Herman Willem Deandels
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, students explore the governance of Herman Willem Dandels in Java from 1808 to 1811. The lecture covers Dandels' rise to power during the Napoleonic Wars, his militaristic policies, and significant economic strategies that favored Dutch interests over local welfare. It highlights his revolutionary governance principles, including military recruitment from locals and the establishment of a forced labor system for road construction. The session concludes with Dandels' eventual removal and the subsequent British takeover of Java, marking a crucial turning point in Indonesia's colonial history.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Daendels governed Java from 1808 to 1811 during a tumultuous period marked by European conflicts.
- ⚔️ He implemented military policies to recruit Indonesian soldiers and build weapon factories in preparation for potential British attacks.
- ☕ Daendels mandated coffee cultivation, capitalizing on its high demand in Europe, which economically benefited the Dutch but exploited local farmers.
- 🏛️ Politically, he divided Java into administrative regions, establishing a system where local leaders worked as Dutch employees to minimize resistance.
- ⚖️ He set up courts to handle opposition against his policies, asserting control over the local population.
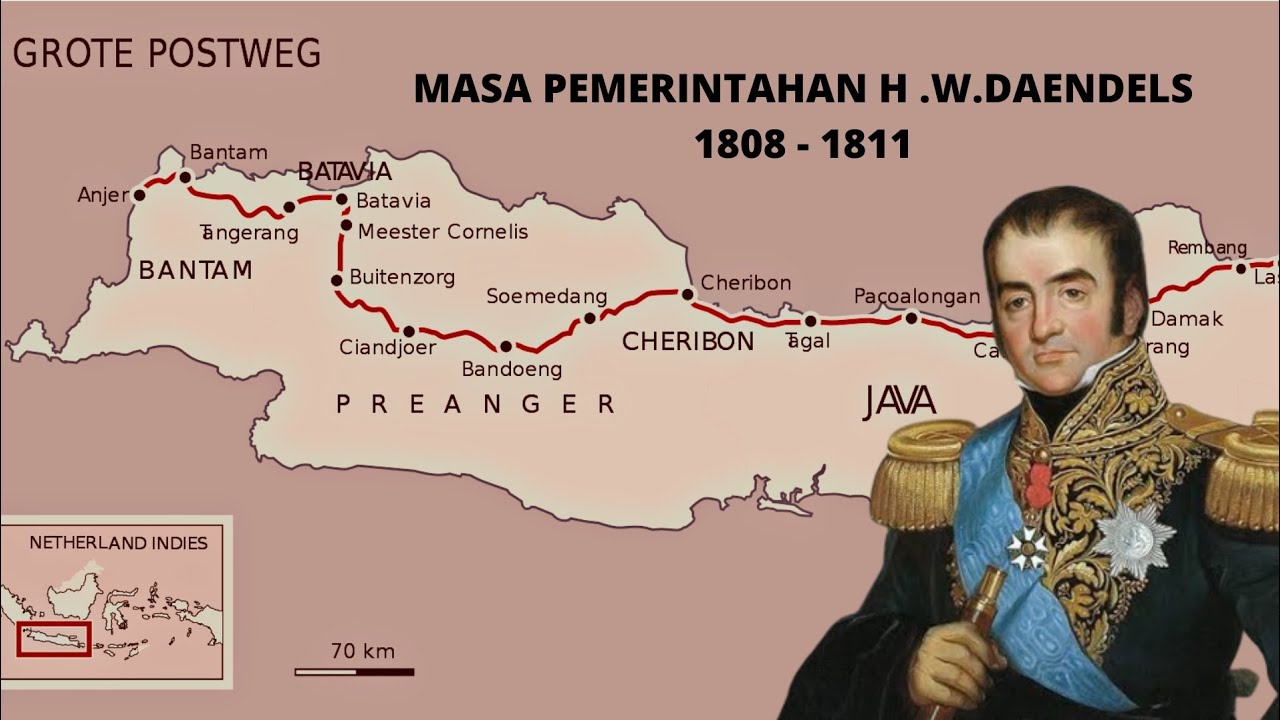
- 🚧 Daendels constructed roads using forced labor, leading to significant suffering and casualties among Indonesian workers.
- 🛡️ The infrastructure improvements aimed to enhance military mobility and communication for Dutch forces in Java.
- 👊 Daendels was known for his harsh governance style, earning him the title 'Governor of Iron Hand' due to his oppressive measures.
- 🔄 He was eventually recalled to France after deteriorating relationships with local rulers and dissatisfaction with his policies.
- 🇬🇧 His successor, Janssens, faced strong British military pressure, leading to the surrender of Dutch forces in Java and the establishment of British control.
Q & A
What historical context led to the appointment of Herman Willem Daendels as Governor-General of Java?
-Herman Willem Daendels was appointed as Governor-General of Java during the Napoleonic Wars when France, under Napoleon Bonaparte, was expanding its influence in Europe. The dissolution of the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and the subsequent political changes in the Netherlands, particularly Louis Napoleon Bonaparte's rise to power, contributed to his appointment in 1808.
What were the main military policies implemented by Daendels during his governance?
-Daendels focused on strengthening the military by recruiting local Indonesians as soldiers, establishing weapon manufacturing facilities in Semarang and Surabaya, and fortifying defenses in preparation for potential British attacks.
How did Daendels' economic policies affect the local population?
-Daendels' economic policies, such as the forced sale of agricultural products at fixed low prices and the taxation on coffee production, primarily benefited the Dutch and Chinese entrepreneurs, leading to economic hardships for the local Indonesian populace.
What administrative changes did Daendels make to govern Java more effectively?
-Daendels divided Java into several residencies governed by appointed residents, established courts to manage dissent, and incorporated local leaders into the colonial administration as a strategy to maintain control and minimize resistance.
What infrastructure project did Daendels initiate, and what were its consequences?
-Daendels initiated the construction of a highway from Anyar to Panarukan, using forced labor from the local population. This project resulted in significant suffering and loss of life among the workers due to the harsh working conditions.
Why is Daendels referred to as the 'Governor with an Iron Hand'?
-Daendels earned the nickname 'Governor with an Iron Hand' due to his harsh and authoritarian rule, which included coercive tactics against local leaders and severe punishments for those who opposed his policies.
What led to Daendels' recall from his position as Governor-General?
-Daendels was recalled due to increasing tensions with local rulers and a growing opposition to his policies, which attracted the attention of Napoleon Bonaparte. His controversial land sales to Chinese entrepreneurs also contributed to his removal.
Who succeeded Daendels as Governor-General, and what was the geopolitical context at that time?
-John William Janssens succeeded Daendels as Governor-General. At that time, the British were gaining military strength, which eventually led to their successful invasion of Java during Janssens' administration.
What was the outcome of the Tuntang Agreement signed in 1811?
-The Tuntang Agreement resulted in the transfer of control of Java and surrounding areas from the Dutch to the British, marking a significant shift in colonial power in the region.
How did Daendels' policies set the stage for British colonial control in Java?
-Daendels' harsh policies and the dissatisfaction they caused among the local population weakened Dutch control and created opportunities for the British to intervene militarily, ultimately leading to the British occupation of Java.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Masa Pemerintahan Daendels (1808 - 1811) Di Indonesia || Materi Sejarah Lengkap

Masa Pemerintahan Prancis di Indonesia [Herman Williem Daendels] Tahun 1808-1811

MASA PEMERINTAHAN GUBERNUR JENDERAL HERMAN WILLEM DAENDELS

Materi Masa Pemerintahan Republik Bataaf (Penjajahan Prancis di Indonesia) / Sejarah Indonesia

KEKUASAAN REPUBLIK BATAAF DI INDONESIA | Sejarah Indonesia Kelas 11 - Video Pembelajaran

KERJA PAKSA ASLINYA DIBAYAR? Dikorupsi Pejabat Lokal? Ada Dana Untuk Pekerja! | Learning By Googling
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)