How Geothermal Energy Works - Educational 3D Animated Video
Summary
TLDRGeothermal energy harnesses the Earth's internal heat, tapping into underground reservoirs heated by magma. Production wells extract hot water and steam, which power turbines to generate electricity. The process involves separating high and low-pressure steam, with excess fluid returning underground to be reheated. This renewable energy source offers a clean, sustainable alternative with minimal environmental impact.
Takeaways
- 🌋 Geothermal energy is a renewable source of power that uses the Earth's natural heat.
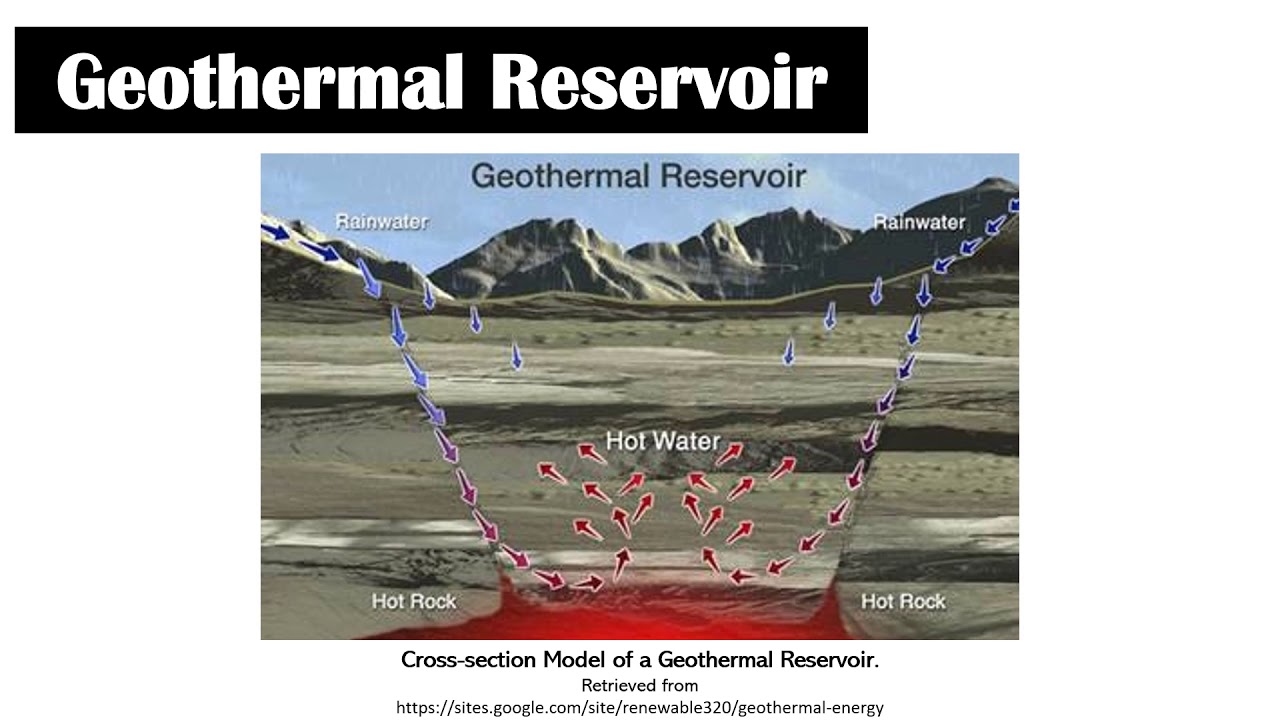
- 💧 Water in underground reservoirs is heated by magma to high temperatures.
- 🚨 Production wells are drilled up to 10,000 ft deep to access the hot fluid.
- 💭 The hot fluid and steam rise to the surface due to pressure reduction.
- 🌡 At the well head separator, pressure is reduced causing most of the fluid to vaporize into high-pressure steam.
- 🔄 Any fluid not turned into steam is processed in a crystallizer to produce standard pressure steam.
- 🔩 The remaining fluid is flashed at lower pressure to create low-pressure steam.
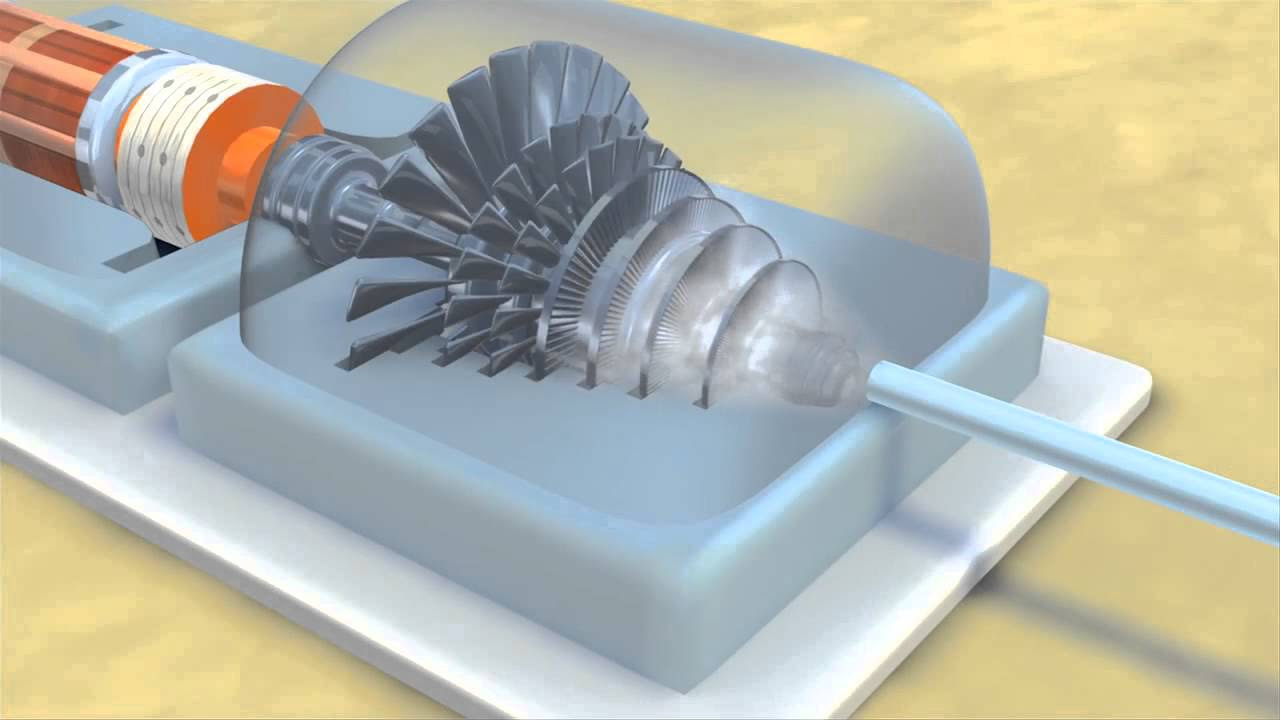
- ⚙️ The steam spins turbine blades, which in turn rotate a shaft connected to an electrical generator.
- 🔌 The electrical charge is then sent to a transformer to increase voltage before being sent down power lines.
- 🔁 Fluids not turned into steam are returned to the underground reservoir to be reheated and reused.
Q & A
What is geothermal energy?
-Geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that uses the Earth's internal heat to generate electricity.
How does geothermal energy have minimal environmental impact?
-Geothermal energy has minimal environmental impact because it produces steady, reliable power with little to no greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the role of underground water reservoirs in geothermal energy production?
-Underground water reservoirs are heated by magma, and the hot water is used to produce steam that drives turbines for electricity generation.
How deep are the production wells drilled for geothermal energy?
-Production wells for geothermal energy can be drilled up to 10,000 feet below the Earth's surface.
What causes the hot fluid to flow towards the surface?
-The hot fluid flows towards the surface due to its own pressure, which decreases as it travels, causing some of it to vaporize into steam.
What is a well head separator in the context of geothermal energy?
-A well head separator is a device where the pressure of the hot fluid and steam is reduced, causing most of the fluid to vaporize into high-pressure steam.
What happens to the fluid that is not flashed into steam in the well head separator?
-Any fluid not flashed into steam is sent to a standard pressure crystallizer to produce standard pressure steam.
How is low-pressure steam created in a geothermal plant?
-Low-pressure steam is created by flashing the remaining fluid at a lower pressure after it has passed through the standard pressure crystallizer.
What is the function of a turbine in a geothermal power plant?
-The force of the steam spins the turbine's blades, which in turn rotates a shaft connected to an electrical generator to produce electricity.
How is the electricity from a geothermal plant transmitted to the grid?
-The electricity generated is directed to a transformer where the voltage is increased before being sent down power lines to the grid.
What happens to the fluids that are not flashed into steam?
-Fluids that are not flashed into steam are returned to the underground reservoir to be reheated and reused in the geothermal process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Panas Bumi; Sumber Energi Terbarukan

Geothermal 101
Energy 101: Geothermal Energy
Geothermal Energy and Geothermal Power Plants | Lesson 7.1| Earth Science

Bagaimana Cara Produksi Energi Geotermal Ketika Suhu Panas Bumi 6.000 Celsius! | DW Business

Química - Energia proveniente de biomassa e biocombustíveis (QEF0067)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)