pembentukan,pengertian,fungsi Sel limfosit B dan sel limfosit T - Biologi kelas 11 Bab sistem imun
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the specific immune system, focusing on B and T lymphocytes. B cells, produced in the bone marrow, are responsible for generating antibodies and forming memory cells for future immune responses. T cells mature in the thymus and play crucial roles in activating B cells, attacking infected cells, and regulating immune activity. The video explains the functions of various T cell types, including helper and cytotoxic T cells, highlighting their importance in the body's defense mechanisms. Viewers are encouraged to subscribe for more biological content.
Takeaways
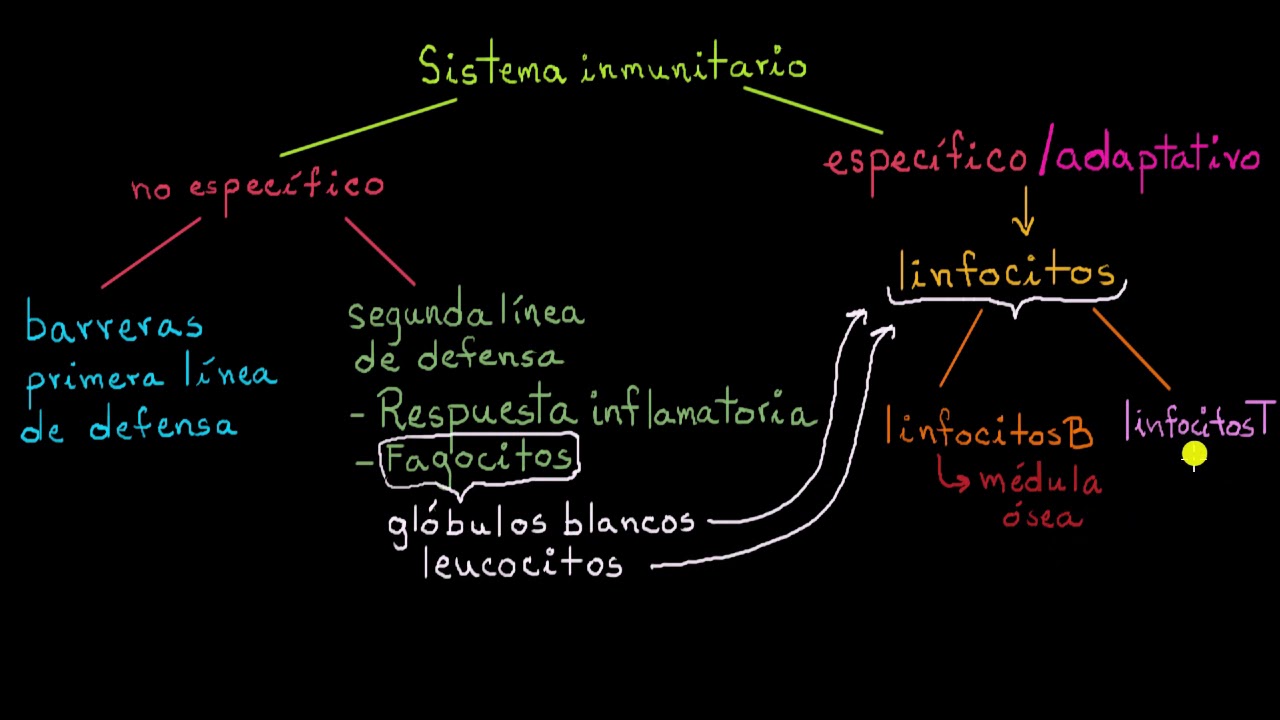
- 😀 The immune system consists of non-specific and specific components, including antibodies and antigens.
- 😀 B lymphocytes (B cells) are a type of specific immune cell developed in the bone marrow, constituting 10-20% of all lymphocytes.
- 😀 The primary function of B cells is to produce antibodies in response to specific antigens.
- 😀 Naive B cells mature in the bone marrow and can recognize specific antigen signals but cannot produce antibodies until activated.
- 😀 Once activated by helper T cells, B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce large amounts of antibodies and memory B cells that retain antigen information.
- 😀 T lymphocytes (T cells) are formed in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus, making up 80-90% of total lymphocytes.
- 😀 T cells play crucial roles in activating naive B cells, activating macrophages, and destroying infected cells.
- 😀 Naive T cells differentiate into helper T cells or cytotoxic T cells, each with specific roles in the immune response.
- 😀 Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs) are essential for T cell activation, presenting antigens through MHC complexes.
- 😀 The different types of T cells have specific functions: helper T cells stimulate B cells, regulatory T cells manage T cell activity, and cytotoxic T cells destroy infected cells.
Q & A
What are the main components of the immune system discussed in the transcript?
-The transcript focuses on specific components of the immune system, particularly B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, which play crucial roles in immune responses.
Where are B lymphocytes produced and matured?
-B lymphocytes are produced and matured in the bone marrow.
What is the primary function of B lymphocytes?
-The primary function of B lymphocytes is to produce antibodies that help neutralize pathogens.
What is the difference between naïve B cells and plasma cells?
-Naïve B cells have not yet encountered antigens and do not produce antibodies, while plasma cells are differentiated B cells that produce large amounts of antibodies.
How do memory B cells contribute to the immune response?
-Memory B cells retain information about previously encountered antigens, allowing for a faster and more effective response if the same antigen is encountered again.
How are T lymphocytes formed and where do they mature?
-T lymphocytes are formed in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus gland.
What roles do helper T cells (CD4+) play in the immune system?
-Helper T cells stimulate the activation of B cells to produce antibodies and assist in activating macrophages and other immune cells.
What is the role of regulatory T cells?
-Regulatory T cells help modulate the immune response, preventing overactivity of other T cells and maintaining immune system balance.
What distinguishes cytotoxic T cells (CD8+) from other T cells?
-Cytotoxic T cells directly kill infected cells using proteins like perforin and granzyme, targeting cells that display specific antigens.
What is the significance of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in T cell activation?
-APCs present antigens on their surface via MHC complexes, which is essential for the activation of T cells, as T cells can only recognize antigens when presented this way.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Tipos de respuesta inmune: Innata y adaptativa, humoral vs. celular | Khan Academy en Español

Sistem Imun Spesifik
Immunity

Cell-Mediated (Cellular) Immunity [aka T-cell immunity] - Physiology & Immunology

Kekebalan di Dapatkan / acquired immunity (Sistem Imunitas)

mekanisme sistem imun humoral dan seluler ,sistem pertahanan tubuh spesifik (lapis 3)bab.sistem imun
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)