Video Animasi Pembelajaran Hukum-Hukum Newton
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Hasna, a student from Universitas Negeri Padang, introduces Newton's Laws of Motion. She explains the significance of each law, starting with the First Law of Inertia, which highlights the concept that objects at rest stay at rest unless acted upon by an external force. The Second Law describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration (F=ma), illustrated by practical examples of pushing objects. Finally, the Third Law emphasizes the principle of action and reaction, using rowing as a key example. The lesson aims to deepen understanding of motion in everyday contexts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Newton's laws of motion were formulated by Sir Isaac Newton and are foundational principles in physics.
- 😀 The First Law of Motion (Inertia) states that an object at rest stays at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion unless acted upon by an external force.
- 😀 Mathematically, the First Law is expressed as ΣF = 0, indicating that if the net force is zero, the object's state of motion remains unchanged.
- 😀 The Second Law of Motion describes the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration, expressed as ΣF = m * a.
- 😀 According to the Second Law, greater force results in greater acceleration, while increased mass results in reduced acceleration.
- 😀 The Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction, mathematically represented as F_action = -F_reaction.
- 😀 Practical examples illustrate the laws, such as passengers feeling a force backward when a car accelerates (First Law).
- 😀 The effectiveness of pushing a table is greater when two people push together, demonstrating the Second Law's principle of force and acceleration.
- 😀 When paddling a boat, pushing water backward leads to the boat moving forward, exemplifying the Third Law of Motion.
- 😀 Engaging students with real-life scenarios enhances their understanding of these fundamental physics concepts.
Q & A
What is the focus of the lesson presented by Hasna?
-The lesson focuses on Newton's laws of motion in physics.
Who discovered Newton's laws and in which work are they compiled?
-Newton's laws were discovered by Sir Isaac Newton and are compiled in his work 'Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'.
What does Newton's First Law state?
-Newton's First Law states that an object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues in motion at a constant speed in a straight line unless acted upon by a net external force.
Can you give an example of Newton's First Law from the transcript?
-An example is when passengers in a car lean backward when the car suddenly accelerates, illustrating their tendency to maintain their state of motion.
What does Newton's Second Law explain?
-Newton's Second Law explains that the acceleration of an object depends on the net force acting on it and is inversely proportional to its mass, expressed as F = ma.
How does pushing a table demonstrate Newton's Second Law?
-When pushing a table with a friend, the combined force allows the table to accelerate faster than if pushed alone, showing that greater force results in greater acceleration.
What is the key principle of Newton's Third Law?
-Newton's Third Law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
What example illustrates Newton's Third Law in the lesson?
-Rowing a boat illustrates Newton's Third Law; when a person pushes water backward, the boat moves forward as a reaction.
What mathematical expression represents Newton's First Law?
-The mathematical expression for Newton's First Law is ΣF = 0, indicating that the net force acting on the object is zero.
How does mass affect acceleration according to Newton's Second Law?
-According to Newton's Second Law, an increase in mass results in a decrease in acceleration when the same force is applied, demonstrating the inverse relationship between mass and acceleration.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

BAB 4 GERAK DAN GAYA || Gaya dan Hukum Newton – IPA Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

Proses Inovasi Pendidikan | VIDEO PEMBELAJARAN

Gerak dan Gaya Kelas 7 - Gaya dan Hukum Newton | IPA Bab 4 Kurikulum Merdeka - Lengkap
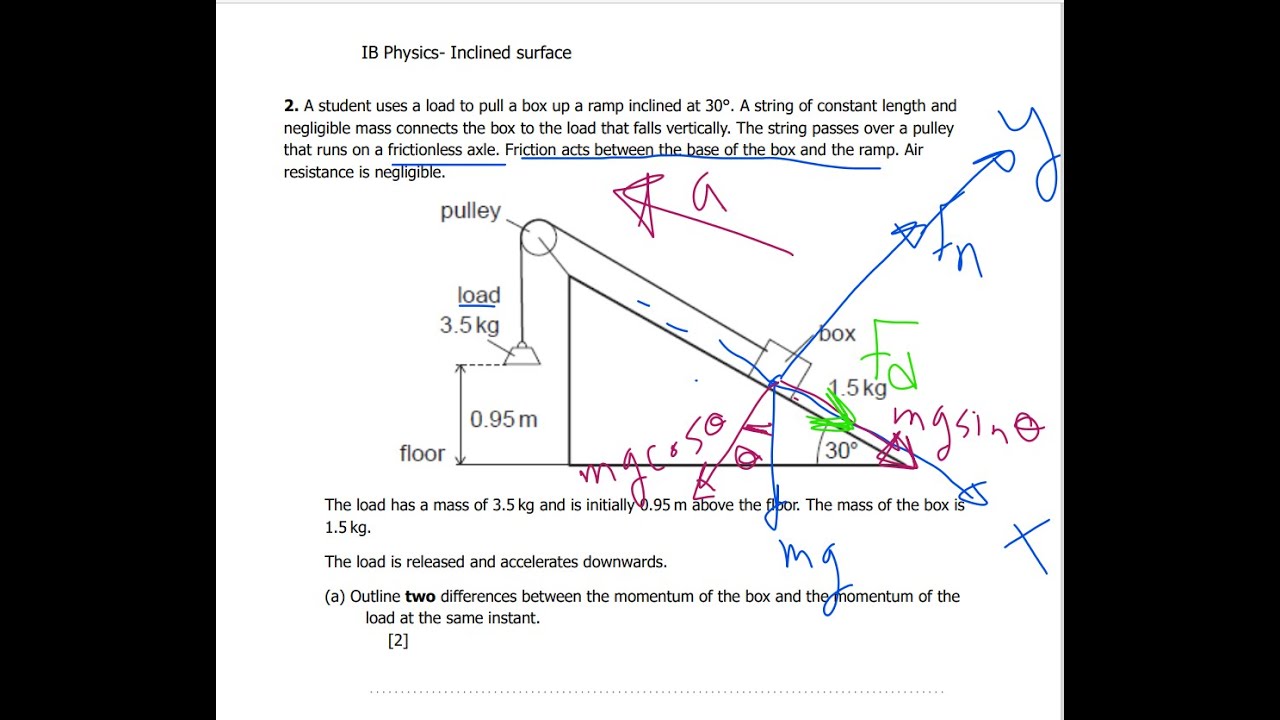
IB Physics-Theme-A2- A student uses a load to pull a box up a ramp inclined

VIDEO ANIMASI PEMBELAJARAN BERBASIS POWTOON PADA MATERI HUKUM NEWTON

Gaya dan Hukum hukum Newton
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)