Temp1 Cap1 Epi3 Microscopía Electrónica
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fundamentals of electron microscopy, detailing the two primary types: Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEM) and Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM). TEM utilizes electron beams to achieve high resolution, allowing for detailed internal cellular imaging, while SEM focuses on surface structures, providing grayscale images that can be color-enhanced with software. The discussion highlights the importance of differentiating images obtained from optical and electron microscopes, illustrated with examples from muscle tissue. Additionally, a virtual microscope developed by the National Autonomous University of Mexico is introduced, enriching the educational experience in microscopy.
Takeaways
- 🔬 There are two main types of electron microscopes: transmission and scanning.
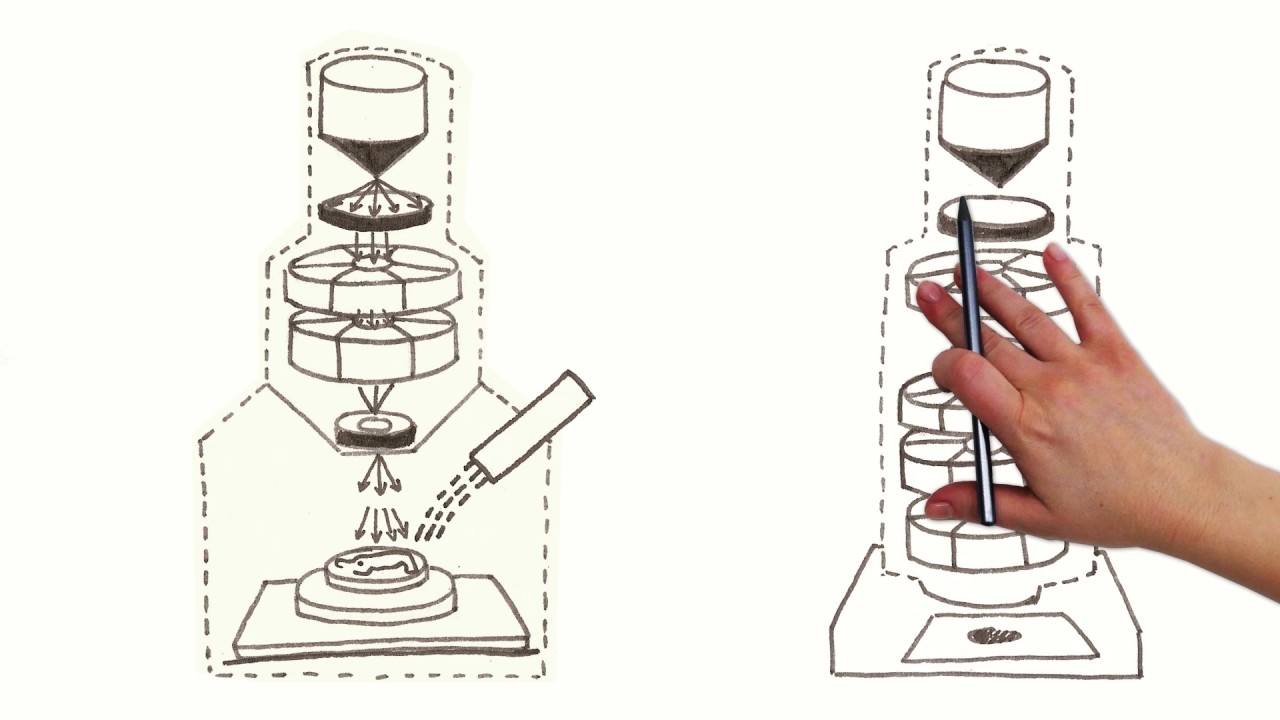
- ⚛️ The transmission electron microscope uses electron beams to form images, allowing for a high resolution of about 0.2 to 1.0 nanometers.
- 🌫️ In transmission electron microscopy, electrons pass through the sample, creating clear and dark zones based on electron density.
- 🖤 The scanning electron microscope, on the other hand, images the surface of specimens rather than their interior.
- 📈 Images from scanning electron microscopy are initially in grayscale but can be enhanced with software to show different colors.
- 🧬 The transmission electron microscope is particularly useful in medical research for studying ultra-structural alterations in diseases.
- 🖼️ It is important to differentiate between images obtained from photon microscopes and electron microscopes.
- 💡 The script discusses a virtual microscope developed by the National Autonomous University of Mexico for educational purposes.
- 📚 The virtual microscope provides interactive images similar to those seen through a traditional light microscope.
- 🌐 Viewers are encouraged to engage with educational resources available on social media and the website.
Q & A
What are the two main types of electron microscopes discussed in the transcript?
-The two main types of electron microscopes discussed are transmission electron microscopes and scanning electron microscopes.
How does a transmission electron microscope (TEM) differ from a photonic microscope?
-A transmission electron microscope uses beams of electrons instead of photons to form images, which allows for much higher resolution, with a limit of about 0.2 to 1.0 nanometers.
What is the primary function of a transmission electron microscope?
-The primary function of a transmission electron microscope is to allow scientists to view the interior of cells by passing electrons through a sample.
What characteristic distinguishes the images produced by a transmission electron microscope?
-Images produced by a transmission electron microscope have varying shades of gray, depending on the electron density of the sample.
How do scanning electron microscopes (SEM) obtain images?
-Scanning electron microscopes obtain images by scanning a beam of electrons across the surface of a specimen and capturing the emitted signals to form images.
What kind of information can be observed using a scanning electron microscope?
-A scanning electron microscope allows observation of the surface of a specimen, providing detailed images in shades of gray that can be enhanced with software to display different colors.
What is the main application of electron microscopy in medicine?
-The main application of electron microscopy in medicine is the study of diseases with ultrastructural alterations, which are changes in organelles or subcellular components.
What unique feature does the virtual microscope provide?
-The virtual microscope provides a simulated experience that allows users to view scanned images as if looking through a photonic microscope, enhancing educational engagement.
What educational institutions were involved in developing the virtual microscope mentioned in the transcript?
-The virtual microscope was developed by the Department of Visualization and Virtual Reality at the National Autonomous University of Mexico, in coordination with the Department of Cellular and Tissue Biology.
What does the presenter encourage viewers to do at the end of the video?
-The presenter encourages viewers to visit their social media pages, subscribe to the channel, and stay tuned for the next chapter on histological techniques.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electron Microscopy (TEM and SEM)
2 The Principle of the Electron Microscope

Tipos de microscópios, conheça na prática

Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Working Principles and application of SEM in biology

Introdução à MICROBIOLOGIA | Videoaula | Flavonoide #1

WHAT ARE LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPES? - HOW DO THEY WORK?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)