FISIKA KELAS XII | RANGKAIAN ARUS BOLAK-BALIK (AC) - PART 2 : RANGKAIAN RLC
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive explanation of RLC circuits in alternating current (AC) systems. The instructor covers key concepts including resistors, inductors, and capacitors, their behavior in AC circuits, and how they interact in series RLC circuits. The video explains impedance, phase shifts, and resonance conditions, with detailed calculations of impedance, current, voltage, and power dissipation. Real-world examples and problem-solving methods are demonstrated to help viewers understand how to analyze and calculate values in RLC circuits, making this an essential resource for students of physics and electrical engineering.
Please replace the link and try again.
Q & A
What does 'RLC' stand for in an AC circuit?
-RLC stands for Resistor (R), Inductor (L), and Capacitor (C). These are the three components that make up the RLC circuit in alternating current (AC) circuits.
What happens when a resistor is connected to an AC voltage source?
-When a resistor is connected to an AC voltage source, Ohm's Law applies, and the voltage across the resistor is directly proportional to the current, i.e., V = I * R.
How does an inductor behave in an AC circuit?
-An inductor in an AC circuit creates a reactance (XL), which opposes changes in current. The voltage across the inductor is given by V = I * XL, where XL = ωL (ω is the angular frequency and L is the inductance).
What is the formula for the capacitive reactance (XC) in an AC circuit?
-The formula for capacitive reactance is XC = 1 / (ωC), where ω is the angular frequency and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
What is the significance of the phase difference between voltage and current in an inductive circuit?
-In an inductive circuit, the voltage leads the current by 90°. This phase difference means that the current reaches its maximum value after the voltage does.
What happens in a capacitive circuit regarding the phase difference?
-In a capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage by 90°. This means that the current reaches its maximum value before the voltage does.
What is the formula for the impedance (Z) in an RLC series circuit?
-The impedance in an RLC series circuit is given by the formula Z = √(R² + (XL - XC)²), where R is the resistance, XL is the inductive reactance, and XC is the capacitive reactance.
What is the power dissipation in an RLC circuit and how is it calculated?
-The power dissipation in an RLC circuit, or real power, is calculated using the formula P = V_eff * I_eff * cos(θ), where V_eff is the effective voltage, I_eff is the effective current, and cos(θ) is the power factor.
What condition must be met for resonance to occur in an RLC circuit?
-Resonance in an RLC circuit occurs when the inductive reactance (XL) equals the capacitive reactance (XC), i.e., when XL = XC, or equivalently when ωL = 1 / (ωC).
How can the resonance frequency of an RLC circuit be calculated?
-The resonance frequency (f) of an RLC circuit is calculated using the formula f = 1 / (2π √(LC)), where L is the inductance and C is the capacitance of the components.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
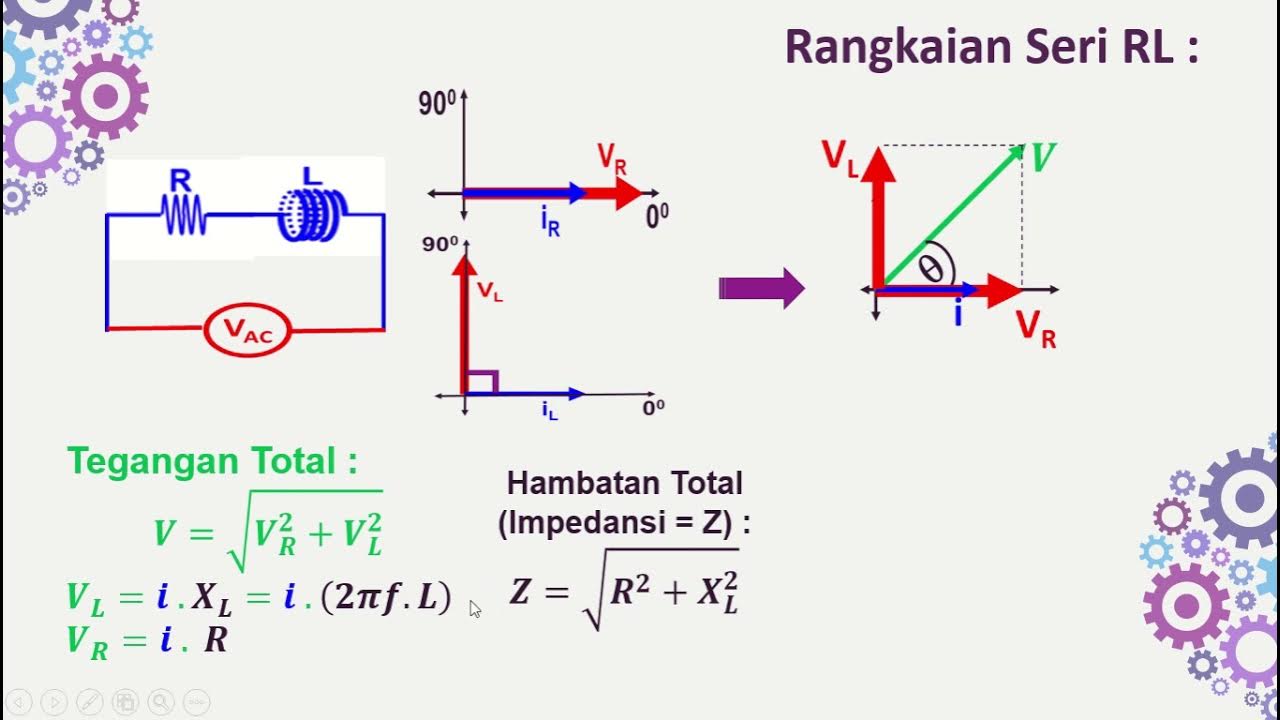
Rangkaian Seri RL-RC-LC dengan Sumber AC

3 Phase AC system / Circuit (3 Phase alternating current need, generation, Phaser diagram) BEE
FISIKA KELAS XII | RANGKAIAN ARUS BOLAK-BALIK (AC) - PART 1 : ARUS DAN TEGANGAN AC

Praktikum Fisika Dasar || ARUS BOLAK BALIK
Lesson 1 - What Is Alternating Current? (AC Circuit Analysis)
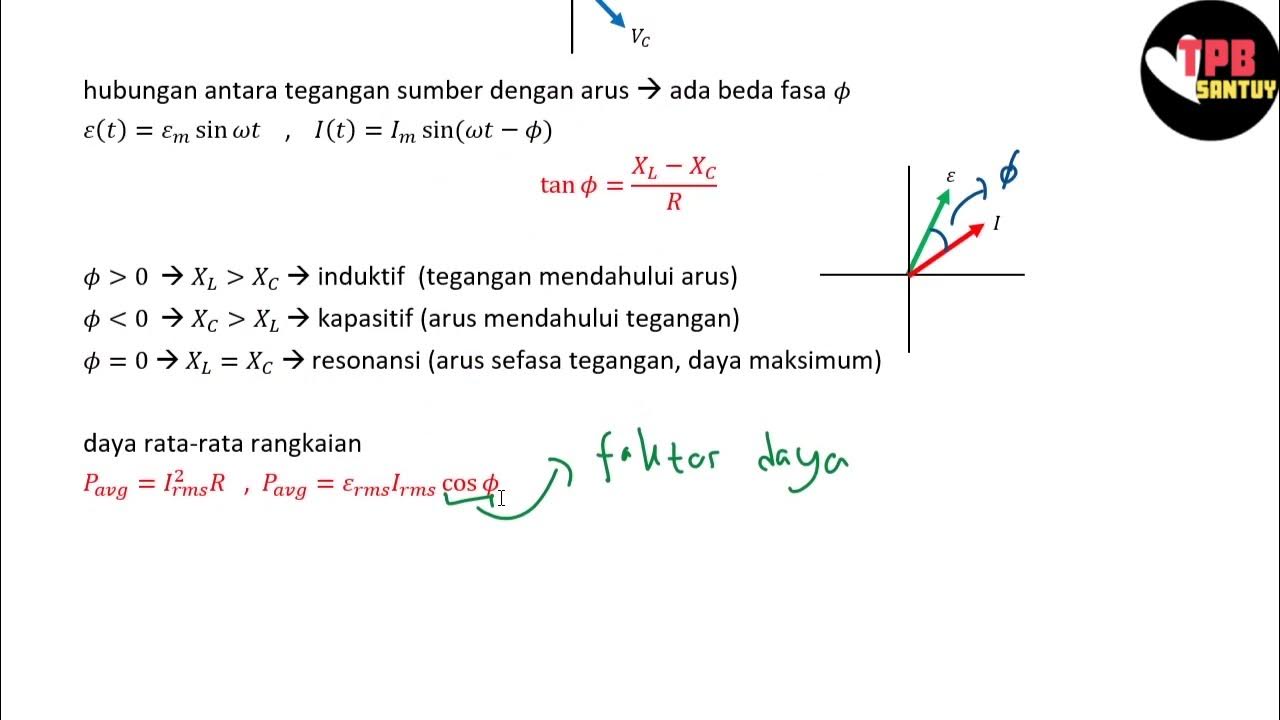
Rangkaian Seri RLC | Rangkaian AC | Part 2 | Fisika Dasar
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)