Gear PITTING - Surface Contact Stress Fatigue Failure in Just Over 10 Minutes!
Summary
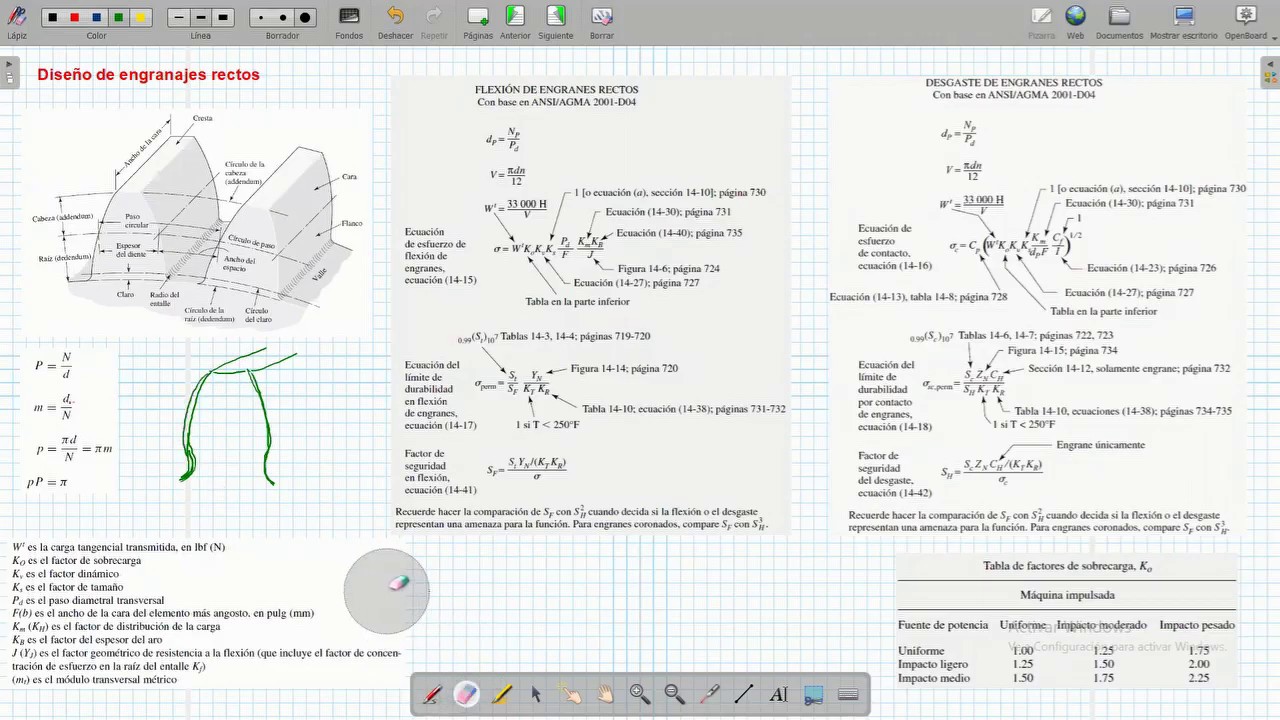
TLDRThis video delves into the surface contact stresses in gears, particularly focusing on pitting and compressive stresses. It introduces the Hertz contact theory, explaining how varying geometries influence stress calculations. The session outlines key parameters like elastic coefficients and surface endurance strength, linking them to gear material properties. A practical example illustrates how to calculate the factor of safety for surface fatigue failure in gears, emphasizing the relevance of material selection. The video concludes by transitioning to bearing design concepts, highlighting the importance of understanding gear dynamics in selecting appropriate components.
Takeaways
- 🛠️ Gears experience two main types of stresses: bending stress in the teeth and surface contact stresses (pitting).
- 🔍 Pitting is a surface fatigue failure caused by repeated contact stresses.
- ⚙️ Hertz contact theory is commonly used to analyze contact stresses between gear teeth.
- 📏 The shape and material properties of gear teeth influence how contact stresses are calculated.
- 📊 The contact stress equation considers factors like force, length, and radius of curvature.
- 🔄 The elastic coefficient (Cp) simplifies the calculations by incorporating material properties.
- 🔒 Surface endurance strength is approximated as a percentage of a material's hardness.
- 📉 The factor of safety for gears is determined using surface endurance strength and surface contact stress.
- 📚 The example provided illustrates how to calculate the factor of safety for a cast iron gear system.
- 🔗 Future lessons will cover bearings and their design considerations in relation to gear systems.
Q & A
What are the two main stresses studied in gears?
-The two main stresses are the bending of the teeth and surface contact stresses, commonly referred to as pitting.
What is pitting and how does it occur?
-Pitting is a surface fatigue failure caused by the repetition of contact stresses between gear teeth.
What theory is commonly used to analyze surface contact stresses in gears?
-The Hertz contact theory is commonly used to analyze surface contact stresses.
How does the geometry of contacting gears affect contact stresses?
-The geometry determines the radii of curvature at the point of contact, affecting how the force distributes and the resulting pressure.
What does the variable 'b' represent in the contact stress equation?
-'b' represents the half width of the contact area, which is influenced by the materials' elastic properties.
How is surface endurance strength approximated in gear design?
-Surface endurance strength is approximated as a fraction of the material's hardness, such as 32% of the Brinell hardness for cast iron.
What is the significance of the factor of safety in gear design?
-The factor of safety helps assess the reliability of a gear system by comparing the loss of function load to the imposed load.
Why is the factor of safety defined differently in this context?
-It is defined as the ratio of the square of the surface endurance strength to the square of the contact stress due to the non-linear relationship between stress and load.
What was the calculated factor of safety for the gear made of cast iron?
-The calculated factor of safety for the cast iron gear was 1.064.
What will the next video cover after discussing gears?
-The next video will cover bearings, focusing on the selection of appropriate bearings for a shaft and gear pulley system.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)