Animated Portrayal of Placenta Accreta Spectrum
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the crucial role of the placenta in pregnancy, detailing its formation, functions, and connection to the fetus through the umbilical cord. It also addresses conditions like placenta previa and placenta accreta spectrum, which can pose risks during childbirth. The video highlights the importance of specialized medical care for managing these conditions to ensure safety for both mother and baby, including potential interventions like cesarean hysterectomy when necessary. Understanding these factors is essential for a healthy pregnancy and delivery.
Takeaways
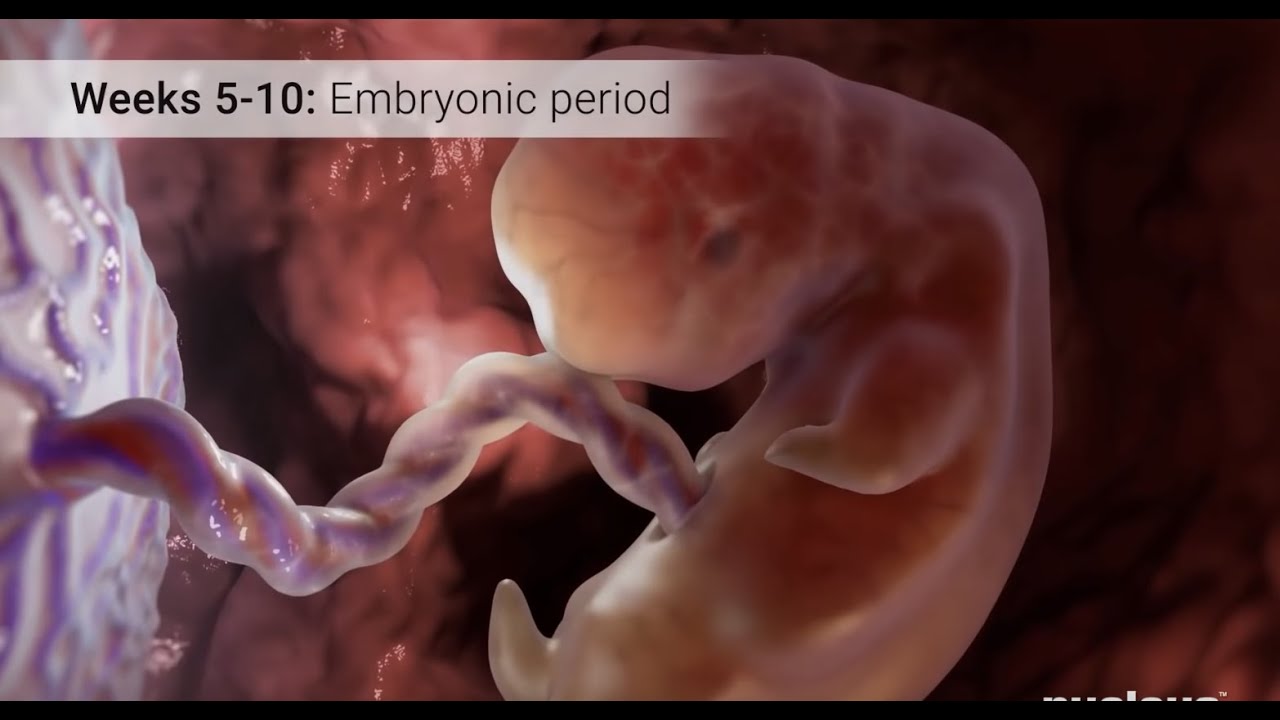
- 🌱 The placenta forms early in pregnancy as trophoblast cells surround the embryo, attaching to the uterine lining.
- 🩸 The placenta facilitates the exchange of oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the fetus while removing waste products.
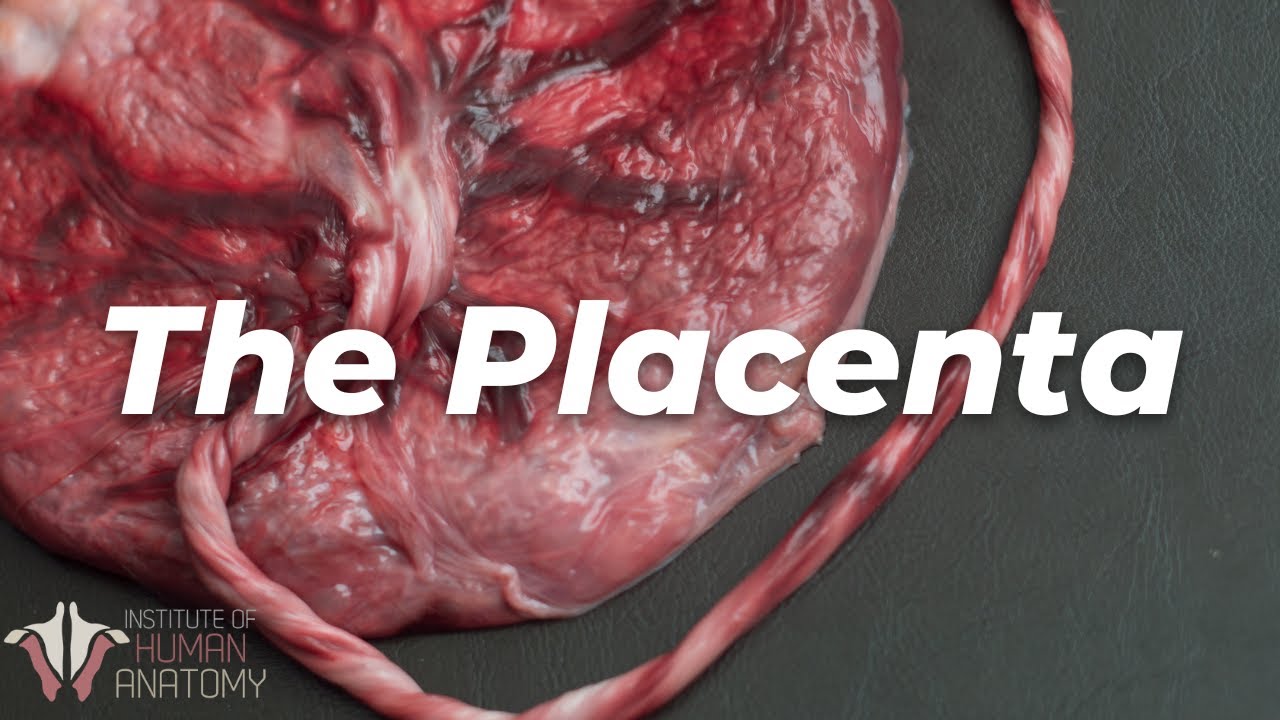
- 🌳 Villi, tree-like structures within the placenta, develop blood vessels that connect to the umbilical cord, enhancing fetal nourishment.
- 🕰️ Around 12 weeks into pregnancy, the placenta starts to function fully, supporting fetal growth as blood from the mother surrounds the villi.
- 📍 Normal implantation occurs at the top or side of the uterus, but abnormal placements can lead to conditions like placenta previa.
- ⚠️ Placenta Accreta Spectrum (PAS) includes three types based on how deeply the placenta attaches to the uterus: Accreta, Increta, and Percreta.
- 🔴 PAS increases the risk of serious bleeding during childbirth, especially in cases of deep attachment and previous uterine scarring.
- 🧠 Specialized medical teams use imaging tests like MRIs to assess PAS and plan safe delivery methods.
- 👶 Early delivery through cesarean section is often required in cases of PAS, with a potential cesarean hysterectomy if complications arise.
- 🤝 Comprehensive care from specialized centers improves safety for both mother and baby throughout pregnancy and delivery.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the placenta during pregnancy?
-The primary function of the placenta is to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the fetus while removing waste from the fetal bloodstream.
How does the placenta develop after conception?
-The placenta begins as trophoblast cells that form a shell around the embryo, attaching to the mother's uterine lining (decidua) and differentiating into various cell types, including villi that branch out and connect to the umbilical cord.
What role do the villi play in the placenta?
-The villi are structures that develop inside the placenta, allowing blood vessels to form and connecting to the baby's umbilical cord, which facilitates the exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the mother and fetus.
What happens to the placenta around 12 weeks into the pregnancy?
-Around 12 weeks, the placenta begins its primary function, as maternal blood surrounds the villi, providing oxygen and nourishment to the fetus.
What is placenta previa?
-Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta implants at the cervix's location, which can cause complications during delivery.
What is placenta accreta Spectrum (PAS)?
-Placenta accreta Spectrum (PAS) refers to a group of conditions where the placenta attaches abnormally to the uterus, categorized into three types based on how deeply the placenta attaches: accreta, increta, and percreta.
What are the risks associated with placenta accreta Spectrum during childbirth?
-PAS increases the risk of serious bleeding during childbirth due to the strong attachment of the placenta to the uterine wall, which can lead to rapid decreases in blood pressure and potential multi-organ dysfunction.
What factors can lead to the development of PAS?
-PAS can be caused by uterine scarring, often due to previous surgeries like cesarean sections, which can create abnormal areas in the uterine lining that allow trophoblasts to invade more easily.
How is PAS typically managed during pregnancy?
-Management of PAS usually involves specialized care from a team of doctors, planning for safe delivery often through a cesarean section, and may include a hysterectomy after delivery to remove the placenta and uterus.
What is the significance of specialized care centers like the Johns Hopkins placenta accreta Center?
-Specialized care centers, such as the Johns Hopkins placenta accreta Center, are crucial in reducing risks and ensuring safe management for patients with PAS, providing tailored plans for delivery and ongoing care for mother and baby.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)