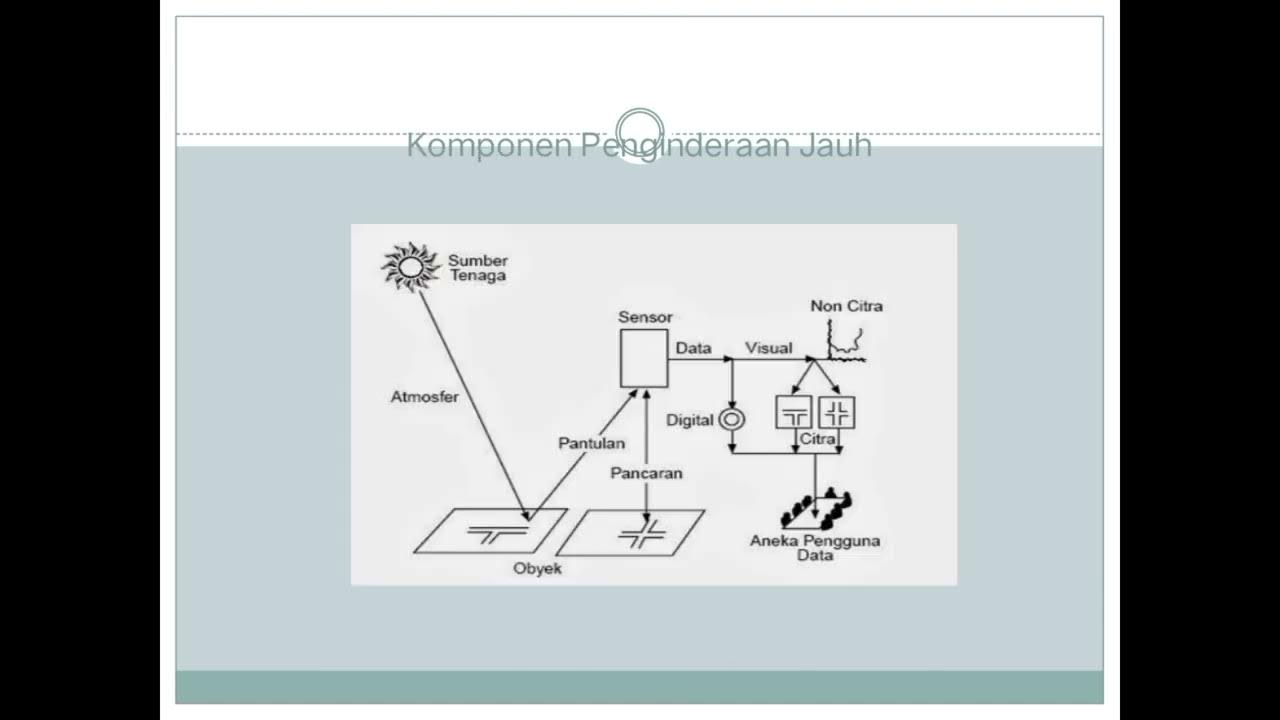
Belajar Bersama, Bab 2 Dasar-dasar Pemetaan, Penginderaan Jauh dan Sistem Informasi Geografi Kelas X
Summary
TLDRThe video lesson introduces the topic of maps and geographic information systems (GIS) in geography, focusing on definitions and key components of maps. It explains different types of maps, including topographic and thematic maps, and the importance of scale in mapmaking. The lesson also covers map functions, such as showing location, distance, and geographical features, and touches on how data for maps is collected through surveys and other sources. Students are encouraged to understand the significance of maps in interpreting spatial information and planning.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Geography lesson focuses on mapmaking, remote sensing, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
- 🗺️ Maps are representations of the Earth's surface using a specific scale and projection system.
- 🔭 Maps can also include celestial objects like constellations and planets, in addition to Earth's surface features.
- 📏 The key elements of a map include scale, projection, and the depiction of significant Earth features.
- 🗂️ Types of maps include general maps (e.g., topographic maps) and thematic maps (e.g., population density, disaster potential).
- 📐 Maps can be classified by scale: cadastral (large scale), medium scale (city or regional maps), and small scale (global or continental maps).
- 🗳️ Dynamic maps show frequently changing data, such as population distribution or road networks.
- 🔨 Making maps involves data collection through primary (direct observation) or secondary (external sources) methods.
- 🖥️ Maps can be created manually or using software, with final presentation in graphic form for clarity.
- 📌 Essential components of a map include title, border, scale, legend, orientation, and source, ensuring accuracy and usability.
Q & A
What is the general definition of a map?
-A map is a representation of the Earth's surface depicted using a projection system and a specific scale, which allows it to be presented on a flat surface.
According to the International Cartographic Association (ICA), what does a map represent?
-The ICA defines a map as a representation of selected abstract elements from the Earth's surface and celestial bodies, related to the Earth.
What are the three key elements related to maps, as described in the lesson?
-The three key elements are: 1) Selection of important Earth surface phenomena relevant to the map's theme, 2) Transferring the Earth's curved surface to a flat one using a projection system, and 3) Reduction of Earth's actual size using a scale.
What is the purpose of using a scale in a map?
-A scale is used to determine the proportion between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the Earth, allowing for accurate representation of size and distance.
What are the two main types of maps based on content?
-The two main types of maps are: 1) General maps, which depict a broad range of Earth surface elements, and 2) Thematic maps, which focus on specific aspects such as population density or disaster potential.
How are maps categorized based on scale?
-Maps are categorized into four types based on scale: 1) Cadastral maps (very large scale), 2) Large scale maps, 3) Medium scale maps, and 4) Small scale maps.
What is the difference between a dynamic map and a stationary map?
-A stationary map contains relatively stable data, such as mountain ranges, while a dynamic map shows data that frequently changes, like population distribution or road networks.
What are the key components of a map?
-Key components include the map title, border, orientation, scale, legend, coordinate system, symbols, lettering, colors, and source data.
What are primary and secondary data in map-making?
-Primary data is gathered through direct surveys and field observations, while secondary data is collected indirectly, often from sources like statistical agencies or pre-existing records.
What are the three map requirements mentioned in the lesson?
-The three map requirements are: 1) Conformity (accurate shape representation), 2) Equidistance (correct distance representation after applying scale), and 3) Equivalence (accurate area representation after applying scale).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)