What is Velocity? - Full Concept of Velocity - Physics | Infinity Learn
Summary
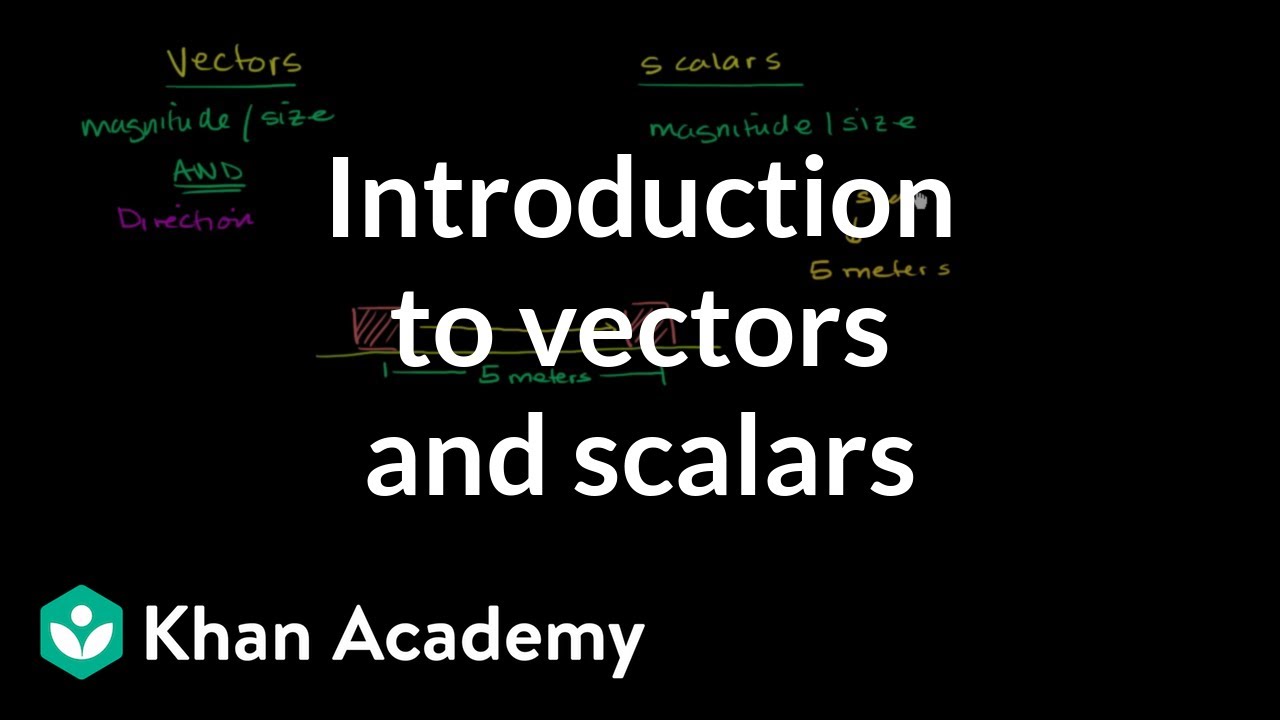
TLDRThis script explores the concepts of speed and velocity, distinguishing speed as a scalar quantity that measures distance over time without direction, while velocity is a vector quantity that includes direction. It explains how to calculate average speed and velocity, using examples like a Formula 1 race to illustrate the difference. The script also clarifies that average velocity can be zero if the starting and ending points are the same, despite covering a distance.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Speed is the distance covered per unit of time, indicating the rate at which an object moves.
- 🕒 If speed and time are known, the distance traveled can be calculated.
- 📏 Speed is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and lacks direction.
- 🧭 Displacement, unlike distance, includes direction and is the shortest path between two points.
- 🚀 Velocity is the vector equivalent of speed, incorporating both magnitude and direction.
- 🚗 When stating velocity, it's crucial to specify the direction of motion, such as 'north' or 'south'.
- 📐 The SI unit for both speed and velocity is 'meters per second', promoting a universal standard of measurement.
- 🔄 Average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance traveled by the total time taken.
- 🔄 Average velocity is determined by the displacement over the time taken, focusing on the start and end points.
- ⚠️ In a race where the start and finish points are the same, the average velocity is zero, regardless of the speed traveled.
Q & A
What is the definition of speed?
-Speed is the amount of distance covered in a given amount of time, which tells us how fast an object moves.
How can you calculate the distance covered if you know the speed and time?
-You can calculate the distance covered by multiplying the speed by the time taken to cover that distance.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
-Speed is a scalar quantity that only provides the magnitude of how fast an object is moving without specifying direction, whereas velocity is a vector quantity that includes both the speed and the direction of motion.
Why is speed considered a scalar quantity?
-Speed is considered a scalar quantity because it only has magnitude and does not specify direction.
Can you provide an example to illustrate the difference between distance and displacement?
-If you travel from town A to town B, and the distance between them is 20 kilometers, but you take a 50-kilometer route, then the distance covered is 50 kilometers and the displacement is 20 kilometers north of point A.
What is the SI unit of measurement for velocity?
-The SI unit of measurement for velocity is meters per second.
Why is 'meters per second' used as the unit for velocity instead of miles per hour or kilometers per hour?
-Meters per second is used as the SI unit for velocity to ensure a common style of measurement worldwide, avoiding confusion from different units like miles and kilometers.
How is average velocity calculated?
-Average velocity is calculated by dividing the total displacement by the total time taken, regardless of the path taken.
In the context of the script, why would a Formula 1 race car driver have an average velocity of zero?
-A Formula 1 race car driver would have an average velocity of zero if they started and finished at the same point, as their displacement would be zero, making the average velocity zero.
What is the relationship between average speed and average velocity?
-Average speed is calculated by dividing the total distance covered by the total time taken, while average velocity depends only on the start and end points, considering the displacement and time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)