07 Introduction to Permanent Deformation
Summary
TLDR该视频讨论了弹性变形和永久变形的区别。通过拉伸橡皮筋和金属回到原始形态来解释弹性行为,而当金属受到过度应力时,会发生不可逆的永久变形。讲者还提到应力-应变曲线,指出在直线末端附近,永久变形最有可能发生。此外,介绍了'塑性'的定义,解释其来源于希腊语'plastikos',意为'成形',并澄清了'塑性变形'与'塑料'材料无关。最后,他将该术语与'整形外科'联系起来,展示了它们的共同词源。
Takeaways
- 😊 弹性变形后,物体可以恢复到原来的尺寸,就像橡皮筋被拉伸后能恢复原状。
- 🔨 金属在弹性变形后也会恢复,但如果变形过大,就会产生永久变形。
- 📏 永久变形意味着当卸载后,物体不会恢复到原来的尺寸。
- 🔄 永久变形的另一个特征是卸载后应变不会回到零。
- ⚛️ 永久变形时,原子会移动到新的平衡位置。
- 📉 永久变形通常发生在应力应变曲线的线性区域结束时。
- 🧩 永久变形有时也被称为塑性变形。
- 🎨 “塑性”一词来源于希腊语“plastos”,意为“塑造或雕刻”。
- 💉 “塑性”不仅指材料类别,也用于描述如整形手术中的永久形变。
- 🏗️ 塑性变形在材料科学和工程学中广泛应用,用于描述金属、陶瓷和聚合物的形变过程。
Q & A
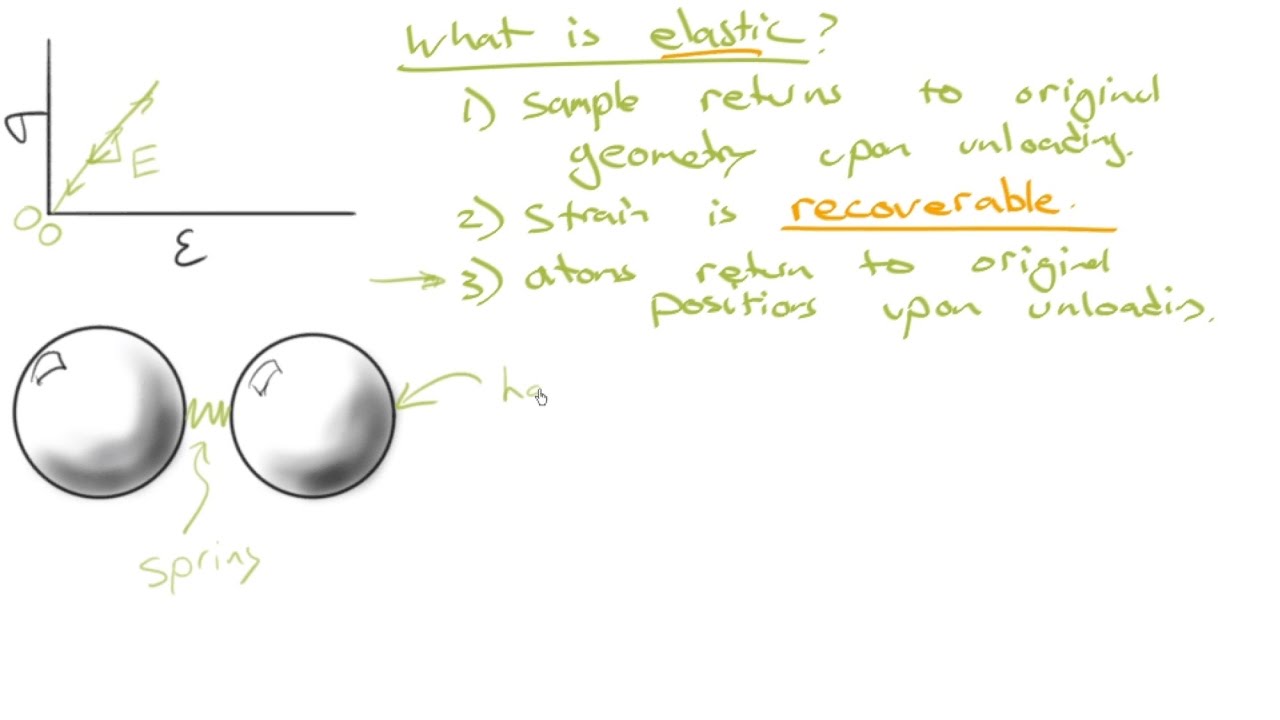
什么是弹性变形?
-弹性变形指材料在外力作用下变形,但在移除外力后,材料可以恢复到其原始形状和尺寸。例如,橡皮筋拉伸后会回到原来的形状。
什么是塑性变形?
-塑性变形是指材料在外力作用后无法恢复原状,发生永久变形。举例来说,金属弯曲后即使移除外力,也不会恢复原来的形状。
塑性变形的一个简单定义是什么?
-塑性变形可以简单定义为在移除外力后,材料不能回到其原始尺寸和形状。
塑性变形与原子的位置变化有什么关系?
-在塑性变形过程中,材料内部的原子会移动到新的平衡位置,这种变化是不可逆的。
应力-应变曲线中的线性区域代表了什么?
-应力-应变曲线中的线性区域代表材料的弹性变形区域,在这一阶段,材料在移除外力后可以恢复原状。
塑性一词的来源是什么?
-塑性一词来源于希腊语“plastos”,意思是“塑造”或“雕刻”,与塑性变形的概念一致。
塑性变形发生在哪个区域?
-塑性变形通常发生在应力-应变曲线的线性区域结束的地方,这个点标志着弹性变形的结束和塑性变形的开始。
为什么塑性变形的定义比永久变形更加准确?
-塑性变形不仅描述了材料无法恢复原状,还强调了原子层面的不可逆变化,因此比仅仅描述形变的永久变形更全面。
塑料与塑性变形有关系吗?
-尽管“塑料”这个词经常用于指代聚合物,但在材料科学中,塑性变形指的是材料形变的性质,而不特指某一种材料类别。
应力-应变曲线的断裂点代表什么?
-应力-应变曲线的断裂点代表材料在经历最大应力后无法承受更多负荷,最终断裂。
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)