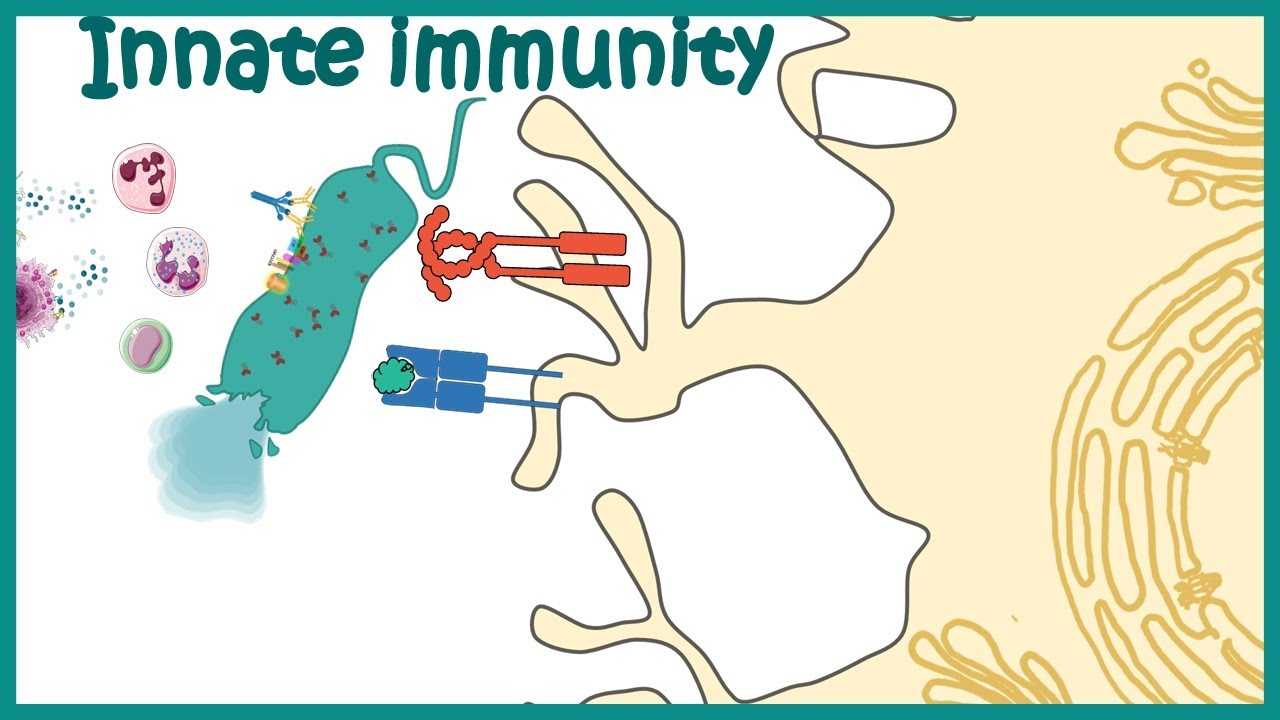
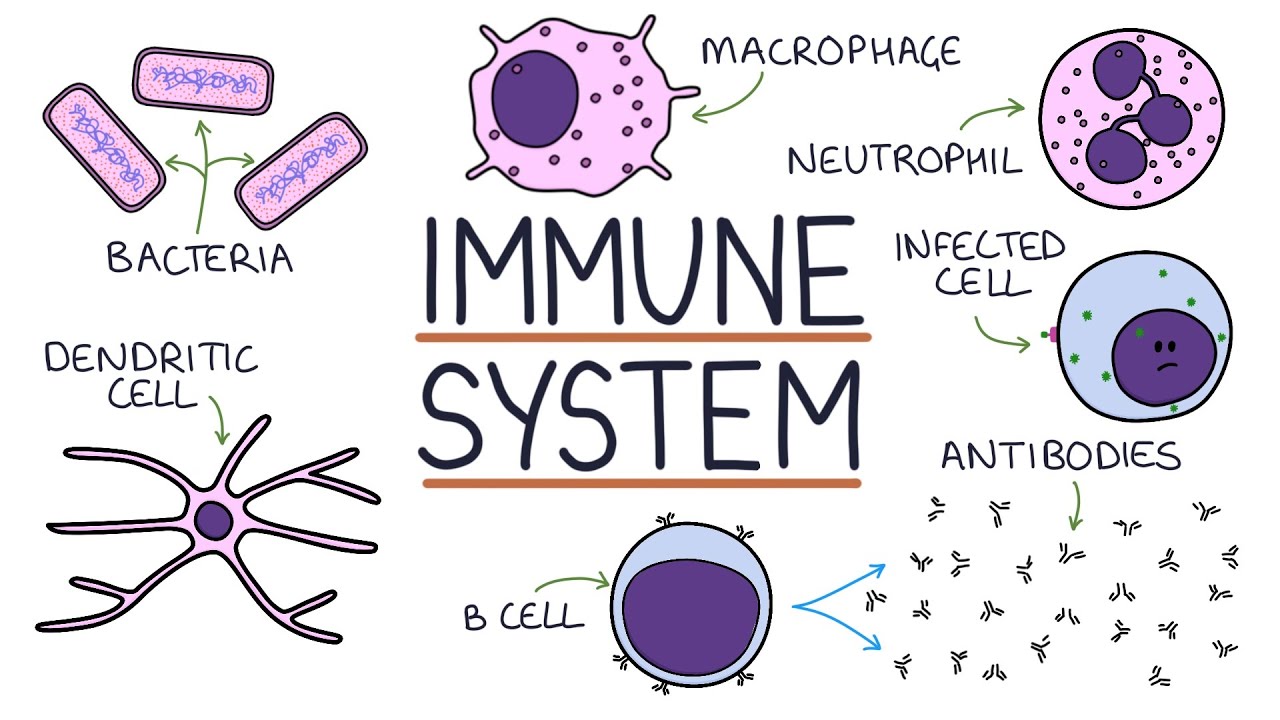
Sistem Imun Spesifik
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the specific immune system, focusing on its ability to recognize and remember pathogens. It covers both humoral immunity, involving B lymphocytes and antibodies, and cellular immunity, involving T lymphocytes. Humoral immunity works through various mechanisms such as neutralization, agglutination, and complement activation, while cellular immunity involves T-helper, cytotoxic, suppressor, and memory T cells. The video also discusses active and passive immunity, including natural and artificial examples, like vaccines. It touches on immunoglobulins, allergies, autoimmunity, and HIV-related immune disorders, emphasizing the importance of studying the immune system from multiple sources.
Takeaways
- 😀 The specific immune system identifies and remembers pathogens that enter the body.
- 😀 Humoral immunity involves B lymphocytes, which produce antibodies to fight infections.
- 😀 B lymphocytes are categorized into plasma cells (which secrete antibodies), memory cells (which remember antigens), and dividing cells (which multiply antibody production).
- 😀 Antibodies work through mechanisms like neutralization, agglutination, precipitation, and complement activation to neutralize or destroy pathogens.
- 😀 Cellular immunity involves T lymphocytes, which are divided into helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, suppressor T cells, and memory T cells.
- 😀 Active immunity can be acquired naturally (after recovering from an infection) or artificially (through vaccination).
- 😀 Passive immunity can be natural (through antibodies from breast milk) or artificial (through administered antibodies, like those from horses).
- 😀 Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are proteins that help identify and neutralize pathogens. They have different forms such as IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, and IgD, each with specific functions.
- 😀 Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the first antibody to be produced in response to an infection and can activate complement and agglutinate antigens.
- 😀 Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most abundant antibody in the body and neutralizes toxins, activates complement, and provides long-term immunity.
- 😀 Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is primarily found in mucosal areas (like saliva and tears) and helps prevent infections by blocking pathogen entry.
- 😀 Disorders in the immune system include allergies, autoimmunity (where the immune system attacks the body’s own cells), and HIV/AIDS, which weakens the immune system by targeting T lymphocytes.
Q & A
What is the primary characteristic of the specific immune system?
-The specific immune system is characterized by its ability to identify and remember pathogens that have previously entered the body.
What are the two main types of specific immunity?
-The two main types of specific immunity are humoral immunity and cellular immunity.
What role do B lymphocytes play in humoral immunity?
-B lymphocytes are involved in humoral immunity, where they produce antibodies. There are three types of B lymphocytes: plasma, memory, and dividing B cells.
What is the function of plasma B cells in humoral immunity?
-Plasma B cells secrete antibodies, which are proteins that specifically target and neutralize pathogens.
What are the four mechanisms of action for antibodies in the humoral immune response?
-The four mechanisms are neutralization (blocking antigens), agglutination (clumping antigens), precipitation (forming antigen complexes), and activating complement proteins to destroy pathogens.
How do T lymphocytes contribute to cellular immunity?
-T lymphocytes are central to cellular immunity, and they are classified into four types: helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, suppressor T cells, and memory T cells, each performing specific roles like activating other immune cells and destroying infected cells.
Where are B and T lymphocytes formed, and how do they mature?
-B lymphocytes are formed in the bone marrow and mature there, while T lymphocytes are formed in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus.
What is the difference between active and passive immunity?
-Active immunity is developed when the immune system is exposed to an antigen, either naturally through infection or artificially through vaccination. Passive immunity involves receiving antibodies from another source, such as through breast milk or antibody injections.
What are the five types of immunoglobulins, and what are their functions?
-The five types of immunoglobulins (Ig) are IgM (first response to infection), IgG (most abundant, neutralizes toxins), IgA (prevents pathogen entry into the body), IgE (involved in allergies and parasitic infections), and IgD (stimulates B cell differentiation).
What are some examples of immune system disorders?
-Examples of immune system disorders include allergies (overreaction to harmless substances), autoimmune diseases (where the immune system attacks the body’s own cells), and immunodeficiency diseases like AIDS, where the immune system is weakened, allowing opportunistic infections.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)