ATAR QCE Chemistry Unit 3 Topic 1: Buffers
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the concept of buffer solutions is explored, emphasizing their role in maintaining pH stability in biological systems, particularly human blood. Buffers resist pH changes when small amounts of acids or bases are added, which is crucial for health, as even slight pH fluctuations can be fatal. The video explains how buffers consist of a weak acid and its salt, demonstrating their mechanisms of action when acids or bases are introduced. Through various examples, the importance of buffers in everyday scenarios, such as food consumption, is highlighted, illustrating their protective role in biochemical processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Buffers are solutions that resist pH changes when small amounts of acids or alkalis are added.
- 😀 They are crucial in biological systems, especially in maintaining blood pH around 7.4 for optimal health.
- 😀 A buffer typically consists of a weak acid and its corresponding salt.
- 😀 When an acid is added to a buffer, the weak acid reacts with excess hydrogen ions (H⁺) to maintain pH stability.
- 😀 Conversely, adding a base to a buffer will either consume H⁺ ions or regenerate them by reacting with the weak acid.
- 😀 Buffers are not designed to handle large amounts of acids or bases, but rather accidental additions.
- 😀 A slight pH change can be dangerous in living systems, emphasizing the importance of buffers.
- 😀 The equilibrium in a buffer system helps maintain a stable concentration of H⁺ ions.
- 😀 Consuming acidic foods does not significantly alter blood pH due to the buffering action in the body.
- 😀 Understanding buffer mechanisms is essential for both laboratory applications and biological processes.
Q & A
What are buffer solutions?
-Buffer solutions are solutions that resist changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or alkali are added.
Why are buffers important in living systems?
-Buffers are crucial in living systems because they maintain the pH of blood and other fluids, which is essential for proper physiological functions.
What is the typical pH level of human blood?
-The typical pH level of human blood is around 7.4.
What can happen if the pH of blood changes significantly?
-Even a change of just half a unit in blood pH can be potentially fatal.
How do buffers work chemically?
-Buffers typically consist of a weak acid and its salt; when an acid or base is added, the buffer reacts to minimize pH changes.
What happens when an acid is added to a buffer solution?
-When an acid is added, the buffer neutralizes it by converting the added H+ ions into the weak acid, preventing significant changes in pH.
How does a buffer respond when a base is added?
-When a base is added, the buffer either reacts with the H+ ions to form water or with the weak acid to release H+ ions, thereby resisting pH changes.
What role does the weak acid play in a buffer solution?
-The weak acid in a buffer solution provides H+ ions that can react with added bases to maintain pH.
What type of acid is commonly used in buffer solutions?
-Commonly used weak acids in buffer solutions include acetic acid (ethanoic acid).
What would be the consequence of consuming large amounts of a strong acid?
-Consuming large amounts of a strong acid can be fatal, whereas small, accidental intakes of acidic foods are generally neutralized by the body's buffering systems.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
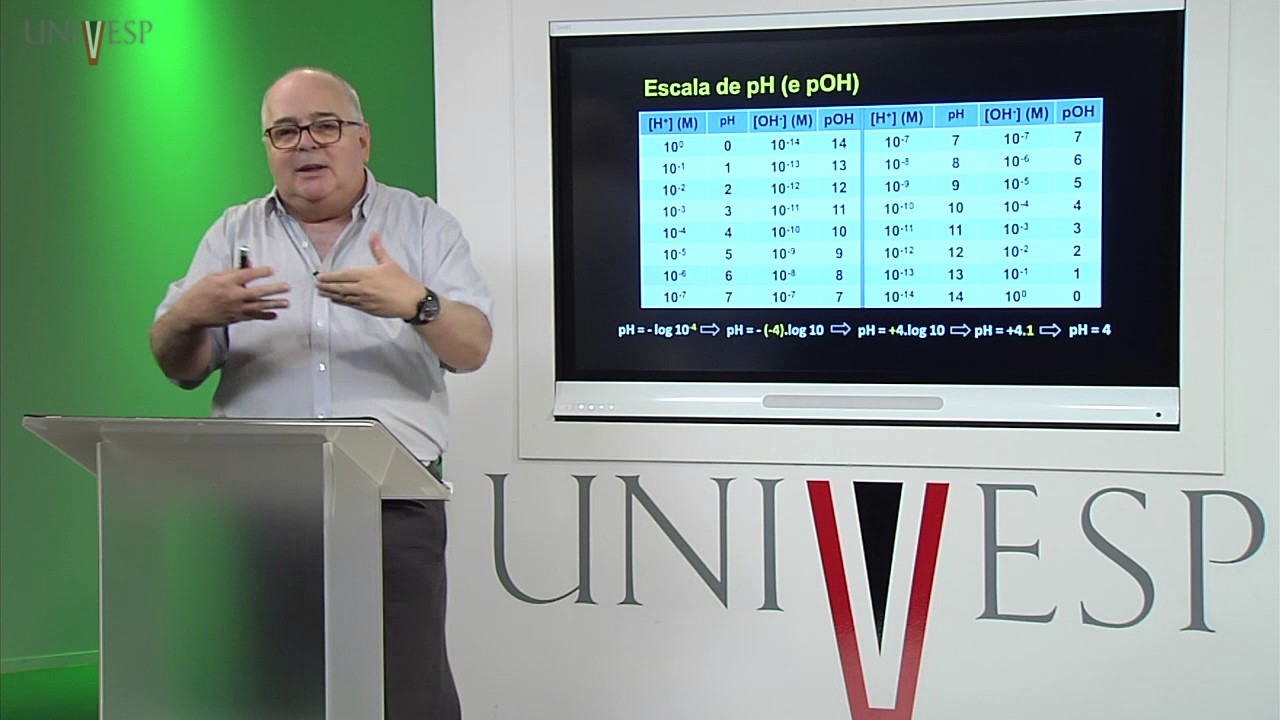
Bioquímica - Aula 03 - Alguns conceitos químicos importantes - 2

Larutan Penyangga • Part 1: Sifat, Komponen & Peran Larutan Buffer / Penyangga

SIFAT SIFAT DAN KEGUNAAN LARUTAN PENYANGGA

SOLUÇÃO TAMPÃO | EQUILÍBRIO QUÍMICO | Aula 26

Buffers (A-level IB Chemistry)

Larutan Penyangga | Jenis dan Prinsip Kerja Larutan Penyangga - Bagian 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)