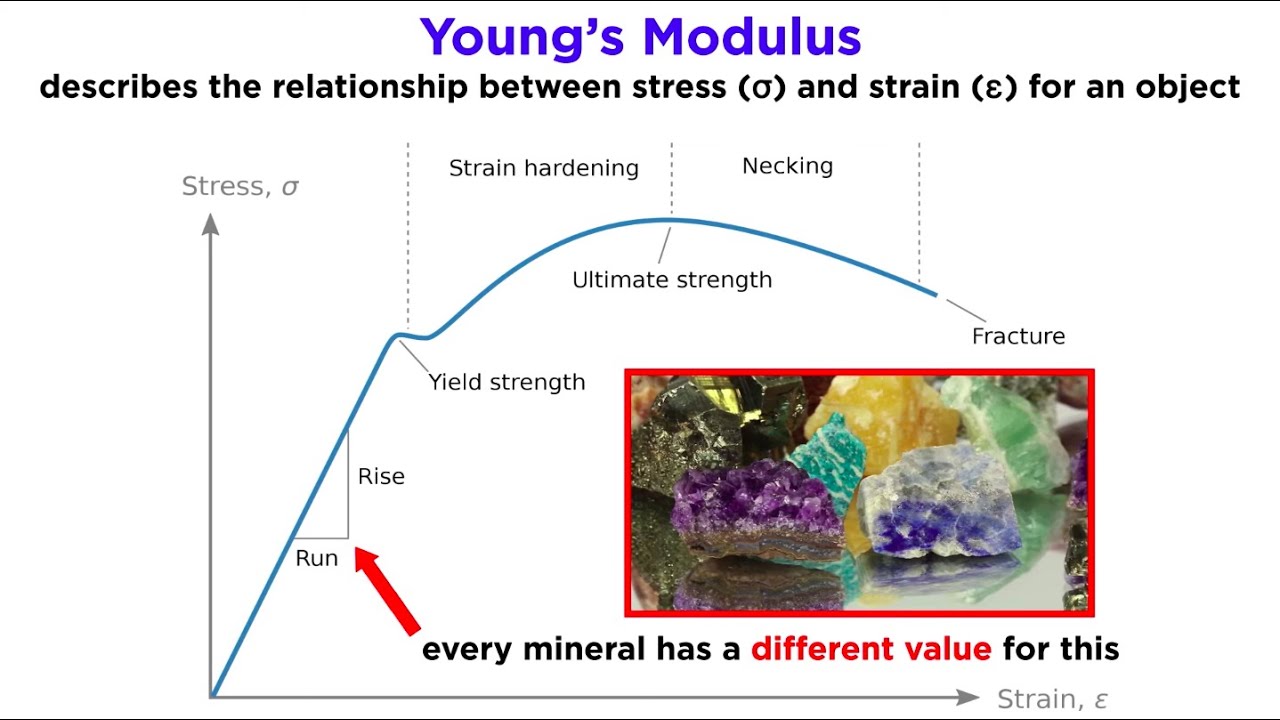
- 📉 The stress-strain plot is used to differentiate between the elastic and plastic regimes of materials, focusing on the elastic regime for determining yield strength.
- 💎 The modulus of elasticity, or Young's modulus, represents the amount of energy needed to deform the reservoir rock, which is crucial for fracture design.
- 🗜 Different rock types, such as hard rock with a high modulus and soft rock with a lower modulus, have different tendencies to transmit stress and deform.
- 🚧 The challenge with soft rock is its tendency to deform rather than transmit stress, which can complicate hydraulic fracturing operations.
- 🛠 The shear modulus is also important in extreme hydrofrac operations, calculated as G = E/(2(1+Poisson's ratio)).
- 🌐 Stress in reservoir rocks is three-dimensional, and it's not a scalar but a tensor, which can be complex to quantify and analyze.
- 📍 The three principal stresses are extracted for analysis, with hydraulic fracturing typically propagating perpendicular to the minimum principal stress.
Q & A
What is the basic concept of material in the context of reservoir rock mechanics?
-In the context of reservoir rock mechanics, the basic concept of material refers to the properties of the rock, such as its hardness and how it responds to stress and strain, which are fundamental in understanding its behavior under various forces.
What is meant by stress and strain in the script?
-Stress is the force applied per unit area, and strain is the deformation that occurs in a material as a result of stress. The script discusses how different materials, including rock, respond to these forces.
How does the script describe the deformation of rock under stress?
-The script describes that even though rock is hard, it will still undergo deformation such as compression or expansion when subjected to stress. This deformation, although it may be microscopic, is significant in the context of reservoir engineering.
What is the Poisson's ratio and why is it important in fracture design?
-Poisson's ratio is the ratio of the lateral strain to the axial strain under load. It is important in fracture design because it helps in understanding how materials will deform in different directions when subjected to stress, which is crucial for predicting the behavior of fractures in reservoir rocks.
What is the range of Poisson's ratio for hard rocks such as granite and limestone?
-The script mentions that the range of Poisson's ratio for hard rocks like granite and limestone is approximately 0.20 to 0.30.
What is the significance of the elastic and plastic regimes in material behavior?
-The elastic regime is where materials return to their original shape after the stress is removed, while the plastic regime is where permanent deformation occurs. Understanding these regimes helps in determining the strength and elasticity of materials, which is essential for designing hydraulic fracturing operations.
What is the difference between hard and soft rocks in terms of stress transmission?
-Hard rocks tend to transmit stress more effectively, which can lead to fractures propagating more easily. Soft rocks, on the other hand, are more likely to deform rather than transmit stress, which can affect the propagation of fractures differently.
What is the role of the modulus of elasticity in reservoir rock?
-The modulus of elasticity, also known as Young's modulus, represents the amount of energy needed to deform a material. In the context of reservoir rock, it indicates how much energy is required to deform the rock, which is important for understanding fracture propagation.
How does the script relate the concept of stress to the direction of hydraulic fracturing?
-The script explains that hydraulic fracturing is provoked and will propagate in the direction perpendicular to the minimum principle stress or along the maximum principle stress, depending on the orientation of the stresses in the reservoir rock.
What is the significance of the three principal stresses in reservoir rock mechanics?
-The three principal stresses are the maximum, intermediate, and minimum stresses experienced by the reservoir rock. They are significant because they determine the orientation and growth of fractures, which is a critical aspect of hydraulic fracturing operations.
How does the script connect the concepts of overburden stress and fracture orientation?
-The script connects overburden stress to fracture orientation by explaining that fractures will tend to open in the direction of the least stress, which is often the direction of the minimum horizontal stress or perpendicular to the maximum horizontal stress, depending on the overburden stress.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

PG 04 A - Stress Strain

Geologi Struktur - Lipatan, Foliasi, Cleavage, dan Lineasi - 4. Foliasi dan Cleavage (Part-1)

Mechanics of Solids Interview Questions
Overview of Geologic Structures Part 1: Rock Deformation, Stress and Strain

ResGeo_10: Hydrocarbon Fluid Distribution in Reservoir Rocks - Key Controls

Fossil Fuel Formation | Lesson 6 | Earth Science
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)