MATERI MARTIKULASI | JARINGAN TUBUH MANUSIA
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the speaker introduces the concept of human body tissues, explaining the four basic types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Epithelial tissue covers and protects organs, connective tissue supports and binds body structures, muscle tissue enables movement (both voluntary and involuntary), and nervous tissue controls bodily functions through signal transmission. The speaker emphasizes the interconnectivity of these tissues in forming organs and systems essential for the body’s function. The video serves as an accessible introduction to these fundamental biological concepts, aimed at enhancing viewers' understanding of human anatomy.
Takeaways
- 😀 Human body tissues start with the formation of cells, which are the basic elements of all tissues.
- 😀 Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform specific functions in the body.
- 😀 There are four primary types of tissues in the human body: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue covers the surface of the body and organs, protecting and aiding in secretion and absorption.
- 😀 Connective tissue binds organs and tissues together and includes cells embedded in a matrix that can have various fibers such as collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers.
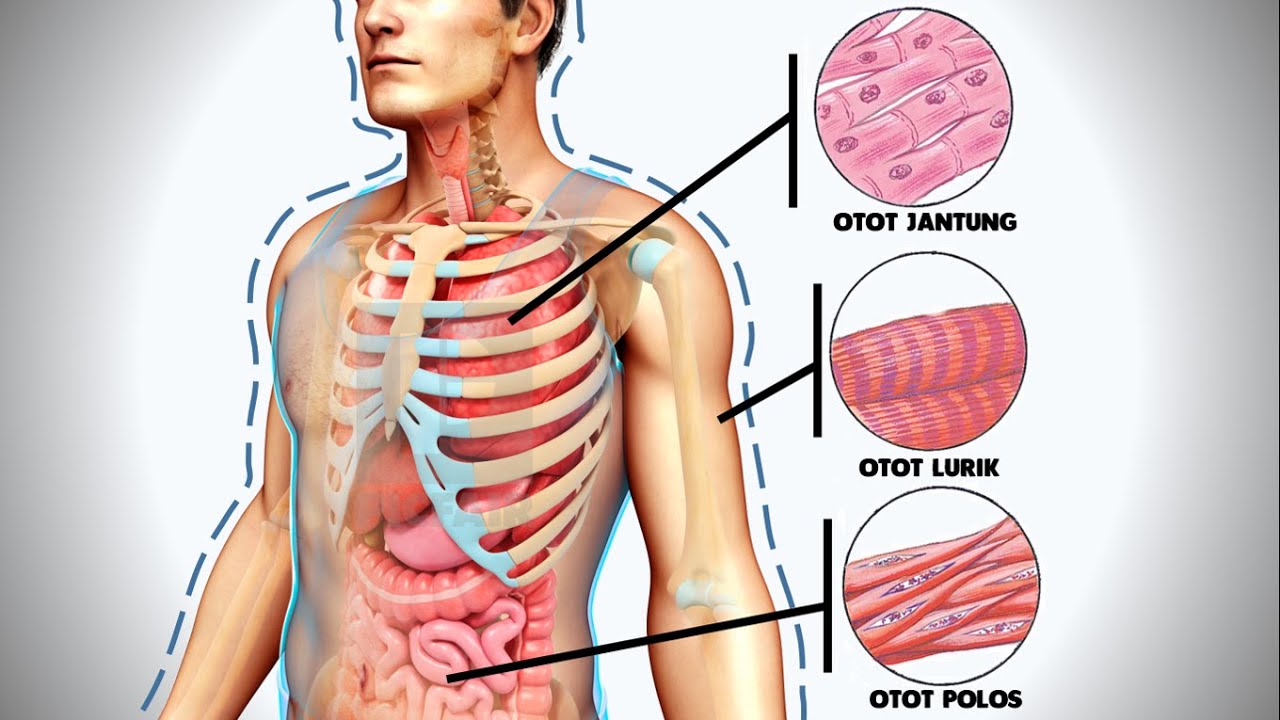
- 😀 Muscle tissue is responsible for movement and comes in three types: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
- 😀 Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in the walls of internal organs like the digestive system and blood vessels.
- 😀 Skeletal muscle is voluntary, attached to bones, and enables body movement through contraction.
- 😀 Cardiac muscle is involuntary, located in the heart, and continuously contracts to pump blood.
- 😀 Nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting signals in the body, controlling movements and activities, and processing sensory information.
Q & A
What are the four primary tissue types in the human body?
-The four primary tissue types in the human body are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is the role of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body, both external and internal. Its primary functions are protection, secretion, and absorption.
How is epithelial tissue related to the skin?
-Epithelial tissue forms the outer layer of the skin, serving as a protective barrier against physical damage and pathogens.
What is the matrix in connective tissue and what is its function?
-The matrix in connective tissue is an extracellular substance secreted by connective tissue cells. It provides structural support, flexibility, and mediates the exchange of nutrients and waste.
What are the three types of fibers found in connective tissue matrix?
-The three types of fibers in the connective tissue matrix are collagen fibers (strong and provide elasticity), elastin fibers (which offer flexibility and are found in structures like blood vessels), and reticular fibers (which help form supportive networks in tissues).
What is the difference between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle?
-Smooth muscle is involuntary, non-striated, and found in internal organs like the digestive tract. Skeletal muscle is voluntary, striated, and attached to bones to facilitate movement.
What are the characteristics of cardiac muscle?
-Cardiac muscle is involuntary, striated, and found in the heart. It is unique because it has branching fibers and a single central nucleus.
How does nervous tissue function in the human body?
-Nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout the body. It helps coordinate the body's functions by sending and receiving information from sensory organs, muscles, and the brain.
What are neurons and glial cells in nervous tissue?
-Neurons are the primary cells of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting electrical impulses. Glial cells provide support and nourishment to neurons.
How do the four tissue types contribute to the formation of organs and systems?
-The four tissue types work together to form organs, which are structures in the body that carry out specific functions. For example, muscle tissue allows movement, epithelial tissue lines organs, connective tissue provides support, and nervous tissue controls functions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Tissues of Human Body | Animation | Simple Explanation

Clase 1 aCelula e introducción a tejidos

what are tissues in human body, what are tissues made of, what are tissues class 9, Human tissues,
Media Pembelajaran Jaringan Hewan - Kelas Daring Biologi SMA Kelas XI

jaringan hewan (bahasa indonesia)

Jaringan Hewan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)