Angle Bisector Construction
Summary
TLDRThe video script outlines the process of constructing an angle bisector, a line that divides an angle into two congruent parts. It begins with creating an acute angle and then using a compass to find a point equidistant from the angle's sides. By drawing arcs from the angle's sides and intersecting them, a point on the angle bisector is determined. Finally, a straight edge connects the vertex to this point, resulting in two congruent angles bisected by the angle bisector.
Takeaways
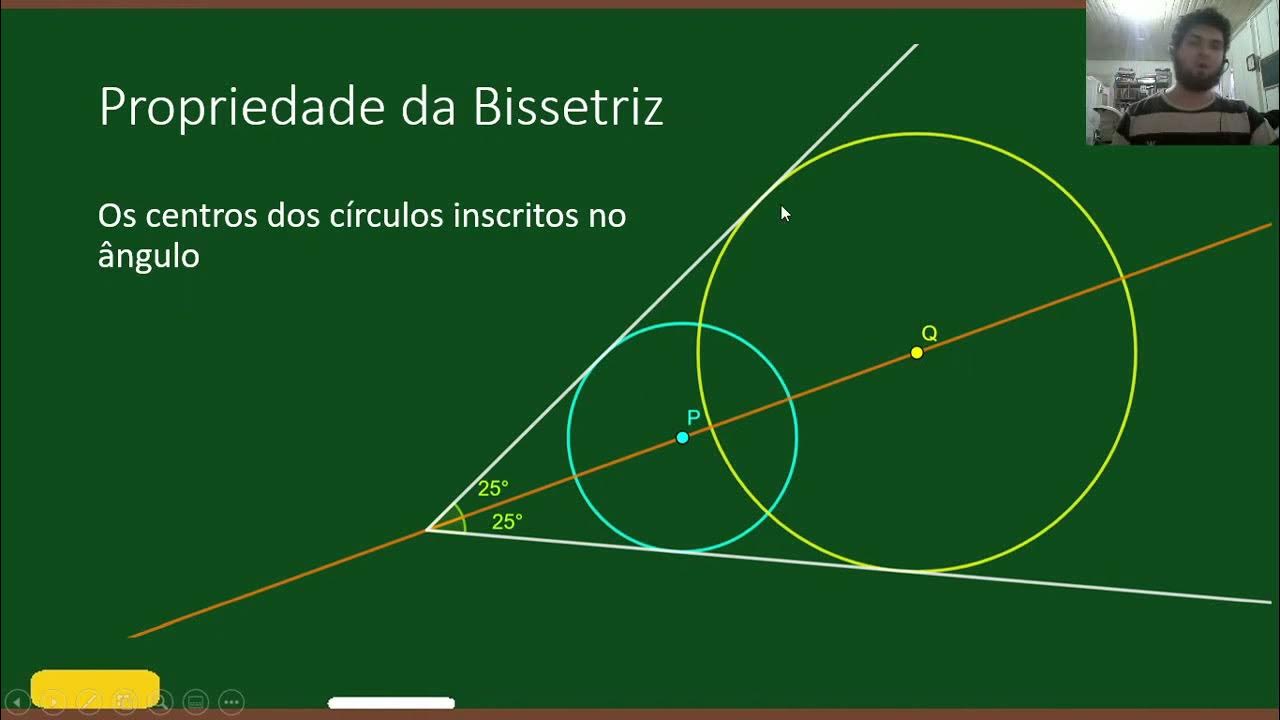
- 📐 An angle bisector is a line that cuts an angle into two congruent parts.
- 🖊️ The construction begins by creating an angle, often an acute one, in the middle of the page.
- 📏 The angle bisector will pass through the vertex of the angle.
- ⚖️ All points on the angle bisector are equidistant from each side of the angle.
- 📌 To draw the bisector, we need a second point on the bisector besides the vertex.
- 🧭 A compass is used to intersect both sides of the angle by drawing an arc.
- 🔗 Two new intersection points are created where the arc intersects the sides of the angle.
- 🔄 From each intersection, arcs are drawn again, meeting in the middle of the angle.
- 🎯 The point where these arcs intersect is equidistant from both sides of the angle.
- 📏 Using a straight edge, the vertex and this new point are connected to form the bisector, creating two congruent angles.
Q & A
What is an angle bisector?
-An angle bisector is a line that divides an angle into two congruent parts.
Why is it necessary to start with an angle for the angle bisector construction?
-An angle is required to perform the angle bisector construction because the bisector is meant to divide the angle into two equal parts.
What type of angle is constructed in the middle of the page?
-An acute angle is constructed in the middle of the page for the angle bisector construction.
Why does the angle bisector go through the vertex of the angle?
-The angle bisector goes through the vertex because it is the point where the two sides of the angle meet, and the bisector must pass through it to divide the angle into two congruent parts.
What is the significance of the points on the angle bisector being equidistant from the sides of the angle?
-The points on the angle bisector being equidistant from the sides of the angle ensure that the line divides the angle into two congruent angles.
How are the compass settings determined for the angle bisector construction?
-The compass is set to a width that allows it to intersect both sides of the angle, which helps in drawing the arcs necessary for finding the point on the bisector.
What is the purpose of drawing arcs from the intersections created by the compass?
-Drawing arcs from the intersections helps in locating a point that is equidistant from both sides of the angle, which is crucial for determining the angle bisector.
How does the construction ensure that the new point found is equidistant from both sides of the angle?
-The construction ensures the new point is equidistant by having the arcs from both sides intersect at a single point, which by definition is equidistant from both sides.
What tool is used to connect the vertex and the new point found on the bisector?
-A straight edge is used to connect the vertex and the new point to complete the angle bisector construction.
What is the final outcome of the angle bisector construction?
-The final outcome is a line that bisects the original angle into two congruent angles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)