JARINGAN PADA HEWAN DAN TUMBUHAN | SISTEM ORGANISASI KEHIDUPAN
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the structure and functions of animal and plant tissues, emphasizing the differences between them. It begins with a discussion of cellular organization, detailing how cells group into tissues, which perform specialized functions. The video covers four types of animal tissues—epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous—each with distinct roles in the body. It then transitions to plant tissues, explaining epidermal, parenchyma, supportive, and vascular tissues, highlighting their functions in protection, support, and transport. The video concludes with a quiz to reinforce understanding, encouraging viewers to engage further with the content.
Takeaways
- 😀 Each cell in an organism varies in size, reflecting its specific function.
- 😀 Single-celled organisms perform all life functions independently, while multicellular organisms rely on cell cooperation.
- 😀 Cells with similar functions group together to form tissues.
- 😀 Animal tissues are categorized into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue.
- 😀 Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces and functions in protection, absorption, and secretion.
- 😀 Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues, providing structure and immunity.
- 😀 Muscle tissue is composed of muscle fibers and includes three types: striated, smooth, and cardiac muscle.
- 😀 Nervous tissue forms the nervous system, responsible for receiving and transmitting stimuli.
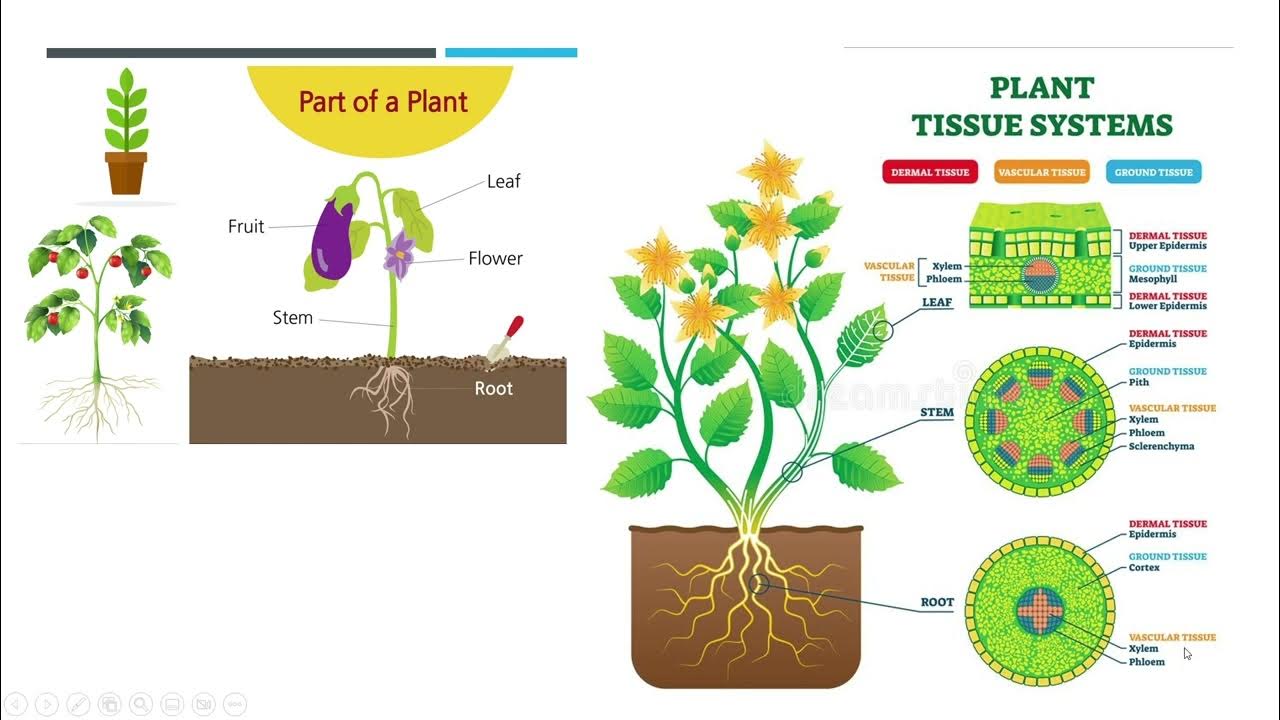
- 😀 Plant tissues consist of various types, including dermal, meristematic, parenchyma, supporting, and vascular tissue.
- 😀 Dermal tissue protects the plant's internal structures, while vascular tissue (xylem and phloem) transports water and nutrients.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video regarding cells?
-The video discusses the characteristics and functions of different types of cells in both unicellular and multicellular organisms, emphasizing how cells work together to sustain life.
What are the two main categories of tissues mentioned in the video?
-The video categorizes tissues into animal tissues and plant tissues, highlighting their differences in structure and function.
What are the four types of animal tissues outlined in the video?
-The four types of animal tissues are epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
-Epithelial tissue serves to cover and protect surfaces, allowing for absorption, secretion, and sensation.
How is connective tissue characterized in the video?
-Connective tissue is described as having various forms and structures that bind, support, and protect other tissues and organs in the body.
What are the three types of muscle tissue mentioned?
-The video mentions three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
What role does nervous tissue play in the body?
-Nervous tissue is responsible for transmitting signals throughout the body, coordinating responses and regulating bodily functions.
What types of plant tissues are discussed in the video?
-The video discusses several types of plant tissues, including epidermal tissue, parenchyma, supporting tissue, and vascular tissue.
What is the function of epidermal tissue in plants?
-Epidermal tissue forms the outer protective layer of plants, helping to prevent water loss and protect against pathogens.
How do xylem and phloem differ in their functions?
-Xylem is responsible for transporting water and minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant, while phloem transports the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Module 6: Cell Modifications- General Biology I

General Biology 1. Cell Types of Plant and Animal Tissues

Struktur Sel (Biologi Sel dan Molekuler)

Por Dentro da Célula: A Menor Fábrica do Mundo

SISTEM ORGANISASI KEHIDUPAN : IPA KELAS 7 SMP

Jaringan pada Hewan dan Tumbuhan | Struktur dan Fungsi Jaringan Hewan dan Tumbuhan - IPA kelas 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)