Generation of AC Voltage - AC Circuits - Basic Electrical Engineering
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the generation of an AC waveform using Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction. It describes how EMF (electromotive force) is induced when there is relative motion between a conductor and a magnetic field. The setup involves a rotating conductor in a steady magnetic field. The video covers the concept of magnetic flux, active conductor length, and velocity. It also explains how maximum EMF is induced when the conductor is perpendicular to the magnetic field, creating a sinusoidal waveform. The key takeaway is that EMF follows a sinusoidal function due to electromagnetic induction.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction states that an EMF is induced in a conductor when there is relative motion between the conductor and a magnetic field.
- 🔄 The key factor for EMF generation is *relative motion*, which can arise either by the movement of the conductor with respect to the magnetic field or the movement of the magnetic field with respect to the conductor.
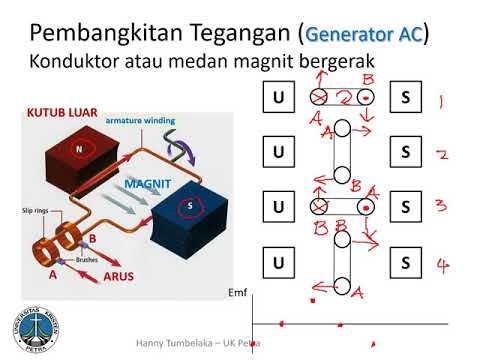
- 🧲 The setup consists of a permanent magnet with north (N) and south (S) poles and a rotating coil made up of two conductors.
- 🔁 The coil's rotation is *anti-clockwise*, cutting through the magnetic flux, which induces the voltage.
- 📐 Three main parameters affect the EMF: magnetic flux density (B), active length of the conductor (L), and velocity of the conductor (V).
- ⚙️ When the conductor is *parallel* to the magnetic lines, no EMF is generated as there is no magnetic flux cut.
- ⏹️ Maximum EMF is generated when the conductor is *perpendicular* to the magnetic field, cutting through the maximum amount of magnetic flux.
- 🔢 The induced EMF is represented by the equation `E = BLV sin θ`, where θ is the angle between the conductor and magnetic field lines.
- 📈 The nature of the induced voltage is *sinusoidal*, following a `Em sin θ` pattern, where `Em` is the maximum EMF value.
- 💡 This explains why AC (alternating current) voltage has a *sinusoidal* waveform, as it directly relates to how the conductor cuts through magnetic lines at varying angles during rotation.
Q & A
What is the main concept discussed in the video?
-The main concept discussed in the video is Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which explains how AC waveform is generated.
What does Faraday's law state?
-Faraday's law states that whenever there is relative motion between a conductor and the magnetic field in which it is placed, an EMF (electromotive force) is induced in the conductor.
What is the key factor for the generation of EMF according to Faraday's law?
-The key factor for the generation of EMF is the relative motion between the conductor and the magnetic field.
What are the two possible sources of relative motion that induce EMF?
-The two possible sources of relative motion are the movement of the conductor with respect to the magnetic field or the movement of the magnetic field with respect to the conductor.
What setup is used in the explanation of EMF generation in the video?
-The setup includes a permanent magnet with north and south poles and a loop made of two conductors. The conductors are connected to brushes to extract the generated voltage, and the coil rotates anticlockwise.
How does the movement of the conductor affect the magnetic flux and EMF generation?
-As the conductor rotates, it cuts through the magnetic flux lines. The EMF is maximized when the conductor moves perpendicular to the magnetic lines, and it is zero when the conductor moves parallel to the magnetic lines.
What is the formula for EMF induced according to Faraday's law?
-The EMF induced is given by the formula E = BLV sin(θ), where B is the magnetic flux density, L is the active length of the conductor, V is the velocity of the conductor, and θ is the angle between the velocity and the magnetic field.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Standard Terminology of AC Voltage Waveform - AC Circuits - Basic Electrical Engineering

Cara Kerja Generator Listrik

GAYA GERAK LISTRIK | KELAS XII | FISIKA ITU MUDAH [Nabila Ratna Az-Zahra]
Prinsip Kerja Generator AC

INDUKSI ELEKTROMAGNETIK || KEMAGNETAN || DINAMO || TRANSFORMATOR || IPA || KELAS 9

Electromagnetic Induction Revision in 20 minute || Chapter 6 class 12 Physics oneshot || CBSE/MP/UP
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)