RNA interference animation
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into RNA interference, a process popularized by experiments involving double-stranded RNA in worms. It explains how RNA polymerase generates pre-mRNAs, which are processed into mature mRNAs and translated in the cytoplasm. The script highlights the role of microRNAs and RNA silencing pathways in gene regulation, antiviral defense, and the creation of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) by Dicer. It also discusses the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which cleaves target mRNAs, and the amplification mechanisms involving RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP), crucial for antiviral responses and gene regulation in organisms like plants, fungi, and worms.
Takeaways
- 🧬 RNA interference is a process where double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) is used to silence genes in a sequence-specific manner.
- 🐛 The technique was popularized by injecting dsRNA into a worm's gonad, which is a common method for introducing transgenes in worms.
- 🛡️ dsRNA blocks the expression of endogenous genes, which is an important tool for studying gene function.
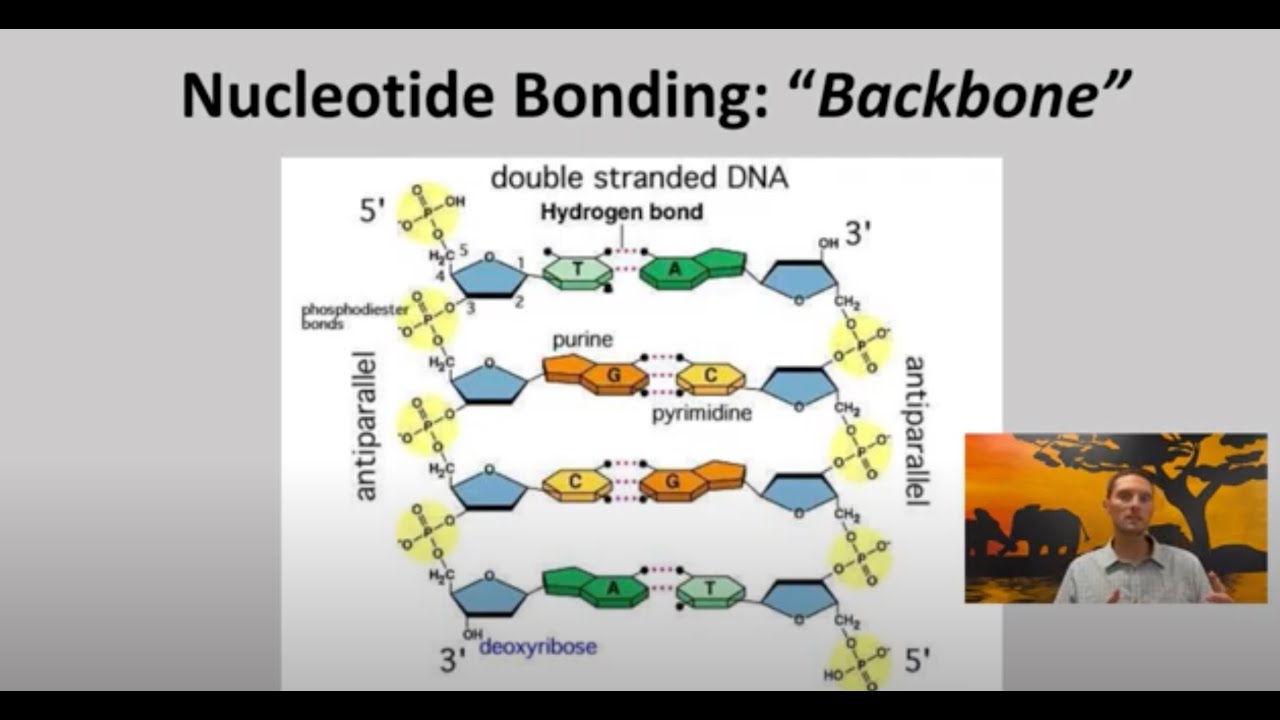
- 📝 Gene transcription by RNA polymerase II generates pre-mRNAs that are processed into mature mRNAs, which are then transported to the cytoplasm for translation.
- 🔄 RNA can regulate endogenous gene expression through mechanisms involving microRNAs and other short regulatory RNAs.
- 🌿 In plants and other organisms, RNA can be activated by endogenous transposition and plays a role in antiviral defense.
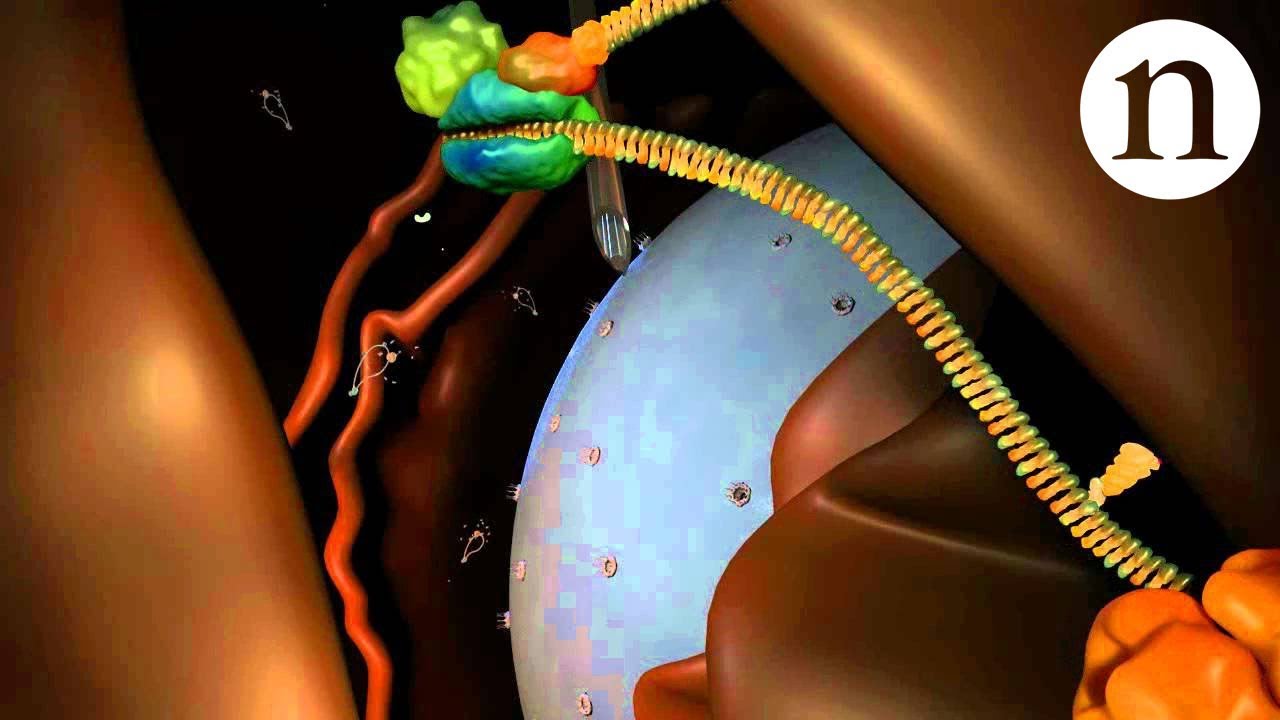
- 🔪 Dicer, a member of the RNase III family, cleaves dsRNA into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) with two-nucleotide 3' overhangs.
- 🤝 siRNAs form a ribonucleoprotein complex called RISC, which includes an argonaute protein with an RNAse H-like domain.
- ⚔️ RISC mediates the unwinding of the siRNA duplex, allowing a single-stranded siRNA to bind to and cleave target mRNA in a sequence-specific manner.
- 🚫 Cleaved mRNA is recognized as aberrant and destroyed, preventing translation and silencing gene expression.
- 🌱 In plants, aberrant RNA from RISC-mediated cleavage can serve as a template for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP), generating more siRNAs.
- 🔄 Some organisms have an amplification step involving single-stranded siRNAs binding to target mRNAs and serving as primers for RdRP to synthesize the antisense RNA strand.
- 🌱 RNA spreading between cells is suggested to underlie germline transmission of RNA in worms and has been described in plants.
- 🐇 RNA spreading has not been described in mammals, indicating differences in RNA interference mechanisms across species.
Q & A
What is RNA interference and how was it popularized?
-RNA interference is a biological process where RNA molecules regulate gene expression. It was popularized by the work of researchers who injected long double-stranded RNAs into a worm's gonad, which blocked the expression of endogenous genes in a sequence-specific manner.
How do genes get transcribed in the cell?
-Genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, which generates pre-mRNAs that are then processed to form mature mRNAs.
What is the role of mRNA in the cell?
-mRNAs are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where they serve as templates for protein synthesis through the process of translation.
What are microRNAs and how do they regulate gene expression?
-MicroRNAs are genomically encoded short regulatory RNAs that can regulate endogenous gene expression in organisms such as algae, worms, and flies.
How does RNA play a role in antiviral defense?
-In antiviral defense, double-stranded RNA from viruses is targeted for destruction by the RNA machinery, preventing viral replication and spread.
What is Dicer and how does it function in RNA interference?
-Dicer is a member of the RNase III family of double-stranded RNA-specific endonucleases. It recognizes and cleaves long double-stranded RNAs into small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) with two-nucleotide long 3' overhangs.
What is the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and what does it include?
-The RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) is a ribonucleoprotein complex that includes Slicer, an Argonaute protein with an RNA-binding domain. It mediates the unwinding and cleavage of target mRNAs.
How does the RISC complex mediate mRNA cleavage?
-RISC first mediates the unwinding of the siRNA duplex, and then a single-stranded siRNA that is coupled to RISC binds to a target mRNA in a sequence-specific manner. This binding mediates target mRNA cleavage by the Slicer protein.
What happens to the cleaved mRNA and how does it lead to gene silencing?
-The cleaved mRNA is recognized by the cell as aberrant and is destroyed, preventing translation from occurring and thus silencing the expression of the gene from which the mRNA was transcribed.
How does the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) contribute to RNA interference?
-RdRP uses the aberrant RNA resulting from RISC-mediated cleavage as a template for unprimed RNA synthesis, generating more double-stranded RNA, which serves as a substrate for Dicer activity, producing more siRNAs.
What is the significance of RNA spreading in the context of RNA interference?
-RNA spreading is a process that allows the RNA interference signal to move between cells, which is thought to underlie the germline transmission of RNA in worms and has also been described in plants.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)