Quantum Mechanics by a Physicist | IIT- kharagpur, CMI
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture, we delve into the intricacies of quantum mechanics, beginning with an understanding of classical mechanics and its limitations. We explore the fundamental principles that govern the physical world, such as Newton's laws and the conservation of energy. The lecture highlights the peculiarities of producing blue light and the photoelectric effect, which challenged classical theories and paved the way for quantum mechanics. The session sets the stage for understanding key quantum concepts and prepares us for deeper exploration in subsequent lectures.
Takeaways
- 📚 Quantum Mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles.
- 💡 The Photoelectric Effect is a phenomenon where light, when shone on a metal surface, can eject electrons from that surface, which was a key experiment that led to the development of quantum theory.
- 🚀 Einstein's explanation of the Photoelectric Effect, which stated that light can be thought of as consisting of individual quanta or particles of energy, known as photons, earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics.
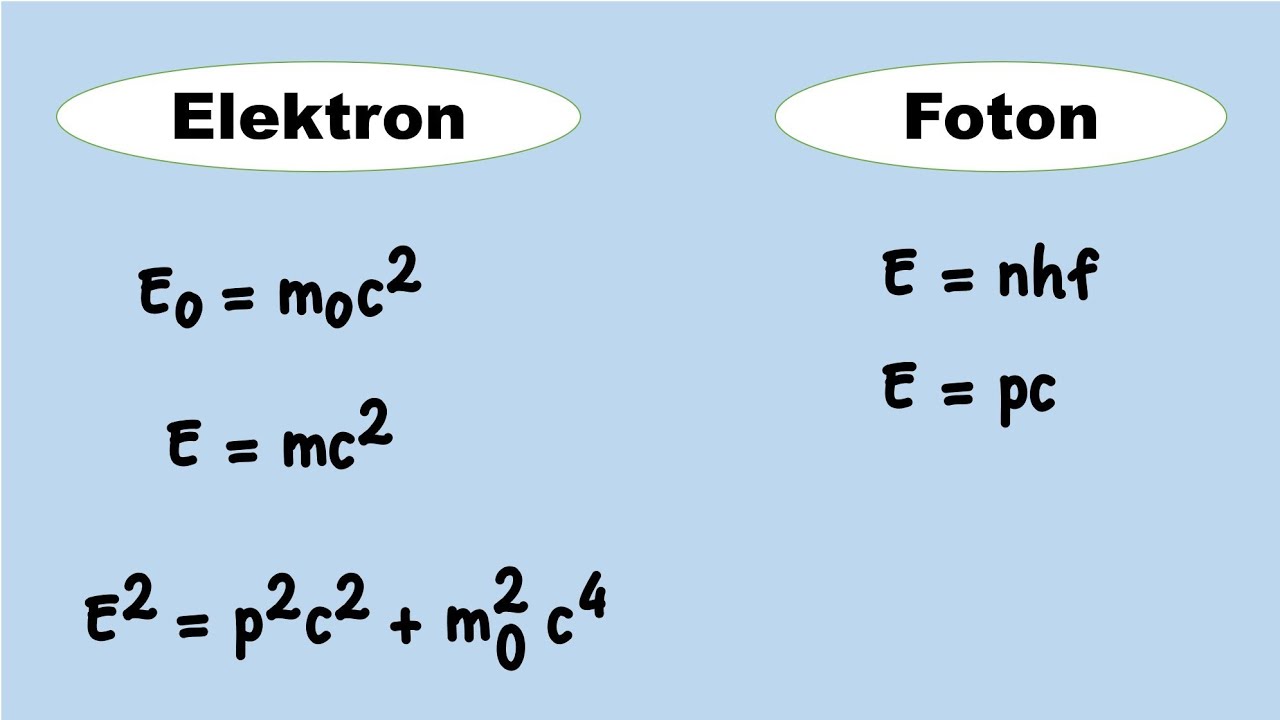
- 🌟 The energy of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency and is described by the equation E=hν, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and ν is the frequency of the photon.
- ⚡ Classical Mechanics fails to explain phenomena at the quantum level, where the discrete and probabilistic nature of events is a fundamental aspect that cannot be predicted by classical deterministic equations.
- 📉 The concept of energy in quantum mechanics is different from classical mechanics, where energy is quantized and not continuous, leading to the idea of energy levels and energy gaps.
- 🎭 Quantum Mechanics introduces the wave-particle duality, where particles like electrons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties, challenging the classical understanding of matter.
- 🛠️ The behavior of particles at the quantum level is described by wave functions and probability distributions, which give the likelihood of finding a particle in a particular state rather than a definite position or velocity.
- 🧲 Quantum Mechanics is essential for understanding the properties of atoms, the interactions between atoms, and the behavior of electrons in molecules, which has significant implications for chemistry and materials science.
- 🔬 The development of quantum mechanics has led to technological advancements such as the development of semiconductors, lasers, and modern computing, which rely on quantum effects.
- 🌐 Quantum Mechanics has profound implications for our understanding of the universe, including the unification of forces, the behavior of black holes, and the fundamental nature of space and time.
Q & A
What is Quantum Mechanics and why is it difficult to understand?
-Quantum Mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that describes the physical properties of nature at the smallest scales. It's considered difficult due to its counterintuitive concepts that often contradict our everyday experiences and classical physics intuition.
What is the significance of the Photoelectric Effect in the development of Quantum Mechanics?
-The Photoelectric Effect is a phenomenon where light causes electrons to be emitted from a material. It was a key experiment that led to the development of Quantum Mechanics because it demonstrated the quantized nature of energy, which could not be explained by classical physics.
What are the two main observations that define Newtonian Mechanics?
-Newtonian Mechanics is defined by two main observations: 1) The laws of nature are the same in all inertial frames, and 2) The state of the universe can be represented by variables such as position, velocity, and acceleration, which evolve according to specific equations.
How does the concept of energy in classical mechanics differ from that in quantum mechanics?
-In classical mechanics, energy is a conserved quantity that can take various forms like kinetic or potential energy. In quantum mechanics, energy is also quantized, meaning it comes in discrete packets or 'quanta', which is a departure from the continuous energy changes described in classical physics.
What is the role of light in the context of the Photoelectric Effect?
-In the Photoelectric Effect, light plays a crucial role as it is the source of energy that ejects electrons from a material. The effect demonstrates that light can be thought of as consisting of particles, or photons, each with a discrete energy.
What is the difference between classical and quantum descriptions of physical reality?
-Classical descriptions of physical reality are based on continuous variables and deterministic laws, such as Newton's laws of motion. Quantum descriptions, on the other hand, involve probabilities and non-deterministic behaviors, where particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured.
What are the three main variables used to describe the state of a system in classical mechanics?
-The three main variables used to describe the state of a system in classical mechanics are position, velocity, and acceleration.
How do the concepts of kinetic and potential energy relate to the conservation of energy in classical mechanics?
-In classical mechanics, the conservation of energy states that the total energy of a closed system remains constant. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is the stored energy due to an object's position in a force field, like a gravitational field. The sum of kinetic and potential energy constitutes the total mechanical energy of the system.
Can you explain the paradox of not being able to produce blue light from a filament as described in the script?
-The paradox mentioned in the script refers to the difficulty of producing blue light from a heated filament. As the filament is heated, it emits light of various colors, but it is challenging to emit blue light because it requires a higher energy transition that is not easily achievable with a simple heated filament.
What is the significance of the term 'ultraviolet catastrophe' mentioned in the script?
-The 'ultraviolet catastrophe' refers to a problem in classical physics where, according to classical theories, a blackbody radiator would emit an infinite amount of ultraviolet radiation, leading to an absurd result. This paradox was one of the factors that led to the development of quantum theory, which resolved the issue by introducing the concept of energy quantization.
What is the basic premise of the experiment involving two metal plates as described in the script?
-The experiment with two metal plates involves setting up a potential difference between the plates, effectively creating an electric field. When light of a certain frequency is shone on the setup, it can cause electrons to be ejected from the metal surface, demonstrating the interaction between light and matter at a quantum level.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)