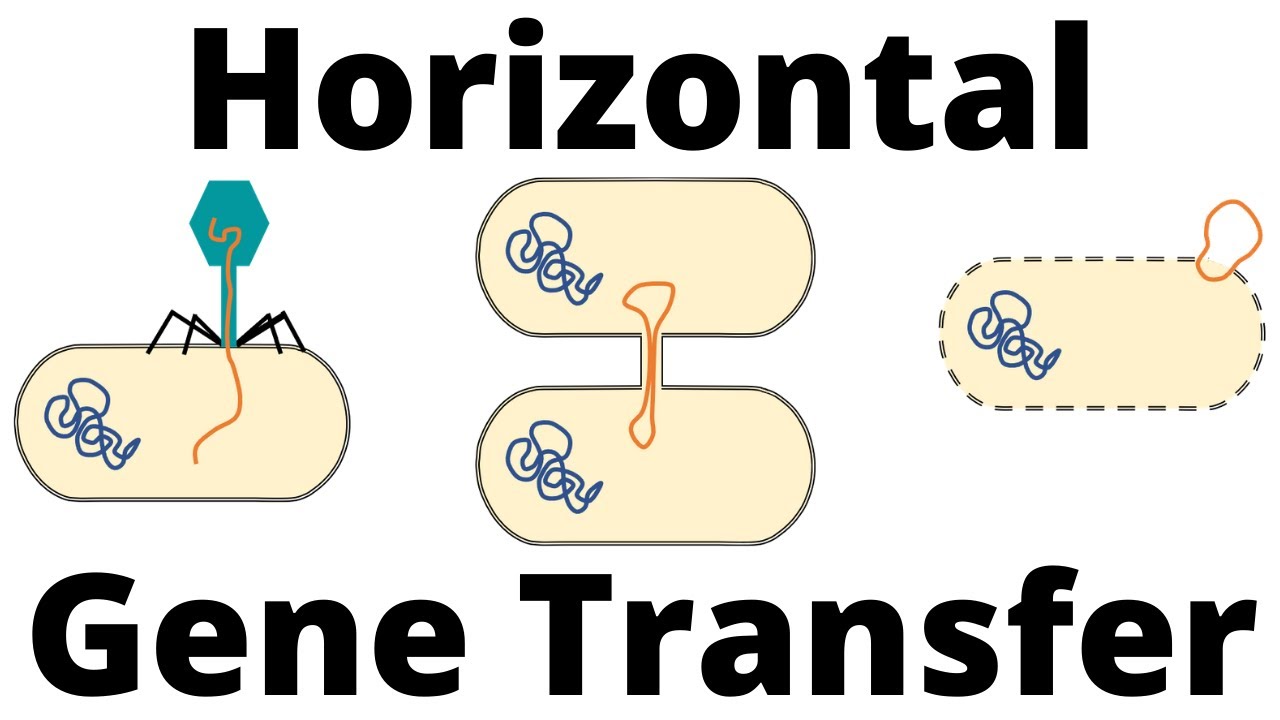
CONJUGATION, TRANSFORMATION, TRANSDUCTION (HORIZONTAL GENE TRANSFER)
Summary
TLDRThis script explores horizontal gene transfer in bacteria, a process that allows for rapid genetic diversity. It details three mechanisms: conjugation, where bacteria exchange DNA directly; transformation, the uptake of extracellular DNA; and transduction, involving bacteriophages transferring DNA. These methods enable bacteria to adapt quickly to new environments and pressures, such as acquiring antibiotic resistance. Despite continuous gene acquisition, genome size remains stable as non-beneficial genes are often lost.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Bacteria can exchange genes horizontally between cells of the same generation, a process known as horizontal gene transfer, which is distinct from vertical gene transfer where genes are passed from parents to offspring.
- 🔄 The three primary methods of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria are conjugation, transformation, and transduction, with conjugation being the most prevalent.
- 🔗 Conjugation involves direct cell-to-cell contact and is facilitated by conjugative plasmids or transposons, which are self-transmissible genetic elements.
- 🧬 Plasmids are circular DNA molecules that replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome, while transposons, or 'jumping genes', are mobile DNA segments capable of moving within or between genomes.
- 🤝 Conjugation requires the formation of a 'mating pair' where one bacterium transfers a single-stranded DNA to another, which is then replicated to restore double-stranded DNA in both bacteria.
- 🌐 Transformation is the process where bacteria take up extracellular DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their own genomes, facilitated by 'competent' bacteria with increased DNA uptake capabilities.
- 🧵 Recombination rearranges the donor and recipient genomes to form new hybrid genomes, potentially leading to new phenotypes such as pathogenicity or antibiotic resistance.
- 🦠 Transduction involves the transfer of bacterial DNA via bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect bacteria and can exist in a lysogenic state or undergo a lytic cycle.
- 🌀 Generalized transduction occurs when a phage accidentally packages bacterial DNA instead of its own, while specialized transduction involves the incorrect excision of bacterial DNA during the viral life cycle.
- 🌿 Horizontal gene transfer, along with mutations, contributes to genetic diversity in bacteria, allowing them to adapt rapidly to new environments and selective pressures.
Q & A
What is horizontal gene transfer in bacteria?
-Horizontal gene transfer is a process where genes are exchanged between cells of the same generation, as opposed to vertical gene transfer where genes are passed from parents to offspring.
What are the three methods of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria?
-The three methods of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria are conjugation, transformation, and transduction.
Why is conjugation the most common method of horizontal gene transfer?
-Conjugation is the most common method of horizontal gene transfer because it allows for direct cell-cell contact and efficient transfer of genetic material, often facilitated by conjugative plasmids or transposons.
What is a conjugative plasmid and how does it facilitate conjugation?
-A conjugative plasmid is a self-transmissible, circular DNA section that replicates independently of chromosomes and contains all the genes needed to connect with another bacterium and transmit itself via conjugation.
How does the formation of a conjugation pilus aid in the process of conjugation?
-The conjugation pilus, also known as an F pilus or sex pilus, aids in conjugation by binding to another bacterium and retracting to pull the two cells together, forming a 'mating pair' that allows for DNA transfer.
What is the role of the enzyme transposase in horizontal gene transfer?
-The enzyme transposase catalyzes the cutting and resealing of DNA during transposition, which is a part of the horizontal gene transfer process involving nonconjugative transposons and plasmids.
How does transformation differ from conjugation and transduction?
-Transformation involves bacteria taking up extracellular DNA and incorporating it into their genomes, which is different from conjugation that requires cell-cell contact and transduction that involves bacteriophage-mediated DNA transfer.
What is the significance of bacterial competency in the process of transformation?
-Bacterial competency is significant in transformation as it refers to the state of increased cell wall and cell membrane permeability that allows cells to uptake DNA from their environment.
How does transduction contribute to horizontal gene transfer?
-Transduction contributes to horizontal gene transfer by transferring DNA from one cell to another via a bacteriophage, which can switch between lysogenic and lytic cycles to facilitate the transfer.
What are the two types of transduction and how do they differ?
-The two types of transduction are generalized and specialized. Generalized transduction occurs when a phage accidentally packages bacterial DNA instead of its own, while specialized transduction involves the incorrect excision of bacterial DNA during the lysogenic cycle of the virus.
How does horizontal gene transfer contribute to bacterial adaptation and genetic diversity?
-Horizontal gene transfer contributes to bacterial adaptation and genetic diversity by allowing bacteria to rapidly acquire beneficial traits such as antibiotic resistance or pathogenicity from other bacteria, thus responding to selective pressures and adapting to new environments.
Why doesn't the genome size of bacteria increase indefinitely despite continuous horizontal gene transfer?
-The genome size of bacteria does not increase indefinitely because if the transferred genes do not provide a selective advantage, they are usually lost by deletion, thus maintaining a relatively constant genome size over time.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)