Kadar Air Tanah dan Pergerakan Air Tanah
Summary
TLDRThe video delves into the vital role of water in soil health and plant growth, emphasizing its function as a solvent and nutrient transporter. It explores factors affecting groundwater, such as soil texture and organic content, and details methods for measuring soil moisture, including practical experiments. The video also discusses water movement within soil, distinguishing between saturated and unsaturated flow, and illustrates how soil type influences water retention and movement. Overall, it highlights the intricate relationship between soil properties and water dynamics, providing valuable insights for effective irrigation and soil management.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Water plays a critical role in soil stability, nutrient transport, and overall plant health.
- 🌱 Groundwater content is influenced by factors such as organic matter, soil texture, climate, and vegetation.
- 📏 Accurate measurement of soil water content can be achieved through practical experiments using specific tools.
- 🌿 Soil exists in three primary water conditions: saturation, field capacity, and permanent wilting point.
- 📊 Saturated conditions occur when all soil pores are filled with water, impacting drainage and aeration.
- 💧 Field capacity refers to the moisture level retained in soil after excess water has drained away.
- 🌵 Permanent wilting point is the critical moisture level at which plants can no longer extract water.
- 🚰 Water movement in soil can occur as saturated or unsaturated flow, influenced by soil texture and structure.
- 🔍 Soil texture, especially clay content, affects water retention and movement dynamics.
- 📚 Understanding soil water dynamics is essential for effective irrigation and agricultural management.
Q & A
What is the primary role of water in soil?
-Water acts as a solvent and binding agent, influencing the chemical stability of soil and supporting various life processes.
What factors affect groundwater levels in soil?
-Groundwater levels are influenced by organic material content, soil texture, climate, vegetation, soil depth, structure, permeability, and porosity.
What are the three main water conditions in soil?
-The three main conditions are saturated, field capacity, and permanent wilting point.
What does the field capacity (FC) represent?
-Field capacity represents the amount of water soil can retain after excess water has drained, where macro pores contain air.
How is the permanent wilting point (PWP) defined?
-The permanent wilting point is the soil moisture level at which plants cannot recover, leading to wilting and potential death.
What tools are used to measure soil moisture content in the experiment?
-The tools used include a cawan, gauze, tray, sponge, tissue, scale, desiccator, and oven.
What was the moisture content for the orange land and former paddy land?
-The moisture content was 23.96% for orange land and 25.53% for former paddy land.
What influences the movement of water in soil?
-Water movement is influenced by soil texture, structure, pore size, and the gravitational pull on water.
What were the results regarding the movement of water in different soil types?
-The experiment showed that sandy soils had faster water movement compared to clay soils, which retained water more due to smaller particle sizes.
How does soil texture impact water retention?
-Finer textures, like clay, have a greater surface area and can hold more water, but may limit availability for plants, whereas coarser textures like sand allow quicker drainage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Hubungan Air Tanah Tanaman
Structure Of Water Molecule - Chemistry Of Water - Properties Of Water - Composition Of Water
Soil Science Introduction

Tanah dan Kehidupan: Sifat Fisika dan Kimia Tanah - SMP Kelas 9 | Part 1
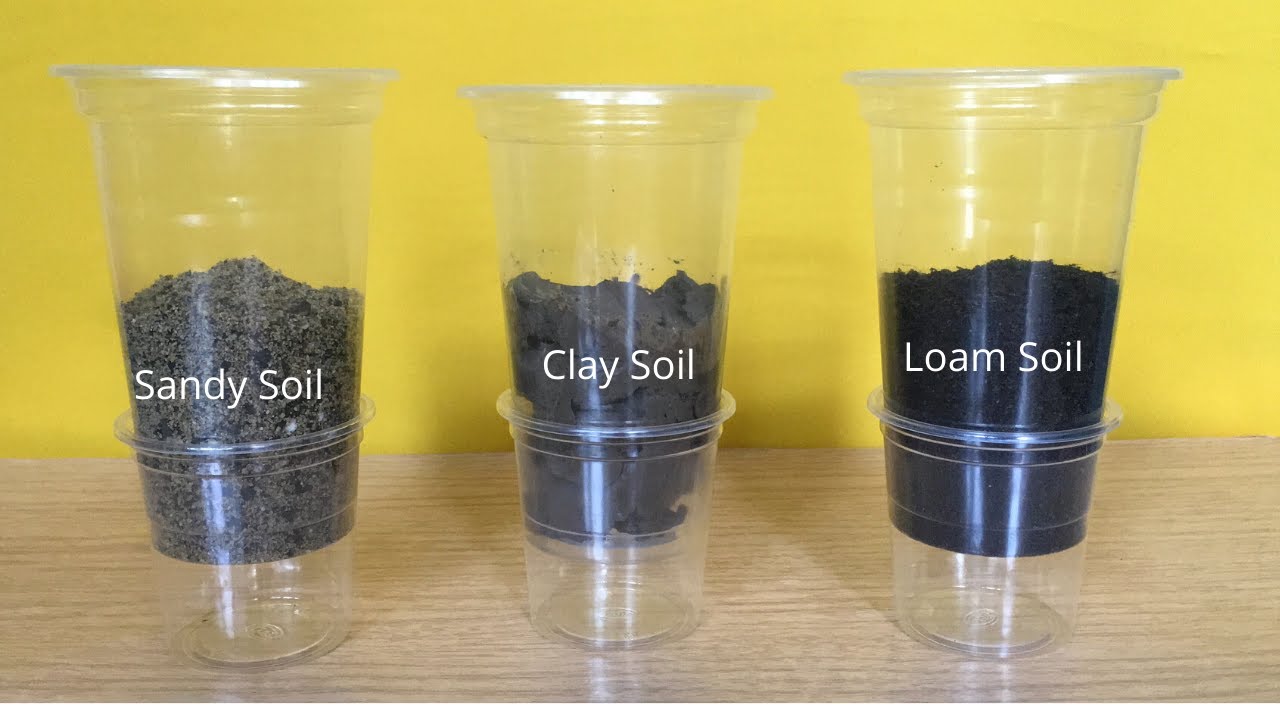

Types of Soil | Water Flow and Absorption Test | Sand, Loam and Clay Soil

Soil Chemistry Introduction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)