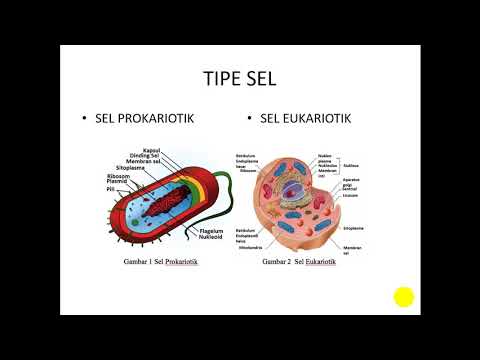
Biology with NAMOO: Plant Cell Structure
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the fascinating world of plant cells, explaining their structure and the function of their organelles. It describes the cell membrane, cell wall, and highlights the nucleus as the control center. Other organelles, like the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and the Golgi complex, are compared to a city's systems. Special focus is given to how proteins are produced and transported within the cell. The video also introduces chloroplasts for photosynthesis, unique to plant cells, and discusses how plant cells store nutrients using vacuoles.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Plant cells are made up of organelles, which perform unique functions.
- 🧫 The cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid that holds organelles within the cell.
- 🛡️ Plant cells have both a cell membrane and an outer cell wall for protection and support, unlike animal cells.
- 🏙️ The cell is like a tiny city with organelles acting as food factories, powerhouses, and post offices.
- 🧠 The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains genetic material.
- 📦 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes involved in protein production, with ribosomes attached to its surface.
- 🌞 Chloroplasts, unique to plant cells, are responsible for photosynthesis, using light to produce sugar.
- 💧 The vacuole is the cell's storage tank, holding water and nutrients, and it can occupy up to 80% of the cell.
- ⚡ Mitochondria, known as the cell's powerhouses, produce energy needed for daily functions.
- 📮 The Golgi complex processes and packages proteins for transport, acting like the cell's post office.
Q & A
What are plant cells made up of?
-Plant cells are made up of organelles that float inside a jelly-like fluid called cytoplasm. The entire cell is protected by a cell membrane and a cell wall.
What is the difference between the cell wall and the cell membrane in plant cells?
-The cell membrane is a light green layer that protects the cytoplasm from the outside environment, while the cell wall is an additional rigid protective layer that helps plants grow tall by providing structural support.
What is the role of the nucleus in a plant cell?
-The nucleus is the command center of the cell, storing genetic information and controlling the cell's complex processes. It also contains the nucleolus, which produces ribosomes.
What does the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) do in a plant cell?
-The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that form interconnected channels connected to the nucleus. Ribosomes on the rough ER produce proteins, which are important for various cell functions.
What are ribosomes and what is their function?
-Ribosomes are small organelles responsible for producing proteins by assembling amino acids. They are found on the surface of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
What are chloroplasts, and why are they important to plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are organelles that carry out photosynthesis, the process by which plants make food in the form of sugar using light. They contain chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and is unique to plant cells.
What is the central vacuole, and what role does it play in a plant cell?
-The central vacuole is a large organelle that occupies up to 80% of the cell. It functions as a storage tank for water, nutrients, waste products, and other chemicals.
What is the mitochondrion, and what is its function in plant cells?
-The mitochondrion is known as the powerhouse of the cell. It produces the energy required for the cell to carry out its daily functions. Both plant and animal cells contain mitochondria.
What does the Golgi complex do in a plant cell?
-The Golgi complex, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi apparatus, processes, modifies, and packs proteins and other materials. It assigns destinations to these materials inside or outside the cell.
How are proteins made in a plant cell?
-Protein production begins in the nucleolus, which produces ribosomes. The ribosomes, located on the surface of the rough ER, assemble proteins from amino acids in a process called translation. Once formed, the proteins are packed into vesicles, processed by the Golgi complex, and sent to their destinations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)