Mengenal Teknologi Infrastruktur IT | Baremetal vs Virtual Machine vs Container | Pemula WAJIB TAU!
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses key elements of IT infrastructure, focusing on bare metal servers, virtual machines (VMs), and containers. It starts by explaining how bare metal servers offer high performance and full control but are limited to a single environment. The video then transitions to virtual machines, which allow multiple environments on one server via hypervisors, and concludes with containers, which enable fast deployment and scalability by isolating applications without needing separate OS instances. The video provides practical examples, including server setups and a comparison of different virtualization technologies.
Takeaways
- 💻 Bare metal refers to a dedicated physical server used for a single environment, offering high performance and full control over hardware configuration.
- ⚙️ Virtual machines (VMs) run on physical infrastructure and allow multiple environments to operate on one server by using a hypervisor for resource allocation.
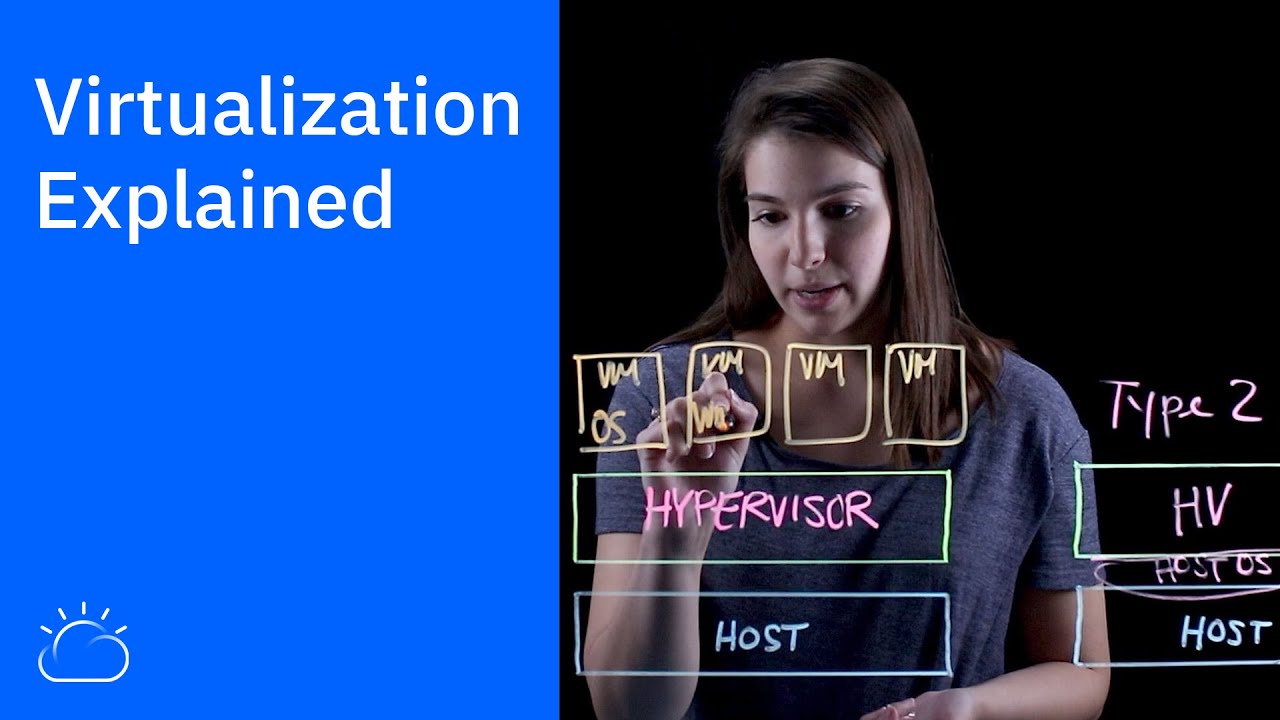
- 🔄 Hypervisor type 1 is installed directly on hardware, often used in enterprise environments, while hypervisor type 2 is installed on top of an existing operating system, used for simulations or learning.
- 🔋 Virtual machines allow sharing of server resources and can run multiple different environments, making them more cost-effective and flexible compared to bare metal.
- 📦 Containers package applications with their dependencies, allowing for isolated and efficient deployment compared to VMs, focusing on fast scalability.
- 🧊 Containers share the host's OS kernel, making them lightweight and more efficient for deployment and scaling compared to virtual machines.
- 🔌 A container engine, such as Docker, is used to run containers, unlike virtual machines that require a hypervisor and a complete OS installation.
- 🚀 Containers enable fast application deployment as they avoid the need for OS configuration, reducing setup time and complexity.
- 🔄 Virtual machines are more suited for running multiple different environments on a single server, while containers are better for deploying specific applications quickly.
- 🏢 Hypervisor type 1 is often used in large-scale, enterprise-level environments, whereas hypervisor type 2 is used for personal or smaller-scale projects to simulate or test environments.
Q & A
What is a bare metal server, and what are its key characteristics?
-A bare metal server is a physical server dedicated to one customer or environment. Its key characteristics include high performance, durability, and full control over hardware configurations, allowing for upgrades such as CPU or memory when needed.
What limitations does a bare metal server have in terms of running multiple environments?
-A bare metal server can only run one operating system at a time, meaning multiple environments cannot be run simultaneously on the same hardware. To run different environments, additional servers would need to be purchased, increasing costs and complexity.
How does virtualization address the limitations of bare metal servers?
-Virtualization allows multiple virtual environments (VMs) to run on a single physical server, overcoming the limitations of bare metal servers. This reduces costs and complexity, as you can run different operating systems and applications on the same hardware.
What is a virtual machine (VM), and how does it differ from bare metal?
-A virtual machine (VM) is a virtual computer that runs on top of physical hardware through a layer called a hypervisor. Unlike bare metal, VMs allow resource sharing, meaning multiple VMs with different environments can run on a single server, increasing flexibility.
What is a hypervisor, and what are its two types?
-A hypervisor is a software layer that allows multiple virtual machines (VMs) to share the resources of a physical server. There are two types: Type 1, which runs directly on the server hardware (bare-metal hypervisor), and Type 2, which runs on top of a host operating system.
What is the difference between Hypervisor Type 1 and Type 2?
-Type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the hardware without needing a host operating system, making it more efficient for enterprise and industrial environments. Type 2 hypervisor runs on top of a host operating system, making it suitable for individual use or learning environments, such as with VMware or VirtualBox.
What are containers, and how do they differ from virtual machines?
-Containers package applications and their dependencies, allowing them to run in isolated environments. Unlike VMs, which require their own OS, containers share the host system's OS kernel, making them more lightweight, faster to deploy, and easier to scale.
What are the main advantages of using containers over virtual machines?
-Containers provide faster deployment, efficient use of resources by sharing the host OS kernel, and ease of scalability. They are ideal for handling high traffic and quickly deploying applications without needing to set up and configure an entire operating system like VMs.
How is scaling handled differently in containers versus virtual machines?
-Scaling in containers is easier and faster because they are lightweight and focus solely on running applications. In contrast, scaling VMs involves creating new virtual environments with separate operating systems, which requires more configuration and resources.
In which scenarios would you use bare metal, virtualization, or containers?
-Bare metal is used when high performance and full control over hardware are needed, such as in specific enterprise environments. Virtualization is best for running multiple environments on a single server to save costs. Containers are ideal for fast application deployment and scaling, especially in cloud-native applications and microservices.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)