Materi Masa Pemerintahan Republik Bataaf (Penjajahan Prancis di Indonesia) / Sejarah Indonesia
Summary
TLDRThis historical overview delves into the French colonial period in Indonesia, known as the Republik Bataaf era, which was a significant interlude between Dutch rule. It explores the impact of the French Revolution and Napoleon's rise on Dutch territories, leading to the establishment of the Bataaf Republic. The script discusses the governance of Herman Willem Daendels, his military and administrative reforms, and the economic policies that shaped the region. It also touches on the brief tenure of Jan Willem Janssens and the eventual British takeover, culminating in the surrender of Java and the surrounding areas to the British under the Tuntang Capitulation in 1811.
Takeaways
- 🏛️ The script discusses the history of the Batavian Republic, a period of French rule in the Dutch East Indies, challenging the common notion that Indonesia was only colonized by the Dutch for about 350 years.
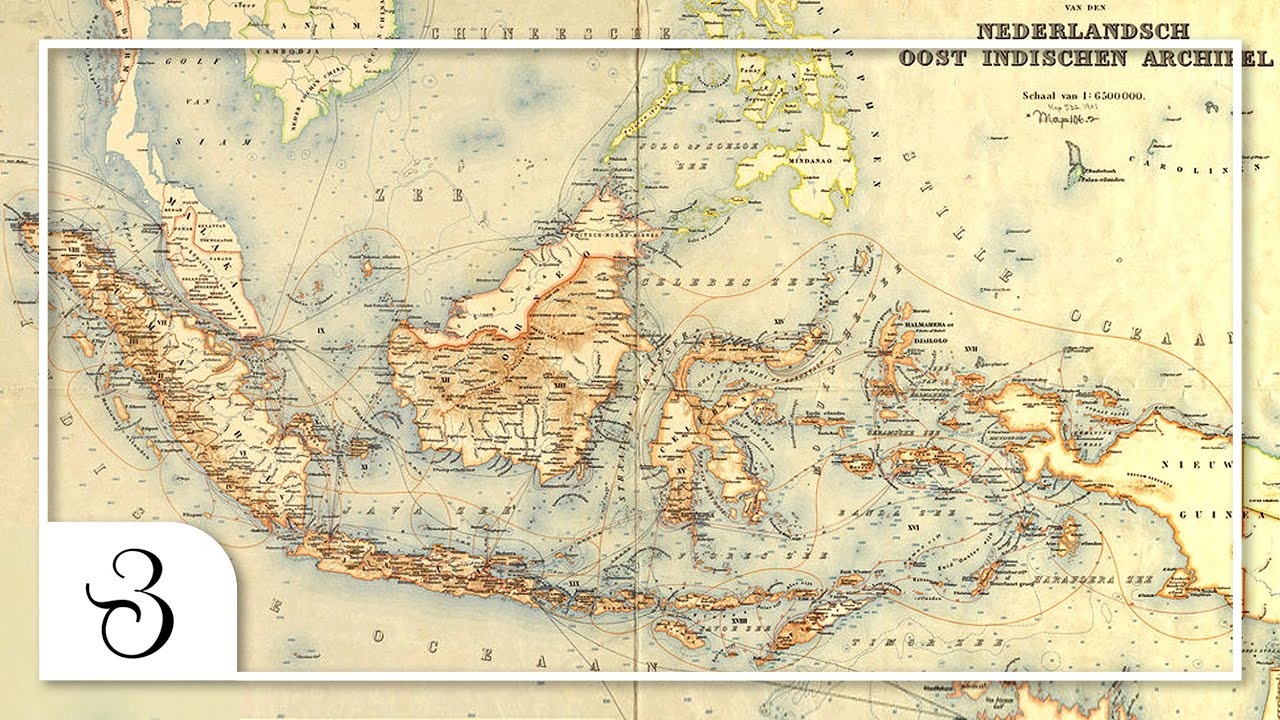
- 🗺️ The Dutch East India Company (VOC) had already established control over strategic areas in Indonesia by the 1600s, including Malacca, Batavia, Makassar, and the Maluku Islands.
- 💥 The French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte in the late 18th century led to a shift in European politics, which impacted colonial territories, including those in the Dutch East Indies.
- 👑 Napoleon Bonaparte's expansionist policies resulted in the Dutch territories in Europe being controlled by France, leading to the establishment of the Batavian Republic from 1795 to 1811.
- 🛫 King William V of the Netherlands fled to England, where he granted the British government the right to take over Dutch colonial territories, including the Dutch East Indies.
- 🛡️ Herman Willem Daendels was appointed as the Governor-General in Indonesia with the mission to fortify Java against British attacks and to reorganize the administration and finances after the fall of the VOC.
- 🛤️ Daendels is known for his iron-fist rule and significant infrastructure projects, including the construction of the Anyer-Panarukan road, now known as the Pantura Highway.
- 👥 Daendels' policies included centralizing power, limiting the authority of local rulers, and introducing a system of residency that divided Java into administrative regions, setting the foundation for the current administrative structure.
- 💼 Economic reforms under Daendels involved the sale of land to private entities, compulsory agricultural delivery, and increased cultivation of profitable crops for the global market.
- 🏛️ The legal system was reformed to establish separate courts for Europeans, indigenous people, and foreign Asians, reflecting the different statuses and treatments of various groups.
- 📜 The script also touches on the social policies of Daendels, including forced labor for infrastructure projects and the continuation of practices similar to those of the VOC era, such as allowing the growth of slavery and removing ceremonial honors for local rulers.
Q & A
What is the historical context of the Dutch and French colonial periods in Indonesia?
-The script discusses the colonial history of Indonesia, mentioning that the Dutch colonial period, often cited as lasting 350 years, was interspersed with other European powers' rule, including the French through the Batavian Republic, the British, Spanish, and Portuguese. The Dutch rule is generally considered to have lasted from the early 1600s until 1945.
What was the impact of the French Revolution on the Dutch East India Company (VOC)?
-The French Revolution, which sought to overthrow the feudal system and establish a new government, indirectly affected the VOC. The script mentions that the revolution led to the rise of Napoleon Bonaparte, who expanded French territories, including taking control of the Netherlands, which in turn affected the VOC's territories in the Dutch East Indies.
Who was Herman Willem Daendels and what was his role in Indonesia?
-Herman Willem Daendels was a Dutch military leader appointed as the Governor-General in Indonesia with the task of defending Java from British attacks. He was known for his iron-fist rule and for implementing various military and administrative measures, including the construction of the 'Jalan Pantura' (Anyer-Panarukan road).
What were the main economic policies of Herman Willem Daendels during his administration?
-Daendels implemented several economic policies, including the sale of land to private parties, the enforcement of compulsory agricultural deliveries, and the promotion of cash crops for the world market. He also aimed to increase revenue through tax collection and land sales to the private sector.
How did the legal system change under Daendels' rule?
-Daendels established a three-tiered legal system: courts for Europeans, courts for the indigenous people, and courts for foreign Asians, such as the Chinese, Indians, and Arabs. This system differentiated the treatment of legal cases based on the ethnicity of the individuals involved.
What was the significance of the 'Jalan Raya Pos Anyer-Panarukan' (Anyer-Panarukan Highway) built by Daendels?
-The 'Jalan Raya Pos Anyer-Panarukan' was a significant infrastructure project that improved communication and transportation across various regions in Java. It was designed to facilitate the rapid delivery of correspondence and was a lasting legacy of Daendels' administration.
What were the social policies of Daendels' administration?
-Daendels' social policies included forced labor for road construction and the continuation of slavery, which was a carryover from the VOC era. He also abolished the ceremonial respect towards the local rulers, such as the Sunan or Sultan.
Why was Daendels considered a failure in managing the Dutch East Indies?
-Daendels was considered a failure due to his involvement in financial corruption, particularly in land sales to private parties. His actions contradicted his initial goal of eradicating corruption, which was prevalent during the VOC era.
Who was Jan Willem Janssens and what was his role after Daendels?
-Jan Willem Janssens was a Dutch politician appointed as the Governor-General to replace Daendels after the latter was dismissed for corruption and financial mismanagement. Janssens' administration was short-lived, lasting only one year, and was marked by the British invasion of Java.
What was the outcome of the British invasion of Java in 1811?
-The British, led by Lord Minto and Thomas Stamford Raffles, successfully invaded Java, leading to the signing of the 'Kapitulasi Tuntang' on September 18, 1811. This agreement marked the end of the French and Dutch rule in the Dutch East Indies and the beginning of British control over the region.
What were the terms of the 'Kapitulasi Tuntang'?
-The 'Kapitulasi Tuntang' terms included the surrender of all Dutch territories in Java and its surroundings to the British. Dutch soldiers became prisoners of war, and Dutch officials who cooperated with the British could retain their positions. The debts of the Dutch government were not transferred to the British but were to be returned to the Netherlands.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SEJARAH HUKUM PIDANA INDONESIA (2/12)

SEJARAH KORUPSI DI INDONESIA BAGIAN PERTAMA

KHOIRUL MUTTAKIN | kemuhammadiyahan kelas XI, materi periodesasi perjuangan muhammadiyah

Sejarah Perjuangan Bangsa Indonesia - Part 1

Hukum Perdata : Pengantar (part 2)
Daftar Provinsi & Kegubernuran di Hindia Belanda - Sejarah Pembagian Administratif Indonesia
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)