Parts of a cell
Summary
TLDRThis script offers an in-depth exploration of cellular anatomy, focusing on the cell membrane, DNA, and the distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It delves into the roles of the nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies in protein synthesis and transport. Additionally, it touches on organelles like lysosomes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts, emphasizing their functions and the theory of endosymbiosis. The script also mentions cell walls and microfilaments, providing a comprehensive overview of cell structure.
Takeaways
- 😀 The cellular membrane is crucial as it separates the cell from the outside world and defines the cell's compartmentalization.
- 🔬 All cells contain DNA, which is a key determinant of an organism's characteristics and is housed within the cell's nucleus in eukaryotes.
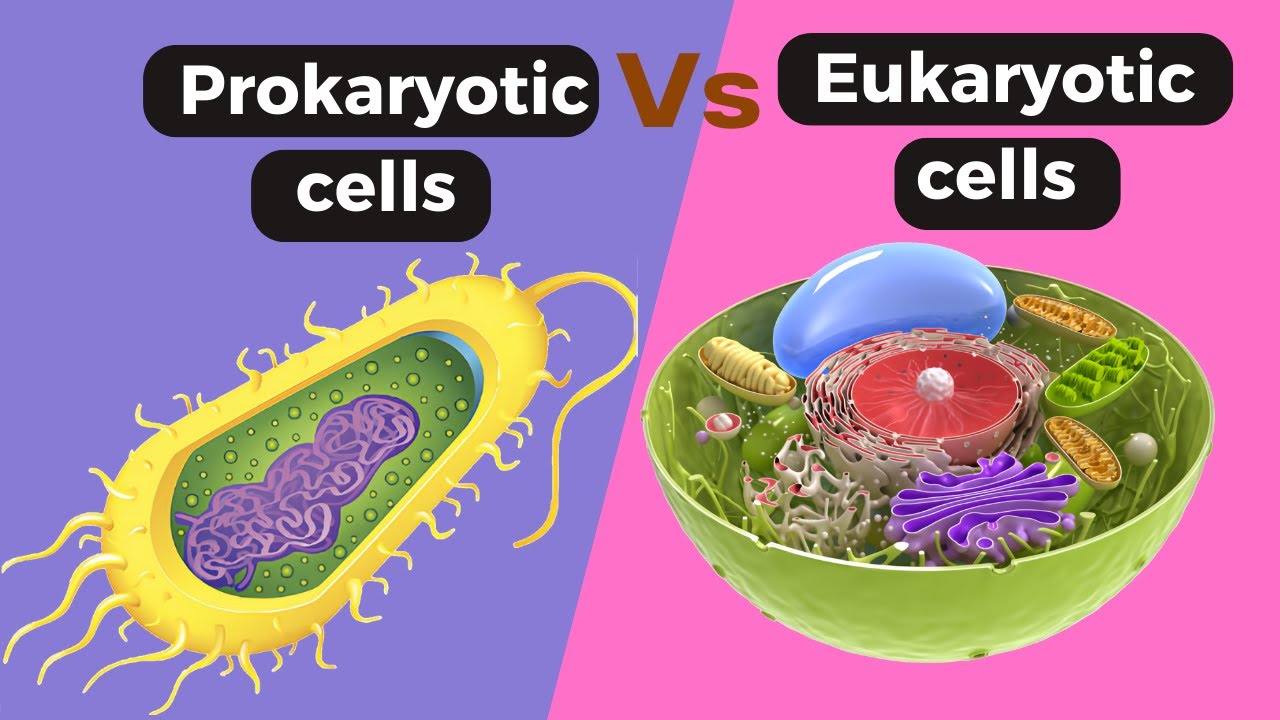
- 🌿 Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus that encloses the DNA, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells like bacteria and Archaea, which lack a nucleus.
- 📚 Ribosomes, composed of proteins and RNA, are the sites of protein synthesis within the cell, translating mRNA into functional proteins.
- 🧬 The nucleolus, a dense region within the nucleus, is responsible for producing ribosomal RNA, which is a key component of ribosomes.
- 🌐 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membrane system that aids in protein synthesis and transport, with ribosomes attached to its 'rough' side for translation.
- 📦 The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or use within the cell, often 'budding' them off in vesicles.
- 🔋 Mitochondria, known as the 'powerhouses' of the cell, generate ATP through cellular respiration and contain their own DNA.
- 🌳 Plant cells have additional structures like cell walls for rigidity and chloroplasts for photosynthesis, which are absent in animal cells.
- 🔬 Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes that break down waste and foreign substances, playing a crucial role in cellular cleanup.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the cellular membrane?
-The cellular membrane separates the cell from the outside world and defines the cell as a small compartment. It plays a crucial role in protecting the cell and regulating the passage of substances in and out.
Why is DNA considered a defining component of a cell?
-DNA is considered a defining component of a cell because it contains the genetic information that determines the characteristics of a living organism. It is present in all cells and is responsible for the instructions needed to build and maintain the organism.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed by a nuclear membrane, where DNA is stored, and they are generally more complex and larger. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and Archaea, do not have a nucleus and are generally simpler and smaller.
What is the role of the nucleolus in a eukaryotic cell?
-The nucleolus is a region within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA, a key component of ribosomes, is produced. It is not a separate organelle and is not enclosed by a membrane, but it is a dense area visible under a microscope.
How are proteins synthesized in a cell?
-Proteins are synthesized in cells through a process that starts with DNA transcription into mRNA within the nucleus. The mRNA then moves to ribosomes, where it is translated into a protein chain. Ribosomes can be free-floating or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum and how does it relate to protein synthesis?
-The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes that plays a role in the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins and lipids. Proteins destined for secretion, insertion into the cell membrane, or use within the cell are synthesized on ribosomes attached to the rough ER and then enter the ER for further processing.
Can you explain the process of protein transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus?
-Proteins synthesized in the ER are transported to the Golgi apparatus through vesicles that bud off from the ER. These vesicles carry the proteins through the cell's cytosol and eventually fuse with the Golgi apparatus, where further modifications and sorting for their final destinations occur.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the cell?
-The Golgi apparatus is responsible for modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids for their final destinations, which may include secretion outside the cell, insertion into the cell membrane, or use within the cell.
How do vesicles facilitate the movement of proteins within the cell?
-Vesicles are small, membrane-bound sacs that transport proteins and other molecules within the cell. They bud off from organelles like the Golgi apparatus and can move to different parts of the cell, fusing with membranes to deliver their cargo or release it outside the cell.
What are lysosomes and what is their function in a cell?
-Lysosomes are organelles containing digestive enzymes that function as the cell's recycling center. They break down and recycle waste materials and cellular debris. In animal cells, they are responsible for the digestion of engulfed substances, while in plant cells, similar functions are performed by lytic vacuoles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

NÚCLEO CELULAR - RESUMO PARA PROVA - Prof. Kennedy Ramos

Organelas Celulares : Estrutura celular e citoplasma - Animação 3D

Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic Cells

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy

Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell | Differences and Similarities | Video 16
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)