PURE SUBSTANCES AND MIXTURES l GRADE 7 SCIENCE WEEK 3 (PART 2) SCIENCE 7 WEEK 2
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the concept of mixtures, contrasting them with pure substances. Mixtures consist of non-identical particles, such as in saltwater, fruit salad, and milk tea, and retain their individual properties without chemical combination. Unlike pure substances with fixed properties and ratios, mixtures lack a definite set and can vary in composition. They are also distinguishable by their physical separability and lack of fixed melting or boiling points. The video concludes with a teaser for upcoming topics on homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Takeaways
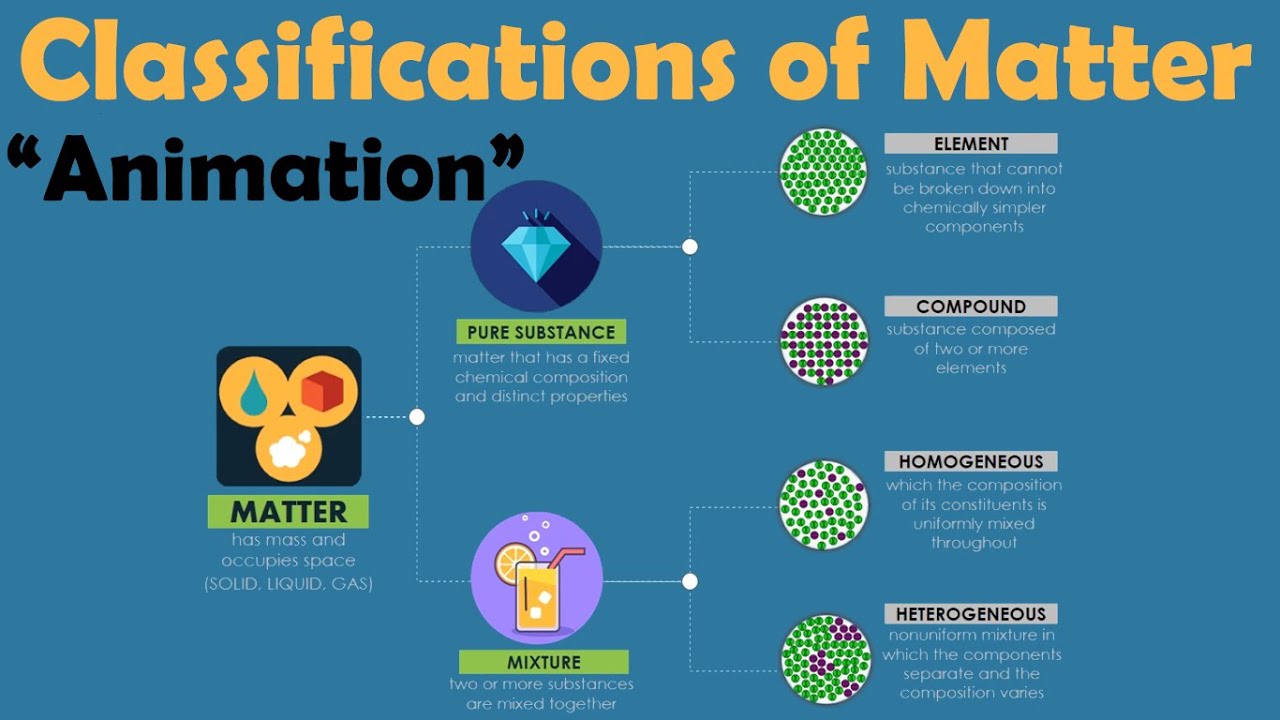
- 🧪 Mixtures are composed of non-identical particles, unlike pure substances which are made up of identical particles.
- 🌊 Examples of mixtures include salt water, fruit salad, and milk tea, which are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically combined.
- 🔬 Physical properties of mixtures can vary since they are made of different substances combined physically, and they do not have a fixed ratio or composition.
- 🌡 Mixtures lack a definite set of properties and do not have fixed melting or boiling points because the components are not chemically bonded.
- 🏗️ Mixtures can be separated into their original components through physical means, unlike pure substances which require chemical processes for separation.
- ⚖️ The properties of mixtures are a result of the individual properties of the substances they are composed of, as there is no chemical reaction between the components.
- 🌐 Mixtures can involve combinations of solid and liquid, solid and solid, liquid and liquid, gas and gas, or liquid and gas.
- 🔩 Alloys are an example of solid and solid mixtures, where different metals are combined to create a new material with distinct properties.
- 💧 Liquid and liquid mixtures, such as vinegar, which is a combination of water and acetic acid, demonstrate how different liquids can mix to form a mixture.
- 🌬️ Gas and gas mixtures, like the air we breathe, are composed of various gases like nitrogen and oxygen, highlighting the diversity within mixtures.
Q & A
What is the main difference between pure substances and mixtures?
-Pure substances are made of identical particles, while mixtures are made of non-identical particles that are not chemically combined but physically combined, retaining their original properties.
What are the examples of mixtures mentioned in the script?
-The examples of mixtures mentioned include salt water solution, halo-halo, fruit salad, milk tea, and alloys.
Why do mixtures not have a fixed melting point or boiling point?
-Mixtures do not have a fixed melting point or boiling point because they are made of two or more substances that are combined physically, not chemically, and they can come in different proportions.
How can mixtures be separated?
-Mixtures can be separated physically, as they are not chemically bonded and their components retain their individual properties.
What is the composition of a salt solution according to the script?
-A salt solution is composed of two types of substances: salt, which is made of sodium and chlorine, and water, which is made of hydrogen and oxygen.
What is an alloy and how does it relate to mixtures?
-An alloy is a mixture of metals, solid and solid, and it is a type of mixture where different metals are physically combined.
Can mixtures involve combinations of different states of matter?
-Yes, mixtures can involve combinations of different states of matter, such as solid and liquid, liquid and liquid, gas and gas, and liquid and gas.
What is a homogeneous mixture and how is it different from a heterogeneous mixture?
-The script does not provide specific details about homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, but typically, a homogeneous mixture has a uniform composition throughout, whereas a heterogeneous mixture has a non-uniform composition with visible differences in its components.
Why are the properties of pure substances consistent throughout?
-The properties of pure substances are consistent throughout because they are made of identical particles, and all particles of a pure substance are the same.
What is the significance of a fixed melting point and boiling point in pure substances?
-A fixed melting point and boiling point in pure substances indicate that they are chemically uniform and have a consistent molecular structure, which is necessary for a specific temperature to change their state.
What is the difference between a pure substance and a compound as described in the script?
-A pure substance is made of identical particles with a definite set of properties, while a compound is a type of pure substance made of atoms of two or more elements that are chemically combined and cannot be separated by physical means.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Pure Substances and Mixtures, Elements & Compounds, Classification of Matter, Chemistry Examples,
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER | Animation

Pure Substances and Mixtures | Science for Kids

Fases e componentes [Módulo 01_Aula 05]

Classification of matter | Structure and properties of matter | High school chemistry | Khan Academy
Pure Substances vs Mixtures
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)