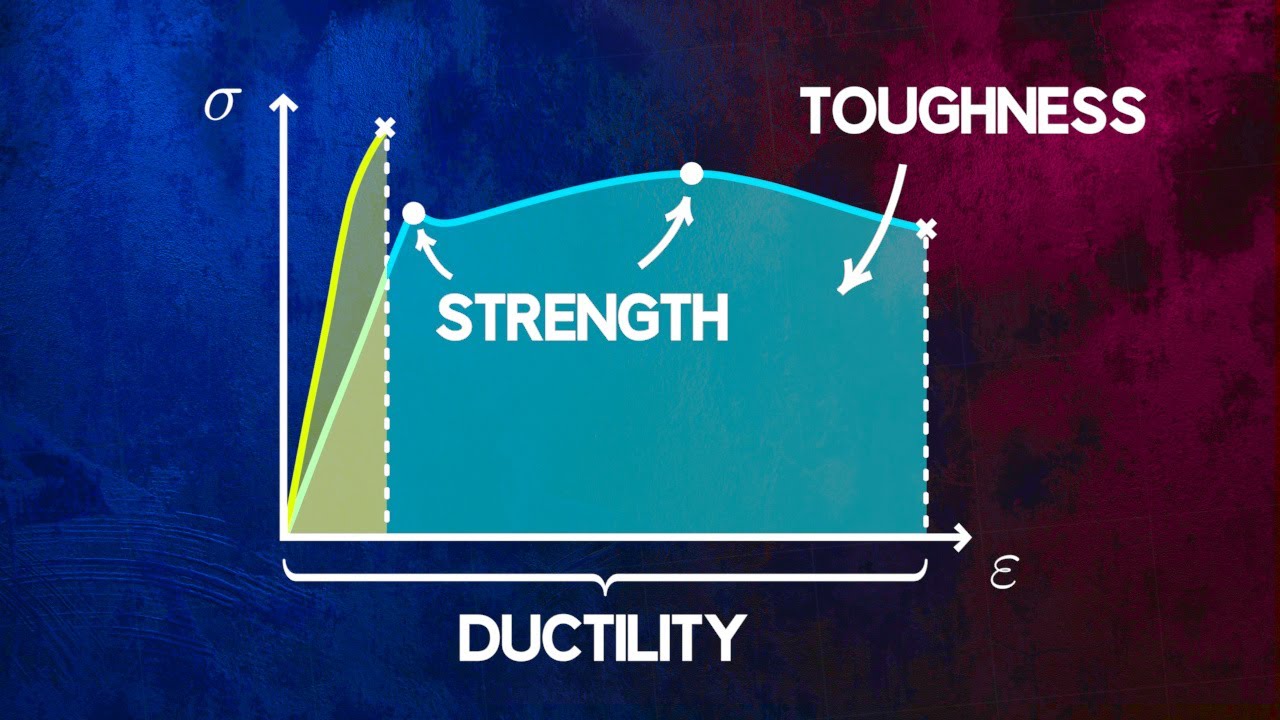
Pitch sobre Fratura (comportamento dúctil e frágil)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the mechanics of material fracture, covering both ductile and brittle fracture behaviors. It highlights the Silver Bridge disaster as a case study, where fracture mechanics helped identify the failure's causes, such as high tension and corrosion. The script details the characteristics of ductile fracture, including plastic deformation and energy absorption, and contrasts it with brittle fracture, marked by rapid crack propagation. It also introduces fracture mechanics concepts, such as stress concentration and the intensity factor (K), which predict crack growth. This video aims to deepen understanding of material failures and fracture mechanics applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fracture behavior can be ductile, brittle, or a combination of both, and depends on factors such as temperature, loading rate, pressure, geometry, and material type.
- 😀 The study of fractures began with the analysis of catastrophic failures, such as the Silver Bridge disaster, where the failure was traced to high tension, corrosion, and design errors.
- 😀 Ductile fracture involves continuous plastic deformation, with a reduction in area before rupture. It typically occurs in materials like carbon steel and is marked by significant plastic deformation at the crack front.
- 😀 Ductile fractures exhibit a fibrous, tough appearance and propagate by shearing, with dislocation motion involved in the fracture mechanism.
- 😀 The fracture mechanism in ductile materials involves necking, microcavity formation, coalescence of cavities, crack formation, and propagation at a 45-degree angle to the applied stress.
- 😀 Brittle fractures, on the other hand, occur without plastic deformation and are often observed in ceramics, cold metals, and glass, with the crack propagating perpendicular to the applied stress.
- 😀 Brittle fractures are rapid and unstable, characterized by low energy absorption before fracture, and exhibit smooth, bright fracture surfaces, either transgranular or intergranular.
- 😀 Transgranular brittle fractures propagate through the grains, presenting a facet-like fracture surface, while intergranular fractures follow the grain boundaries, often due to impurity segregation.
- 😀 Fracture mechanics helps determine the type of fracture and predict whether a crack will lead to catastrophic failure under service stresses.
- 😀 In fracture mechanics, the stress intensity factor (K) quantifies the intensity of stress at the crack tip and helps predict whether a crack will grow, based on material properties and crack geometry.
Q & A
What is fracture mechanics?
-Fracture mechanics is the study of how cracks form and propagate in materials under stress. It helps engineers predict material failures and design safer components.
What are the two main types of fracture behavior discussed?
-The two main types of fracture behavior are ductile fracture and brittle fracture. Ductile fractures involve significant plastic deformation, while brittle fractures occur with little deformation.
How does ductile fracture behave at a macroscopic level?
-At a macroscopic level, ductile fracture appears fibrous and cone-shaped. The crack propagates at a 45° angle to the applied stress and is stable, absorbing significant energy before failure.
What is observed at the microscopic level during ductile fracture?
-Microscopically, ductile fracture involves the formation of micro-cavities that grow and coalesce, leading to a crack. This process is accompanied by significant plastic deformation.
What materials typically experience ductile fracture?
-Materials like carbon steel, which are capable of undergoing significant plastic deformation, commonly exhibit ductile fracture.
How does brittle fracture behave at a macroscopic level?
-Brittle fracture appears smooth or shiny and propagates quickly without significant deformation. The crack typically propagates perpendicular to the applied stress.
What is the difference between transgranular and intergranular brittle fracture?
-Transgranular fracture occurs when the crack passes through the grains of the material, while intergranular fracture occurs along the grain boundaries, which are weaker due to impurities.
What types of materials are prone to brittle fracture?
-Brittle fracture is typically observed in materials like ceramics, some metals at low temperatures, and certain composites.
What is the role of the K-factor in fracture mechanics?
-The K-factor measures the intensity of stress at the crack tip and helps predict whether the crack will grow or stop. It is essential for assessing the stability of cracks in materials.
How do stress and strain influence material fracture?
-Stress and strain dictate how materials respond to forces. High stress can lead to crack formation, while strain determines whether a material will undergo plastic deformation (ductile) or fracture without deformation (brittle).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)