U1 L3 Moments Harony minis
Summary
TLDRThis educational video discusses the concept of moments in physics, focusing on the relationship between forces and rotational motion. It explains how varying distances from a pivot affect the moment generated by a force. The video also covers conditions for equilibrium, highlighting how forces and moments must balance for a system to remain stable. Additionally, it introduces the concept of the center of gravity and its significance in determining an object's stability when subjected to external forces.
Takeaways
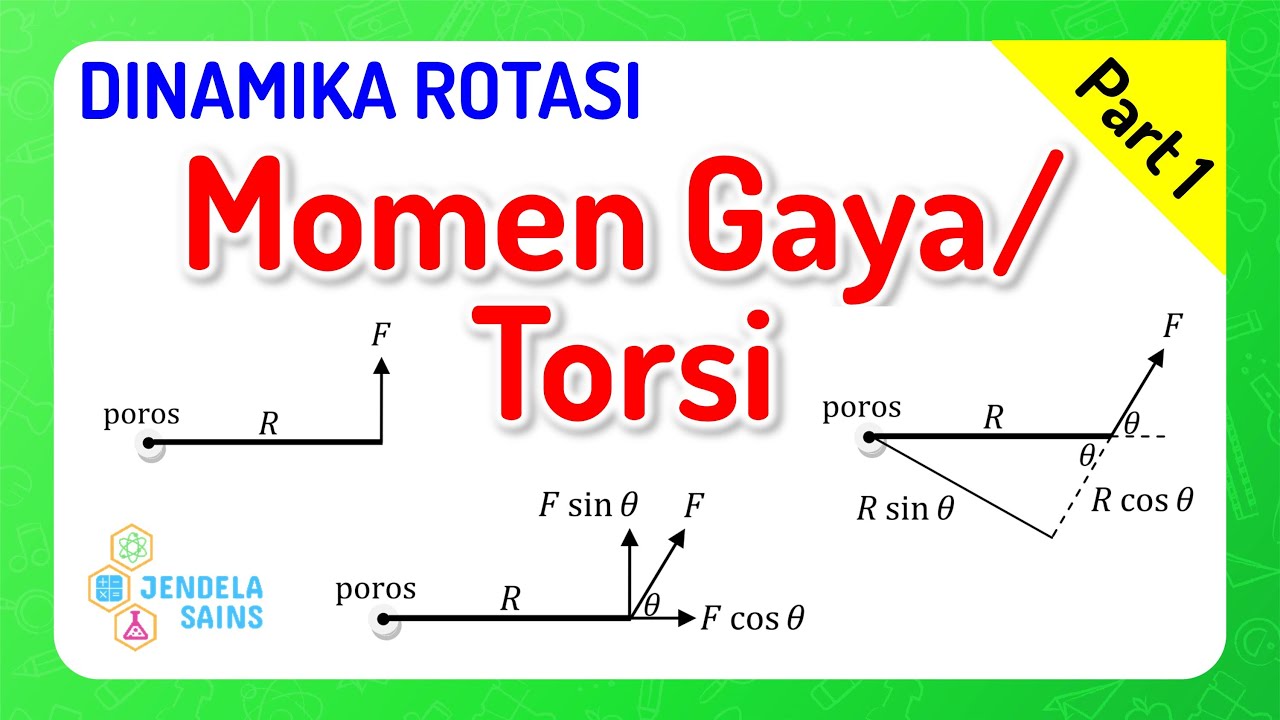
- 🔄 The concept of 'moment' is introduced as the rotational effect produced by a force applied at a distance from a pivot point.
- ⚖️ The moment is influenced by both the magnitude of the force and the distance from the pivot, emphasizing that the same force can create different moments depending on the distance.
- 📏 A moment can be calculated by multiplying the force by the distance (moment = force × distance).
- ⚙️ When multiple forces act on an object, it is crucial to analyze their directions and distances to determine the net moment.
- 🌀 For an object to be in rotational equilibrium, the sum of the clockwise moments must equal the sum of the counterclockwise moments.
- 📐 The weight of uniform objects like rulers is assumed to act at their midpoint, simplifying the calculation of moments.
- 💡 The center of gravity (or centroid) of an object is its balance point, which can change if the object is not uniform.
- ⚡ Stability can be increased by widening the base of support, as seen in racing cars designed for high stability.
- 📊 When solving moment problems, it's essential to identify the system's forces, their distances, and the moments involved.
- 🔍 The conditions for an object not to rotate or break are that the total upward forces equal the total downward forces and that the net moment is zero.
Q & A
What is the definition of moment as discussed in the script?
-Moment refers to the turning effect produced by a force acting at a distance from a pivot point, causing rotation.
How does the distance from the pivot affect the moment?
-The further the force is applied from the pivot, the greater the moment produced. For example, a force of 100 Newtons applied at a distance of 2 meters creates a moment of 200 Newton-meters.
What is the significance of counterclockwise and clockwise moments?
-Counterclockwise moments are typically considered positive, while clockwise moments are negative. This helps in analyzing and calculating net moments acting on a system.
What condition must be met for an object to be in rotational equilibrium?
-For an object to be in rotational equilibrium, the sum of clockwise moments must equal the sum of counterclockwise moments, ensuring no net rotation occurs.
How does force affect stability in physical systems?
-For stability, the total upward forces must equal the total downward forces. If this condition is not met, the system may collapse or fail.
What is the role of the center of gravity in determining stability?
-The center of gravity is the point where an object's weight is balanced. If a vertical line from this point falls within the base of support, the object will return to its original position; otherwise, it may tip over.
How can we increase the stability of a physical object?
-Stability can be increased by widening the base of support or lowering the center of gravity, making it less likely to topple over.
Why is the weight of a uniform beam considered in the center when calculating moments?
-In a uniform beam, the weight is evenly distributed, so its effect can be considered at the center, simplifying calculations of moments acting on it.
What happens when forces are unequal in a system?
-When forces are unequal, the system may rotate or shift in the direction of the greater force, leading to instability or failure.
What is meant by a neutral equilibrium in the context of stability?
-Neutral equilibrium occurs when an object neither falls over nor returns to its original position after being displaced. It can rest in a new position without any net force acting on it.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)