Supplier Relationship Management Process: System, Tools and Types of Collaboration - AIMS UK
Summary
TLDRThis script discusses the importance of supply chain relationships, highlighting two types: vertical and horizontal. Vertical relationships are traditional linkages between firms like retailers, distributors, and manufacturers. Horizontal relationships involve independent logistics providers working together based on trust and shared goals. The script outlines steps for forming logistics relationships and emphasizes three types of collaboration: vertical, horizontal, and full. It also introduces seven laws of collaborative logistics that foster successful partnerships.
Takeaways
- 🔗 Supply chain relationships are crucial for achieving coordination and integration among partners.
- 🔄 There are two types of logistics relationships: vertical and horizontal.
- 🏢 Vertical relationships are traditional linkages between firms in the supply chain like retailers, distributors, manufacturers, and suppliers.
- 🤝 Horizontal relationships involve service agreements between independent logistics providers based on trust and shared goals.
- 📊 The intensity of involvement in relationships ranges from transactional vendors to strategic alliances.
- 🔍 A strategic assessment is the first step in forming a logistics relationship, identifying needs and strategies.
- 🚀 The decision to form a relationship is based on core competencies and the assessment of drivers and facilitators.
- 🤔 Evaluating alternatives is key to selecting the most appropriate type of relationship.
- 👥 Partner selection is critical and should consider the credentials of potential candidates.
- 🛠 The operating model of a relationship includes activities, processes, and priorities for building and sustaining the partnership.
- 🔄 Implementation and continuous improvement are essential for the success and evolution of the relationship.
- 🔄 Three types of collaboration are vertical, horizontal, and full collaboration, with full collaboration leading to the most significant efficiency gains.
- 📚 The seven laws of collaborative logistics guide the creation of successful partnerships.
Q & A
What is the significance of developing meaningful relationships in the supply chain?
-Developing meaningful relationships in the supply chain is significant as it helps to achieve coordination and integration among partners, which is a high priority for firms to achieve individual and collective supply chain objectives.
What are the two types of logistics relationships mentioned in the script?
-The two types of logistics relationships are vertical and horizontal. Vertical relationships refer to the traditional linkages between firms in the supply chain, while horizontal relationships involve service agreements between independent logistics providers based on trust and cooperation.
Can you explain the concept of vertical relationships in supply chain logistics?
-Vertical relationships in supply chain logistics refer to the traditional linkages between firms such as retailers, distributors, manufacturers, and material suppliers. These relationships are transactional and involve buyers and sellers in ways that are common across all industries.
What characterizes horizontal relationships in logistics?
-Horizontal relationships in logistics are characterized by service agreements between two or more independent logistics provider firms. They are based on trust, cooperation, shared risk, and investments, with the aim of following mutually agreeable goals.
What is the difference between a vendor relationship and a strategic alliance in the context of supply chain logistics?
-A vendor relationship is transactional with little or no collaboration, representing a low level of involvement between the parties. In contrast, a strategic alliance involves cooperation where business organizations willingly modify their practices to achieve long-term goals, implying a high level of relational involvement.
What is the first step in forming a logistics relationship according to the script?
-The first step in forming a logistics relationship is performing a strategic assessment, which involves becoming fully aware of the manufacturer's logistics and supply chain needs and the overall strategies that will guide its operations.
What factors are considered when deciding to form a relationship with a logistics service provider?
-When deciding to form a relationship with a logistics service provider, a careful assessment of the company's core competency is considered, along with the evaluation of apparent levels of drivers and facilitators that suggest the most appropriate type of relationship.
How should a logistics or supply chain partner be selected?
-A logistics or supply chain partner should be selected following very close consideration of the credentials of the most likely candidates, ensuring they align with the company's strategic goals and operational needs.
What components are included in the structure of an operating model for a logistics relationship?
-The structure of an operating model for a logistics relationship includes activities, processes, and priorities such as planning, joint operating controls, communication, risk and reward sharing, trust, commitment, contract style, and financial investment.
Why is continuous improvement important in the implementation of a logistics relationship?
-Continuous improvement is important in the implementation of a logistics relationship because the future success of the relationship is directly linked to the ability of the involved organizations to achieve ongoing and breakthrough improvements.
What are the seven immutable laws of collaborative logistics mentioned in the script?
-The seven immutable laws of collaborative logistics are: real and recognized benefits to all members, dynamic creation, measurement, and evolution of partnerships, co-buyer & co-supplier relationships, flexibility and security, collaboration across all stages of business process, integration, open integration with other services, and collaboration around essential logistics flows.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Assoc. Prof. Muhammad Findi - Merger / Integrasi Horizontal dan Vertikal
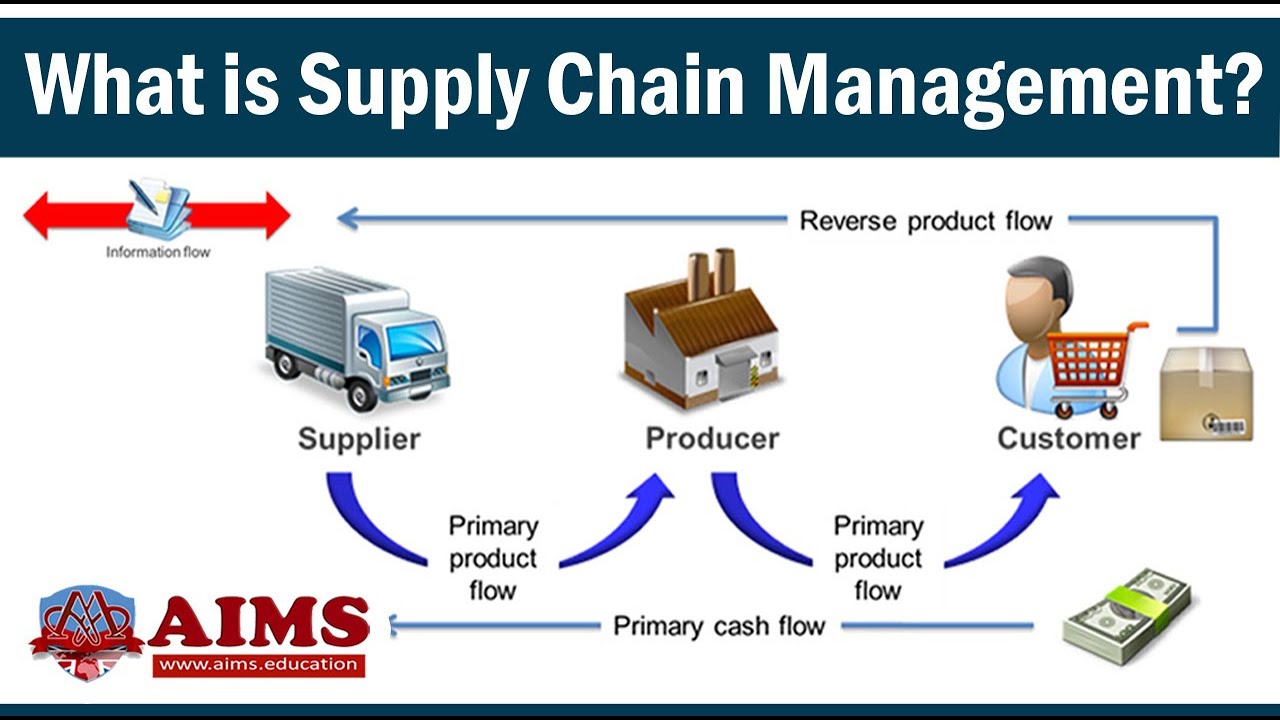
What is Supply Chain Management? Definition, Introduction, Process & Examples - AIMS UK

Horizontal and Vertical Integration (Business Growth Strategy)
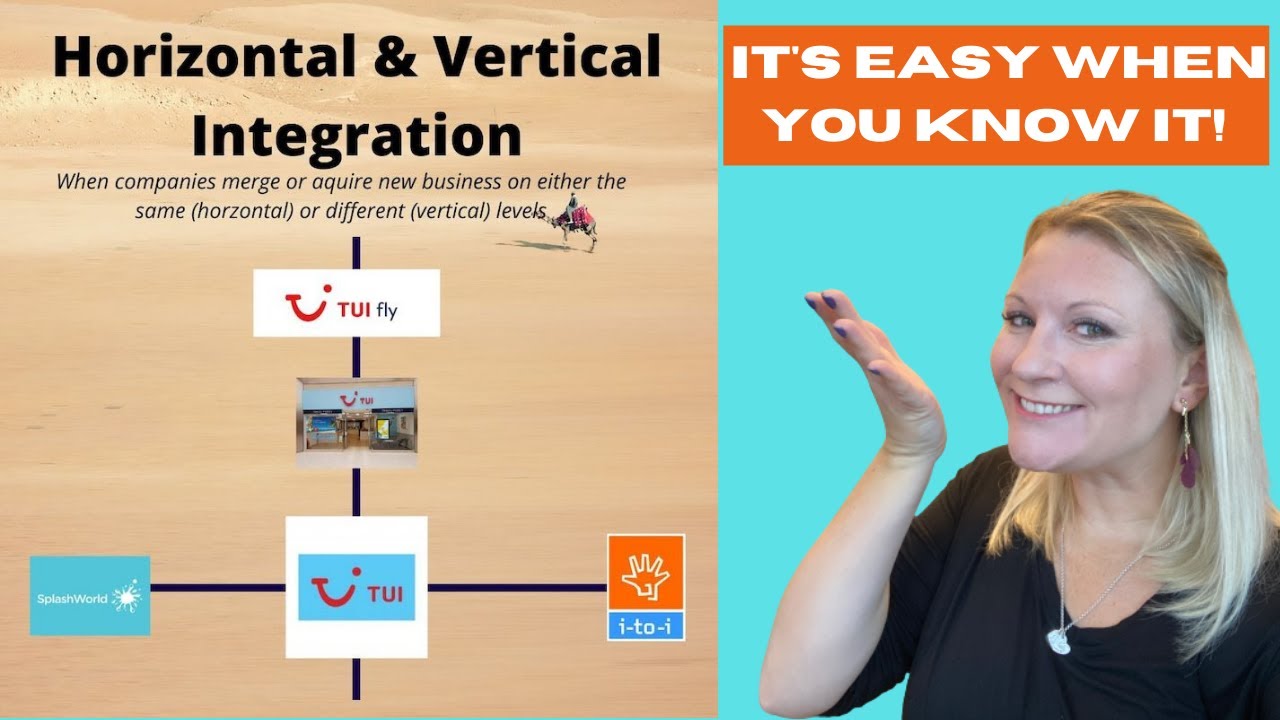
Horizontal And Vertical Integration Made EASY! Advantages, disadvantages and examples.

Bodybuilding Simplified: Back

Keberagaman Antargolongan Masyarakat Indonesia|Part 1|Pendidikan Pancasila Kelas 7
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)