What is microRNA (miRNA)?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the significance of microRNA, short RNA sequences that play a crucial role in regulating gene expression by silencing target messenger RNA. Initially thought to be 'junk DNA,' introns are now recognized for their essential function in producing microRNAs. These molecules are synthesized in two stages and form a complex with Argonaut proteins to inhibit protein production by binding to and potentially degrading messenger RNA. The video promises further insights into microRNA biogenesis and its pivotal role in cellular processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Introns, once considered junk DNA, play crucial roles in gene regulation.
- 😀 Several types of small non-coding RNA exist, including micro RNA, si RNA, and pi RNA.
- 😀 Micro RNA (miRNA) is approximately 22 nucleotides long and regulates gene expression.
- 😀 miRNA is produced in two stages: first in the nucleus and then processed in the cytoplasm.
- 😀 The protein Drosha initiates the formation of miRNA in the nucleus.
- 😀 Dicer further processes miRNA into its mature form in the cytoplasm.
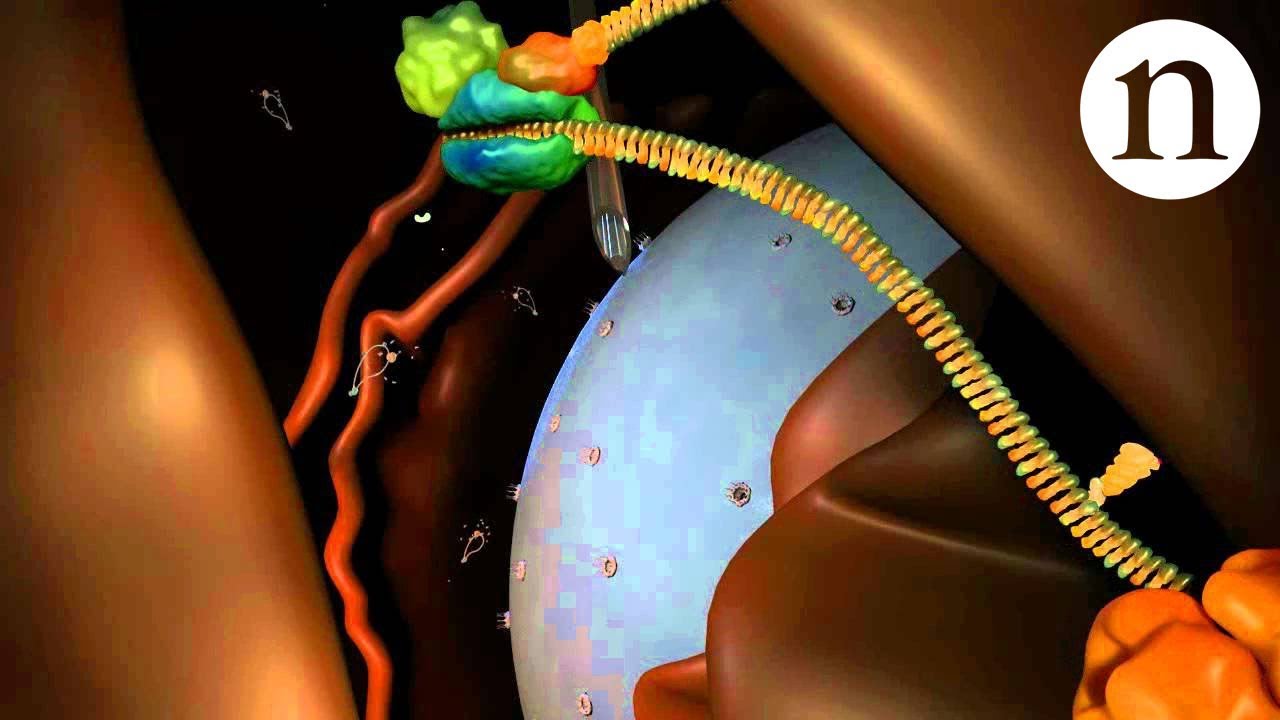
- 😀 The Argonaut protein (AGO) binds to mature miRNA to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).
- 😀 miRNA silences genes by binding to complementary messenger RNA (mRNA) sequences.
- 😀 This binding prevents translation by creating a roadblock for ribosomes or degrading mRNA.
- 😀 The video will explore miRNA biogenesis and the intricate processes involved.
Q & A
What were introns previously believed to be?
-Introns were once thought to be 'junk DNA' with no purpose.
What has recent research revealed about non-coding RNAs?
-Recent research has shown that several types of non-coding RNAs, including micro RNA, play crucial roles in gene regulation.
What are the main types of small non-coding RNAs mentioned in the video?
-The main types mentioned are micro RNA, small interfering RNA (siRNA), and PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA).
How long are micro RNAs, and where are they formed?
-Micro RNAs are approximately 22 nucleotides in length and are formed in the nucleus.
What is the role of micro RNA in gene expression?
-Micro RNA regulates gene expression through a process called RNA interference, which can silence or degrade messenger RNA to prevent protein synthesis.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology, and how does micro RNA interact with it?
-The central dogma describes the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. Micro RNA interacts by preventing the translation of messenger RNA into proteins.
What proteins are involved in the synthesis of micro RNA?
-The synthesis of micro RNA involves the proteins Drosha, which acts in the nucleus, and Dicer, which processes the RNA in the cytoplasm.
What is the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)?
-RISC is a complex formed when a mature micro RNA binds to an Argonaut protein, allowing it to silence target messenger RNAs.
How does micro RNA silence target genes?
-Micro RNA silences target genes by binding to complementary sequences in messenger RNA, preventing ribosomes from translating the mRNA or causing degradation of the mRNA.
What will be discussed in the video on micro RNA biogenesis?
-The video on micro RNA biogenesis will cover in more detail how micro RNA is made and the entire process involved in its function.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

MicroRNA miRNA animation || Gene regulation || Nobel Prize 2024

Gene Silencing by Micro RNA - Medical Animation

RNAi: Slicing, dicing and serving your cells - Alex Dainis

RNA interference animation

RNA structure, Function and types || Primary Structure of RNA || A Type Of Nucleic Acid
RNA interference (RNAi): by Nature Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)