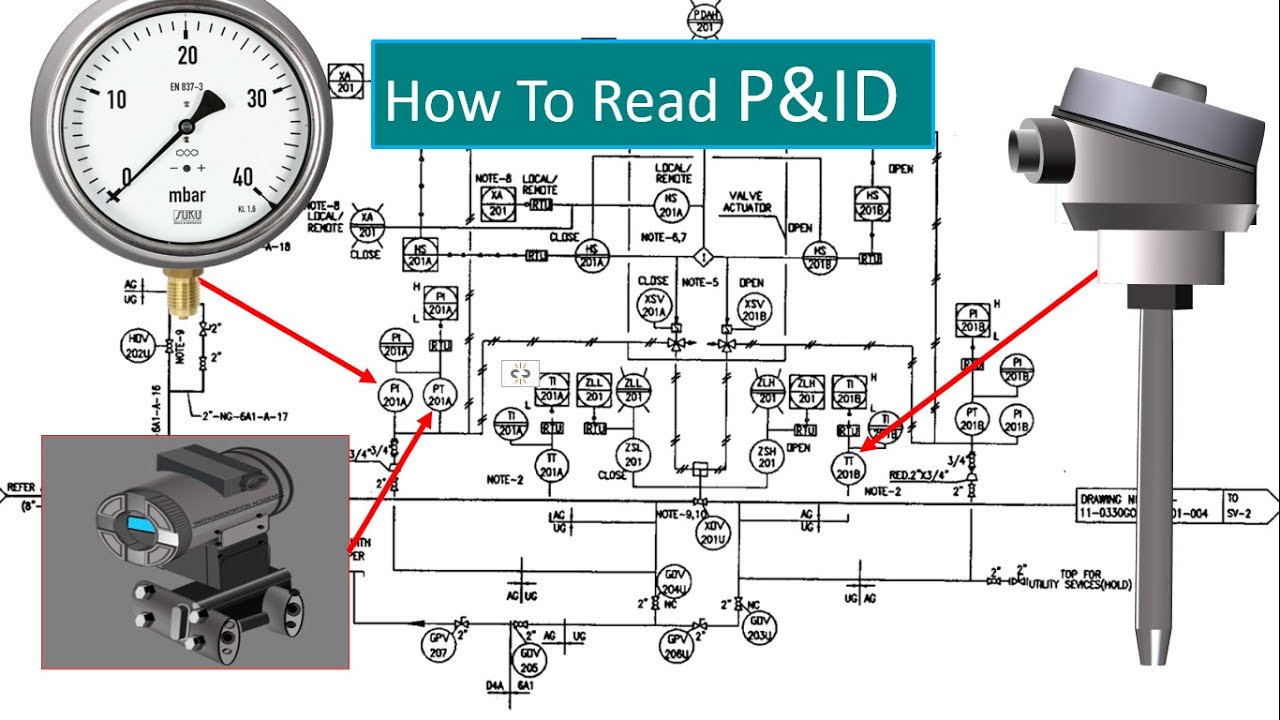
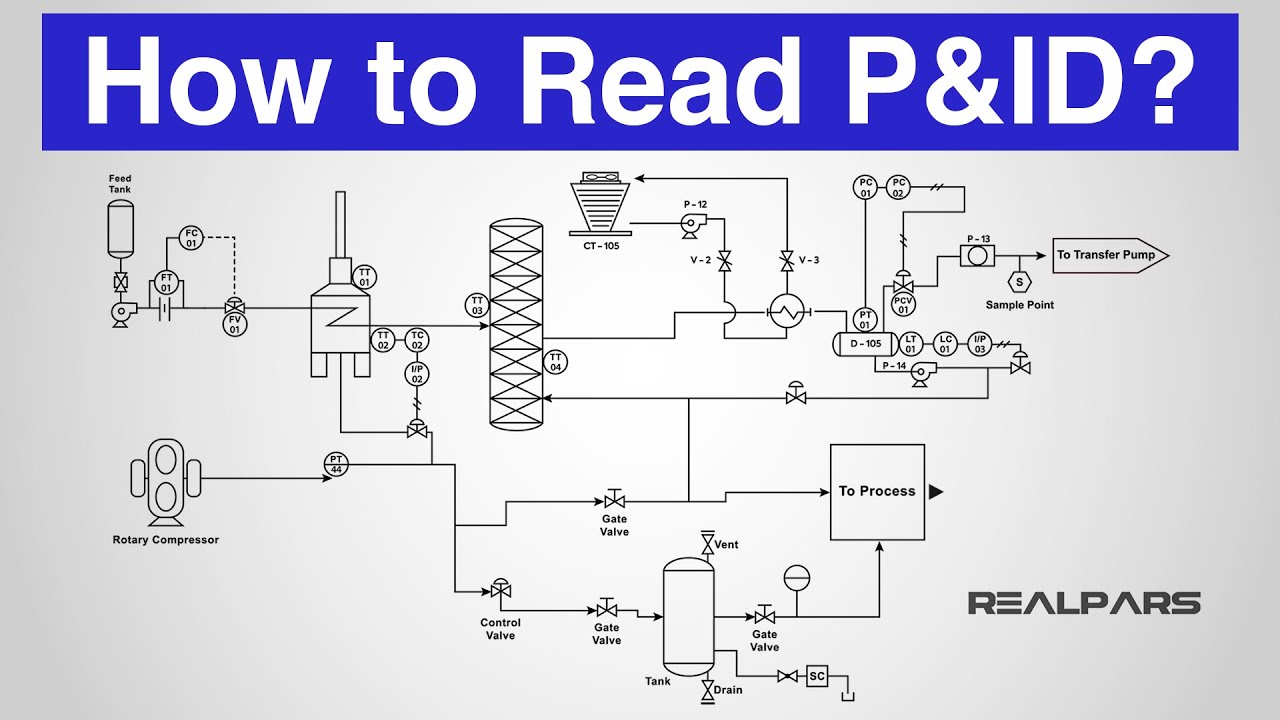
Key P&ID Details for HAZOPS - A HAZOP Crash Course
Summary
TLDRThis lesson delves into PIDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams) and their critical role in Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP). PIDs illustrate process flows and equipment interconnections, essential for identifying potential hazards. Key topics include determining maximum pressures and temperatures, identifying spec breaks, evaluating energy sources, and understanding valve positions. The knowledge of these factors helps ensure a safe and operable process by anticipating risks and implementing necessary safeguards.
Takeaways
- 😀 A PID (Piping and Instrumentation Diagram) is a schematic representation used to illustrate how process equipment is interconnected and the flow of materials.
- 😀 PIDs are crucial in Hazard and Operability Studies (HAZOP) for identifying potential hazardous scenarios and modes of failure in a system.
- 😀 Understanding the flow path of products through the system is essential for evaluating processes effectively.
- 😀 It's important to determine the maximum incoming pressure and temperature for pipelines to identify risks like blocked flow and overpressure scenarios.
- 😀 Spec breaks in piping, indicating changes in design pressure and temperature, help identify sections of piping susceptible to overpressure and ruptures.
- 😀 The location of pipe ruptures (inside or outside buildings) affects the severity of loss of containment and the associated cleanup costs.
- 😀 Knowledge of energy sources (like pumps and compressors) in the system is critical for assessing potential hazards and their impact on piping.
- 😀 Car seal valves (CSO/CSC) are used to mitigate human error and ensure valves are in the correct position for safety.
- 😀 The fail positions of valves and their closure times are crucial for ensuring safety during emergency shutdowns and preventing transient overpressure.
- 😀 Understanding the instrumentation and control system philosophy helps in detecting and mitigating risks, particularly regarding alarms and shutdowns.
Q & A
What is a PID and what purpose does it serve in a HAZOP study?
-A PID, or piping and instrumentation diagram, is a schematic representation of a process that uses symbols and piping connections to show how equipment is connected and the direction of process flow. In a HAZOP study, PIDs help understand the process and identify potential hazardous modes of failure.
Why is it important to identify maximum incoming pressure and temperature in a system?
-Identifying maximum incoming pressure and temperature is essential to detect potential blocked flow and reverse flow scenarios that could lead to overpressure conditions in the piping system.
What are spec breaks and why are they significant?
-Spec breaks refer to changes in design pressure or temperature of piping. They are significant because they help identify sections of piping that are more susceptible to overpressuring and where ruptures are most likely to occur.
How do building limits affect the severity of a loss of containment?
-Building limits can define the severity of a loss of containment since a pipe rupture inside a building may have different consequences than one outside. The consequences of a spill are typically much higher outside the building due to the larger potential for environmental impact.
What role do energy sources play in identifying hazardous scenarios?
-Energy sources, such as pumps, compressors, and external factors like ambient temperature, can create hazardous scenarios by influencing how piping and equipment behave under certain conditions. Evaluating these sources helps in understanding risks associated with piping.
What are car seal valves and why are they important in a HAZOP study?
-Car seal valves are valves that are administratively controlled to ensure they are in the correct position. They are important in a HAZOP study to mitigate human error and ensure that valves critical for safety are maintained in their designated positions.
What should be noted about pressure safety valves (PSVs) during a HAZOP?
-When reviewing PSVs, it's crucial to note their location and sizing to ensure that overpressure risks are adequately mitigated. Additionally, PSVs should relieve to a safe location.
Why is the fail position of valves important?
-The fail position of valves indicates where a valve will default during a facility shutdown. This information is crucial for ensuring that the system reaches a safe state in the event of an emergency shutdown or loss of power.
What does transient overpressure refer to, and why is valve closure time significant?
-Transient overpressure refers to sudden spikes in pressure that can occur when a valve closes too quickly. The closure time is significant because it needs to be managed to prevent potential overpressure conditions that could damage the system.
How can understanding instrumentation and control systems enhance safety in a HAZOP?
-Understanding instrumentation and control systems can enhance safety by identifying how risks can be detected and mitigated. PIDs show transmitters and meters that provide alarms and shutdowns, which are crucial for maintaining a safe operational environment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)