What is DICOM | vs HL7 in the Radiology Workflow
Summary
TLDRThe script explains the roles of DICOM and HL7 in radiology workflows. DICOM is a file format for medical images, ensuring compatibility between applications through standardization. HL7, on the other hand, is a protocol for healthcare applications to communicate, including textual information exchange. The script illustrates how an MRI appointment is ordered via HL7, with details like patient identifiers and exam specifics. These details are then used to populate a DICOM modality worklist, which is queried by the MRI machine. The final report, generated by a radiologist, is sent back to the patient's record via HL7, making it accessible alongside the DICOM images.
Takeaways
- 📄 **DICOM as a File Type**: DICOM is the standard for medical images, requiring applications to adhere to specific compatibility standards.
- 🌐 **HL7 as a Communication Protocol**: HL7 is a protocol that enables various healthcare applications to communicate with each other, not limited to imaging.
- 🔗 **DICOM and HL7 Relationship**: DICOM and HL7 work together in the radiology workflow, with HL7 facilitating orders and DICOM handling image data.
- 🏥 **Order Entry with HL7**: Physicians use HL7 to send MRI exam orders, which are then processed by the Radiology Information System (RIS).
- 📋 **DICOM Modality Worklist**: The RIS populates a DICOM modality worklist with patient study details, which can be queried by MRI modalities.
- 🔎 **Querying with DICOM C-FIND**: MRI technologists use DICOM C-FIND operations to query the RIS for patient study details.
- 🏷️ **DICOM Tag Metadata**: Once a patient is selected, study details are applied to images as DICOM tag metadata, creating a complete DICOM file.
- 💾 **Storing DICOM Files**: DICOM files, with their metadata, are stored in Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) using the C-STORE operation.
- 📑 **HL7 for Report Association**: After an MRI exam, radiologists' reports are sent to PACS via HL7 messages, linking textual reports with DICOM images.
- 📚 **Educational Resources**: For deeper understanding, resources like Health Level Seven International (HL7), National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), and PAX Bootcamp are recommended.
Q & A
What is DICOM and how does it relate to medical imaging?
-DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) is a standard protocol for the transmission and sharing of medical images. It defines the format in which these images are stored and the method for exchanging them between systems. DICOM is not limited to images; it also supports patient information, waveforms, and textual data.
How is HL7 different from DICOM?
-HL7 (Health Level Seven) is a set of international standards for the transfer of clinical and administrative data between different healthcare providers. Unlike DICOM, which is focused on medical imaging, HL7 is a broader protocol that facilitates the exchange of various types of healthcare data, including textual information and patient records.
What is an HL7 ORM message and why is it important?
-An HL7 ORM (Order Message) is a type of message used in healthcare to communicate orders for medical tests or procedures, such as an MRI exam. It is important because it contains essential patient identifiers and details specific to the ordered exam, ensuring the correct patient receives the correct procedure.
Can you explain the DICOM Modality Worklist and its function?
-The DICOM Modality Worklist is a list of studies that need to be performed, populated with information from HL7 messages. It allows imaging modalities, such as MRI machines, to query and retrieve patient study details for the day, ensuring that the correct exams are performed on the correct patients.
What is a DICOM C-FIND operation and how does it interact with the RIS?
-A DICOM C-FIND operation is a query mechanism used by imaging modalities to retrieve information from the Radiology Information System (RIS). The modality sends a C-FIND request, and the RIS responds with a list of studies that match the query parameters, helping to ensure the correct patient and study details are applied to the imaging process.
How does the DICOM C-STORE operation contribute to the storage of medical images?
-The DICOM C-STORE operation is used to transmit and store medical images in the Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS). After an image is acquired and the study details are applied as DICOM tags, the C-STORE operation is used to send the complete DICOM file to the PACS for storage and further use.
What is the role of HL7 in report association with DICOM?
-HL7 is used to associate textual reports, such as those generated by radiologists after interpreting an MRI exam, with the corresponding DICOM images. This is done through an HL7 Observation Result (ORU) message, which ensures that the final text report is linked to the patient's record and can be accessed alongside the DICOM images for review.
How does the integration of DICOM and HL7 standards facilitate the radiology workflow?
-The integration of DICOM and HL7 standards facilitates the radiology workflow by ensuring seamless communication between different systems involved in patient care. DICOM handles the imaging data, while HL7 manages the transfer of orders, patient information, and reports, creating a cohesive and efficient workflow from order placement to report generation and image storage.
What is the significance of the HL7 message in the context of a patient's MRI appointment?
-In the context of a patient's MRI appointment, the HL7 message is significant as it carries the order for the MRI exam from the physician to the radiology information system. It contains crucial information such as patient identifiers and exam details, which are then used to populate the DICOM Modality Worklist and ensure the correct exam is performed.
How can healthcare professionals ensure compatibility with DICOM and HL7 standards?
-Healthcare professionals can ensure compatibility with DICOM and HL7 standards by using compliant software and systems, participating in training, and staying updated with the latest versions of these standards. Regular system updates and adherence to the standard specifications are also crucial for maintaining compatibility.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Informatics - Radiology Workflow
Digital Radiography: Medical Informatics: PACS System and Quality Control-Assurance
Digital Radiography: Image Post Processing: PACS System and Quality Control-Assurance
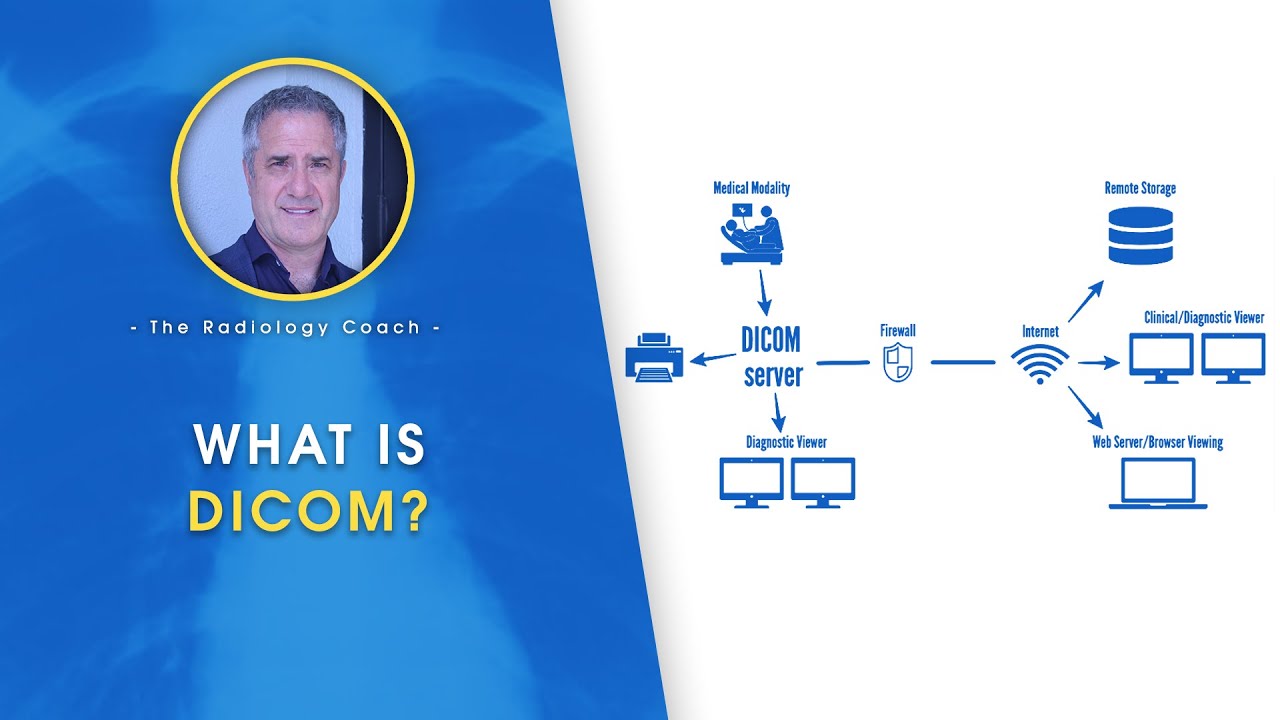
What is DICOM
PACS Systems and Quality Control Part 1 - Image Post Processing

Healthcare Interoperability Standards
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)