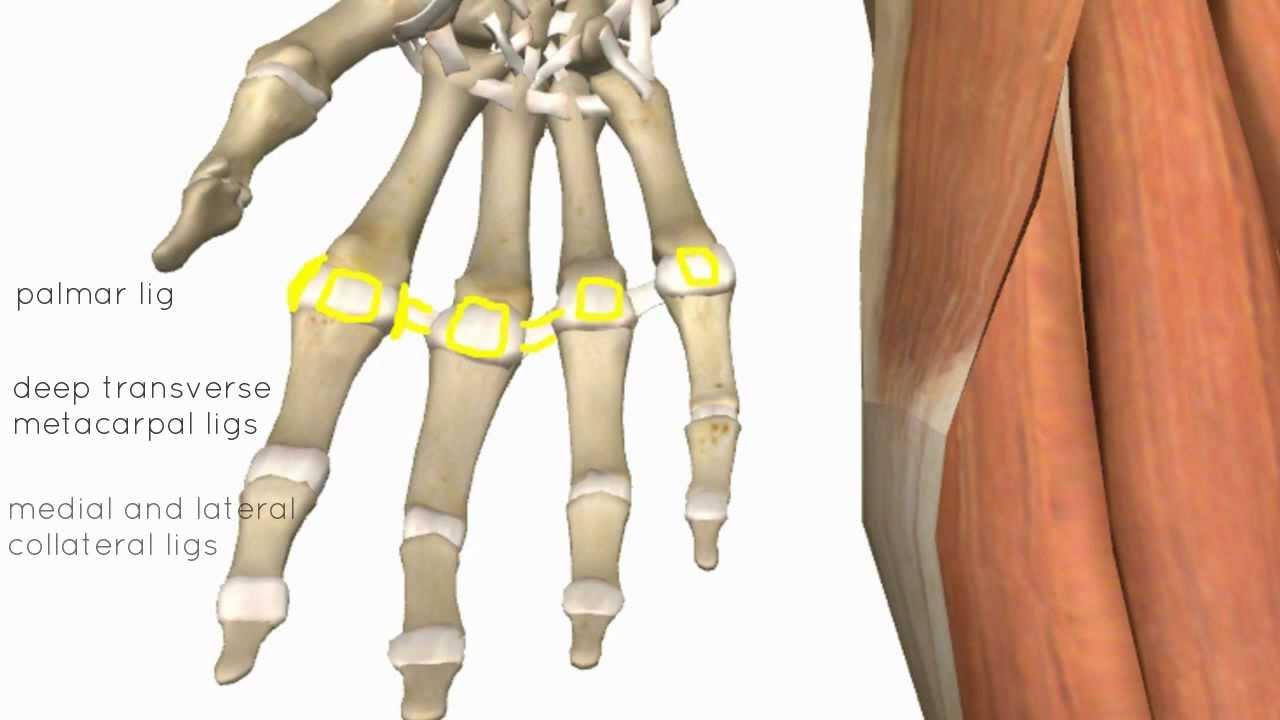
Nerve Injury Position of the Hand & Fingers - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of hand nerve injuries, detailing specific conditions associated with ulnar, median, and radial nerve injuries. Key signs such as claw hand, Wartenberg's sign, and the Benedictine sign are discussed, along with the implications of these injuries on hand functionality. The video also highlights important diagnostic tests, including Froment's test and the okay sign, which help assess nerve integrity. By explaining the clinical presentations and underlying mechanisms of these injuries, the video serves as an informative resource for understanding nerve damage and its effects on hand movement.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ulnar nerve injuries can lead to claw hand deformity due to the unopposed action of the flexor digitorum profundus.
- 😀 Wartenberg's sign, characterized by the abduction of the fifth finger, is indicative of ulnar nerve damage.
- 😀 Froment's test assesses for ulnar nerve palsy; flexion of the thumb IP joint while pinching paper suggests weakness in the adductor pollicis.
- 😀 Median nerve injuries can result in the Benediction sign, where the first two digits remain extended when trying to make a fist.
- 😀 The 'Abe Hand' appearance occurs due to paralysis of the thenar muscles, causing all fingers to align in the same plane.
- 😀 The anterior interosseous nerve injury is evaluated using the 'Okay Sign,' where the inability to form this sign indicates paralysis of specific flexor muscles.
- 😀 Radial nerve injuries lead to wrist drop, affecting the ability to extend the wrist and fingers.
- 😀 High radial nerve injuries are often caused by humeral shaft fractures and can result in significant functional impairment.
- 😀 Posterior interosseous nerve injury affects finger extension, even when wrist extension may be intact.
- 😀 Understanding these clinical signs is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management of hand nerve injuries.
Q & A
What is the appearance of a claw hand in relation to nerve injury?
-A claw hand typically results from ulnar nerve injury, leading to paralysis of intrinsic muscles, causing the fourth and fifth fingers to flex while the others remain extended.
What does Wartenberg's sign indicate?
-Wartenberg's sign is characterized by the abduction of the fifth finger, indicating ulnar nerve injury due to the unopposed action of the extensor digiti quinti.
How does the Froment's test work?
-The Froment's test assesses ulnar nerve function; a positive result shows flexion of the thumb when pinching paper, indicating weakness in the adductor pollicis muscle.
What is the benediction sign associated with?
-The benediction sign occurs in patients with high median nerve injuries, where the patient cannot flex the first two digits when making a fist, resulting in the fourth and fifth digits flexing.
What is the difference between a claw hand and an ape hand?
-A claw hand occurs due to ulnar nerve injury, while an ape hand is associated with median nerve injury, leading to paralysis of thenar muscles and the thumb being aligned with other fingers.
What indicates an anterior interosseous nerve injury?
-An anterior interosseous nerve injury is indicated by the inability to make the 'okay' sign, which involves paralysis of muscles responsible for flexing the thumb and index finger.
What is wrist drop and what causes it?
-Wrist drop is caused by radial nerve injury, leading to paralysis of wrist and finger extensors, typically from fractures of the humeral shaft.
What occurs in a posterior interosseous nerve injury?
-In a posterior interosseous nerve injury, the patient may have preserved wrist extension but cannot extend the fingers, indicating a more localized issue compared to wrist drop.
How do intrinsic muscles affect finger movement?
-Intrinsic muscles, innervated by the ulnar nerve, are crucial for finger abduction and adduction; their paralysis leads to characteristic hand deformities.
What muscles are primarily affected by median nerve injuries?
-Median nerve injuries primarily affect the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor pollicis longus, and the radial half of the flexor digitorum profundus, leading to typical signs like the benediction hand.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)