How does a Battery Charger work? CCCV Battery Charging | CCCV regulator | Li-ion cell charger
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the operation of a DC-DC converter used for battery charging, functioning as both a constant current (CC) and constant voltage (CV) regulator. It highlights the two-phase charging process: first, constant current charging to prevent battery damage, followed by constant voltage charging as the battery nears full capacity. The charger ensures safe and efficient charging, including trickle charging for deeply discharged batteries. The process is commonly used for Li-ion batteries in devices like electric vehicles and portable electronics. The video also sets the stage for a deeper dive into the control mechanisms of the CC/CV converter in future content.
Takeaways
- 😀 CC/CV DC-DC converters regulate both current and voltage to match the load's requirements, making them ideal for battery charging.
- 😀 In constant current (CC) mode, the converter provides a fixed current, while the voltage varies based on the battery’s charge.
- 😀 In constant voltage (CV) mode, the charger adjusts to maintain a constant voltage, while the current decreases as the battery nears full charge.
- 😀 The CC/CV charging method is widely used for charging rechargeable batteries, especially **Li-ion** batteries in portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- 😀 During the charging process, the converter first operates in CC mode and switches to CV mode once the battery voltage reaches a certain threshold.
- 😀 The charging cycle concludes when the charging current falls to 10% of the full charging rate, marking the end of charge (EOC).
- 😀 A simple analogy for the charging process is filling a paper cup with water, where the water flow (current) is adjusted to prevent overflow (overcharging).
- 😀 Trickle charging is employed when the battery is deeply discharged, charging at a very low rate (10% of the full charge rate) to prevent damage.
- 😀 Once the battery voltage reaches a certain pre-charge threshold, the charger increases the charging rate to 100% of the full rate.
- 😀 The charger uses a combination of CC and CV modes to maximize both safety and efficiency, ensuring that the battery is charged without overloading it.
- 😀 The voltage threshold for Li-ion batteries typically ranges from 2.8V to 4.2V, depending on the state of charge and the specific battery chemistry.
Q & A
What is a CC/CV DC-DC converter, and how does it work?
-A CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) DC-DC converter is a type of power supply that regulates both the current and voltage to meet the load's requirements. In CC mode, the current is constant while the voltage can vary, and in CV mode, the voltage remains constant while the current adjusts based on the load.
Why is it not possible to control both current and voltage at the same time for resistive loads?
-According to Ohm's Law, for a given resistive load, if you control one of the parameters (either current or voltage), the other will automatically be determined by the load's resistance. Hence, you can control either current or voltage, but not both simultaneously.
What are some common applications for CC/CV converters?
-CC/CV converters are widely used for LED driving, battery charging, and charging supercapacitors. They are especially popular for charging rechargeable batteries, including Li-ion batteries used in devices like electric vehicles, smartphones, laptops, and portable appliances.
How does the CC/CV charging method work for Li-ion batteries?
-The CC/CV charging method starts with constant current (CC) charging, where the current is fixed while the battery voltage rises. Once the battery reaches a certain voltage threshold, the charger switches to constant voltage (CV) mode, where the voltage is maintained while the charging current gradually decreases. The charging process ends when the current falls to a low value, indicating the battery is fully charged.
Can you explain the analogy of the water tap used to explain CC/CV charging?
-In this analogy, the battery is compared to a coffee cup, and the water supply represents electrical energy. The water tap is analogous to the battery charger, and controlling the water flow mimics regulating the charging current. During the initial CC phase, the water tap is opened to a certain flow (constant current), and during the CV phase, the tap is tightened to reduce the flow as the battery nears full charge.
Why is constant current (CC) used in the initial phase of charging?
-Constant current charging ensures that the battery receives a steady current at the beginning, which prevents overloading the battery and helps it charge efficiently and safely. This method prevents potential damage caused by excessive current during early stages of charging.
What happens when the battery voltage reaches the constant voltage threshold?
-When the battery voltage reaches the constant voltage (CV) threshold, the charger shifts from constant current mode to constant voltage mode. In this mode, the charger regulates the voltage while allowing the current to decrease gradually as the battery nears full charge.
How does the charger detect when the battery is fully charged?
-The charger detects the end of the charging process by monitoring the current. When the charging current drops to about 10% of the full charge rate, this is considered the End-of-Charge (EOC) threshold, signaling that the battery is fully charged and the charger can stop supplying power.
What is trickle charging, and when is it used?
-Trickle charging is a slow charging process used when the battery is deeply discharged, and its voltage is below the pre-charge threshold. This method supplies a small current to safely bring the battery's voltage up to a level where normal charging can begin, preventing damage from high surge currents.
What happens if the battery voltage drops after it has been fully charged?
-If the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold (such as 4.03V for Li-ion batteries), the charger will begin the charging cycle again to bring the battery back to full charge. This is essential to prevent self-discharge and ensure the battery stays charged and ready for use.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electrical Engineering: Basic Concepts (4 of 7) Electric Current: DC vs AC
entrance into the DC DC Converter Basic Topologies

Memahami Arus Bolak-Balik

How to build an Arduino controlled solar charger

Direct Current (DC)
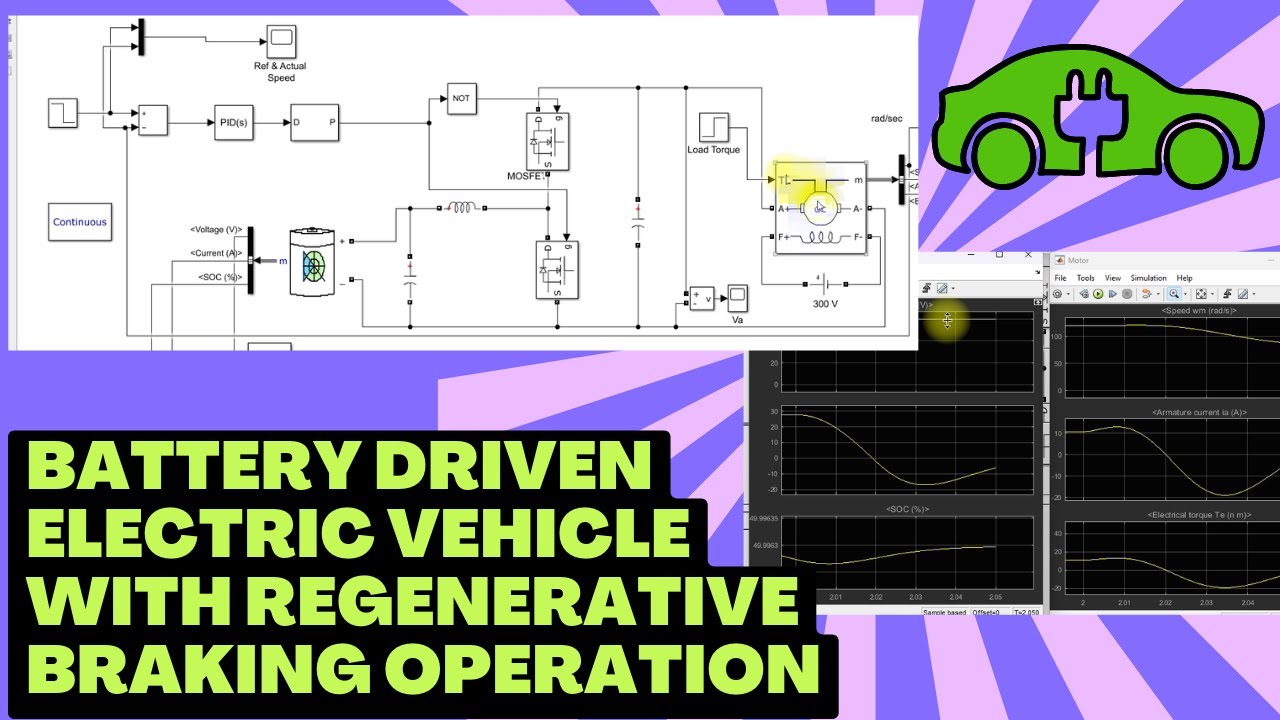
Battery driven Electric vehicle with regenerative Braking operation | Electric vehicle Simulation |
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)