Pendalaman Siklus Akuntansi Perusahaan Part 2
Summary
TLDRThis transcript provides an in-depth explanation of general journal recording in accounting, highlighting key concepts like double-entry accounting, debit and credit positions, and the process of analyzing transactions. It also covers the various steps involved in recording transactions, such as documenting the date, description, and amounts for both debit and credit sides. The second part of the transcript introduces Universitas Teknokrat Indonesia, detailing its faculties, study programs, facilities, and its commitment to producing future leaders equipped for the globalized world.
Takeaways
- 📝 The date column in a journal starts with the year, followed by the month, and finally the transaction date.
- 📜 A general journal is based on transaction proof documents such as invoices, receipts, and checks.
- 💰 Double-entry accounting involves recording transactions that affect at least two accounts: one debit and one credit.
- 📅 The date of each transaction is crucial for accurate financial records and is recorded in the journal.
- 🔗 Debit accounts are on the left side, and credit accounts are on the right side in double-entry accounting.
- 💼 Assets are categorized into current and non-current assets, such as cash, receivables, equipment, and vehicles.
- 💳 Liabilities are divided into short-term and long-term debts, and both must be recorded accurately.
- 📚 The posting column remains empty during journal entry and is only filled when transferring data to the general ledger.
- 💡 When writing account names, credits must be indented to distinguish them from debits in the journal.
- 🏫 Universitas Teknokrat Indonesia offers a range of study programs and emphasizes the development of future leaders with strong character and academic achievements.
Q & A
What is the first step in recording a business transaction in a general journal?
-The first step in recording a business transaction in a general journal is to write the date, starting with the year, followed by the month and day when the transaction occurred.
What is the purpose of using source documents in accounting?
-Source documents, such as invoices, receipts, or checks, serve as evidence of transactions. These documents are used as a basis for recording entries in the general journal.
What are the key components of a general journal entry?
-A general journal entry consists of several columns: date, description (account name), reference (posting column), debit, and credit.
Why is the 'debit' placed on the left and 'credit' on the right in double-entry accounting?
-In double-entry accounting, the left side (debit) represents asset increases, while the right side (credit) represents liability or equity increases. This system ensures that every transaction affects at least two accounts, keeping the books balanced.
What is the significance of the 'posting' column in a general journal?
-The 'posting' column is used to transfer the amounts from the journal entries to the general ledger. Initially, this column remains empty until the information is posted to the appropriate ledger accounts.
How should accounts be written in the debit and credit columns of a journal?
-When recording a transaction, accounts listed in the debit column should be placed on the left side, and accounts in the credit column should be indented slightly to the right. This distinction helps differentiate between debits and credits.
How do you record the owner's capital investment in a business in the general journal?
-To record an owner's capital investment, first enter the date of the transaction, then list 'Cash' under the debit column for the amount invested and 'Owner's Capital' under the credit column for the same amount.
What is the difference between current assets and non-current assets?
-Current assets are those that can be easily converted into cash within a short period, like cash and accounts receivable, while non-current assets, such as equipment or buildings, are long-term resources not readily convertible into cash.
How do you analyze a transaction involving the purchase of a vehicle for the company?
-When analyzing a vehicle purchase, determine that the vehicle falls under fixed assets (non-current). Since it's an asset, debit 'Vehicles' or 'Equipment' and credit either cash or a liability account depending on the payment method.
What are the three faculties and their study programs mentioned in Universitas Teknokrat Indonesia?
-Universitas Teknokrat Indonesia has three faculties: Faculty of Engineering and Computer Sciences (Electrical Engineering, Civil Engineering, Computer Engineering, Information Technology, Informatics, Information System), Faculty of Economics and Business (Management, Accounting), and Faculty of Arts and Education (English Literature, Mathematics Education, English Education, Physical Education).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Debit and Credit | Odoo Accounting

RAZONETES E PARTIDAS DOBRADAS - CONTABILIDADE BÁSICA - DÉBITO E CRÉDITO - CONTAS T 📊☑️

Studi Kasus Jurnal, Posting, Neraca Saldo

teks prosedur | cara membuat jurnal umum (nancy angelina xi akl)

DASAR AKUNTANSI : Buku Besar
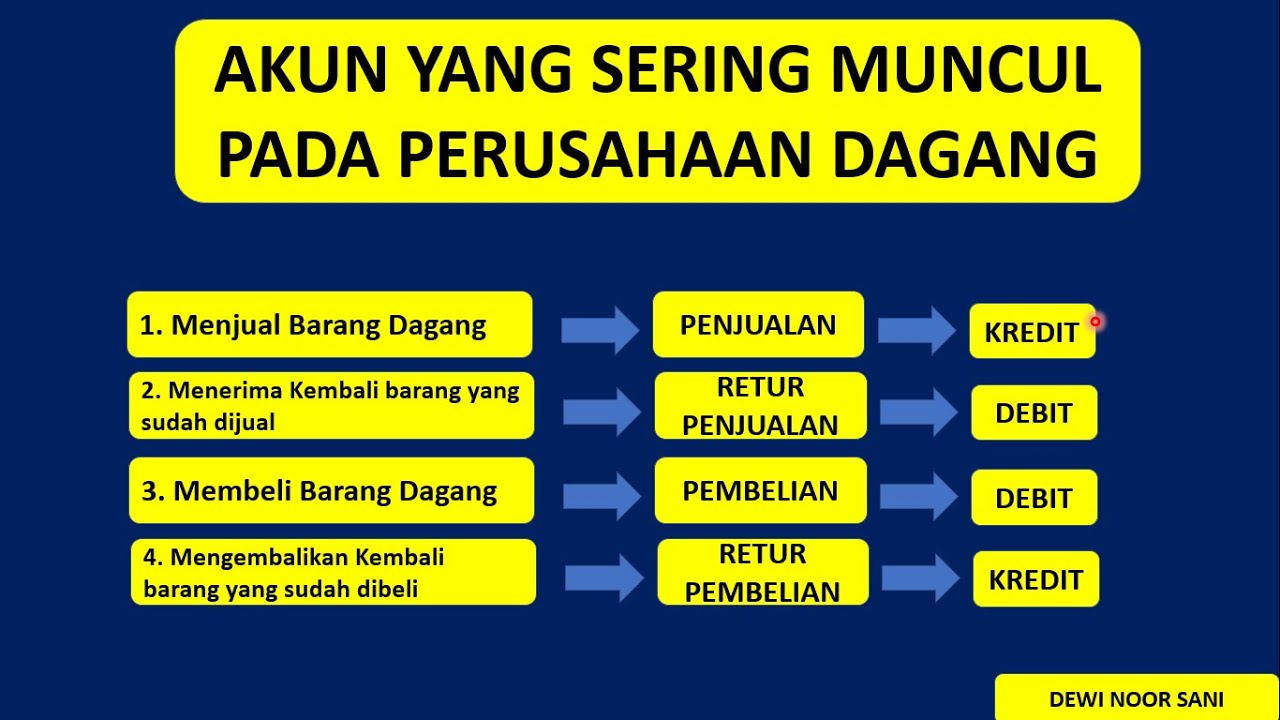
JURNAL UMUM PERUSAHAAN DAGANG (tips & trik menganalisis Posisi Debit Kredit pada Perusahaan Dagang)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)