Instrumen Analisis - 6
Summary
TLDRThis script discusses confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), a powerful tool for high-resolution 3D imaging of samples. It explains the technology's advantages over traditional microscopy, including better detail, reduced crosstalk, and the ability to perform optical sectioning. The script also highlights the technique's applications in various fields, emphasizing its capacity for detailed analysis and the generation of colorful, clear images that facilitate the study of biological materials and processes.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) is a powerful imaging technique used for high-resolution 3D imaging of samples.
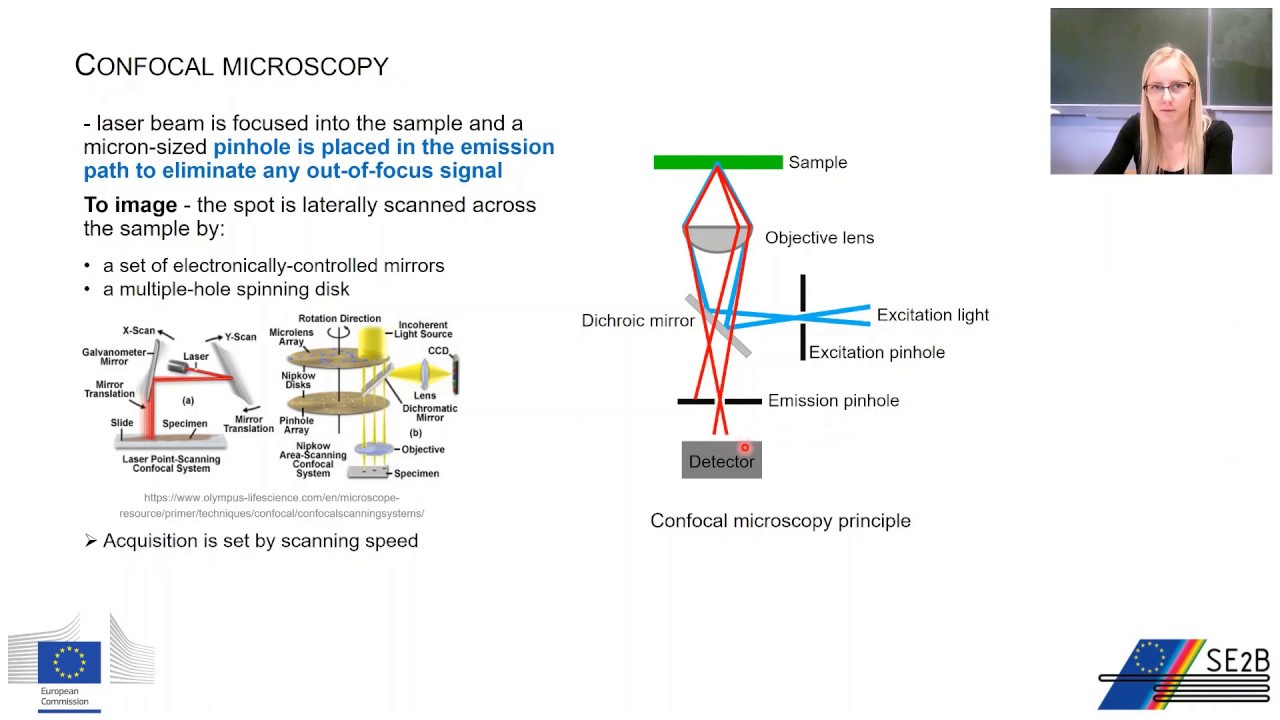
- 🌟 CLSM uses a laser as a light source and employs a pinhole to increase the depth of field, resulting in sharper and more detailed images compared to traditional microscopy.
- 🔍 It offers superior resolution, down to 1-10 micrometers, making it suitable for detailed observation of samples at a microscopic level.
- 🚫 CLSM has limited penetration depth compared to ultrasonic and endoscopic techniques, which is a trade-off for its high-resolution capabilities.
- 🌈 CLSM allows for multi-color imaging, which enhances analysis by providing varied color representations based on the interaction between the laser and the stained sample.
- 👁️🗨️ Optical sectioning is a key feature of CLSM, enabling the separation of signals from different depths without physical contact, thus preserving the sample's integrity.
- 📈 The technique reduces crosstalk, which is the interference between different fluorescent signals, leading to clearer and more accurate images.
- 🧬 CLSM is widely used in biological research for observing living materials, such as cells and tissues, and can differentiate various cellular components based on their absorption of specific colors.
- 📊 It provides the ability to reconstruct 3D images from 2D slices, offering a comprehensive view of the sample's structure.
- 📈 The resolution of CLSM can be enhanced through techniques like laser scanning, which allows for more detailed imaging of smaller areas.
Q & A
What is confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM)?
-Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) is a high-resolution imaging technique that uses a laser to scan a sample and produce detailed 3D images.
What are the common abbreviations for confocal laser scanning microscopy?
-CLSM is commonly abbreviated as CSLM or LSM, and sometimes referred to as laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM).
How does the resolution of confocal microscopy compare to other imaging techniques like ultrasound or OCT?
-Confocal microscopy offers higher resolution than ultrasound or optical coherence tomography (OCT), allowing observation down to 1-10 micrometers, making it more suitable for detailed analysis.
What is the principle behind confocal microscopy?
-The principle behind confocal microscopy involves using a pinhole between the specimen and the detector to filter out out-of-focus light, resulting in a sharper image.
What is the role of the laser in confocal microscopy?
-In confocal microscopy, the laser is used as a light source to illuminate the sample, and the reflected or emitted light is then detected to form an image.
How does confocal microscopy enable 3D imaging?
-Confocal microscopy enables 3D imaging by capturing a series of 2D images at different focal planes, which can then be reconstructed into a 3D image.
What is optical sectioning in the context of confocal microscopy?
-Optical sectioning is a technique in confocal microscopy that allows for the selective visualization of a single plane within a thick specimen without physical slicing.
How does confocal microscopy reduce the issue of crosstalk?
-Confocal microscopy reduces crosstalk by minimizing the overlap of spectra from different fluorophores, leading to clearer separation of signals and improved image quality.
What are some advantages of using confocal microscopy for biological samples?
-Confocal microscopy is advantageous for biological samples as it allows for detailed analysis without damaging the sample and can produce colorful, clear images that facilitate understanding of the sample's morphology.
Can confocal microscopy be used to enhance the contrast of images?
-Yes, confocal microscopy can enhance image contrast by using specific staining techniques that interact with the laser light to produce different colors, highlighting various structures within the sample.
What is the significance of the term 'multitracking' in confocal microscopy?
-Multitracking in confocal microscopy refers to the ability to capture images from multiple focal planes simultaneously, which can be used to create detailed 3D reconstructions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Fluorescence microscopy

Introduction to the Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Working Principles and application of SEM in biology

Temp1 Cap1 Epi3 Microscopía Electrónica

Microscopy: What Can You Learn With a Light Microscope (Ron Vale)

Part 1: Sample Chamber - G. Jensen
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)