Lingkaran (Bagian 1) - Unsur-unsur, Hubungan Sudut Pusat dan Sudut Keliling | SMP MTs Kelas VIII
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the concept of circles in a mathematical context, focusing on their two-dimensional properties. It explains key elements of a circle, including the center, radius, diameter, chord, and arc. The script further delves into the relationship between the central angle and the inscribed angle, emphasizing that the central angle is twice the inscribed angle when they subtend the same arc. Practical examples are used to illustrate these concepts, making the video a valuable resource for understanding the fundamentals of circles in geometry.
Takeaways
- 📘 Circles are two-dimensional shapes consisting of points equidistant from a central point, known as the center of the circle.
- 🔵 The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circumference, often denoted by 'r'.
- 📏 The diameter is a straight line passing through the center of the circle and touching two points on the circle, represented by 'd'.
- 🔶 The chord is a straight line connecting any two points on the circle, with the diameter being a special type of chord that passes through the center.
- 🌀 An arc is a portion of the circumference of the circle, and a sector is the area enclosed by two radii and an arc.
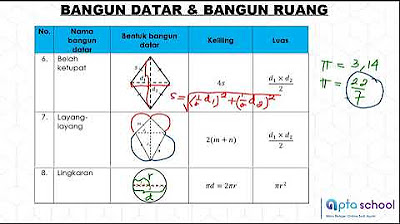
- 🔼 The circumference of a circle is the total length of the circle's edge, and it can be calculated using the formula C = 2πr.
- 📐 The central angle is an angle formed by two radii at the center of the circle, while the inscribed angle is formed by two chords at a point on the circumference.
- 🔄 The relationship between a central angle and an inscribed angle subtended by the same arc is that the central angle is twice the measure of the inscribed angle.
- 🔄 Conversely, the inscribed angle is half the measure of the central angle subtending the same arc.
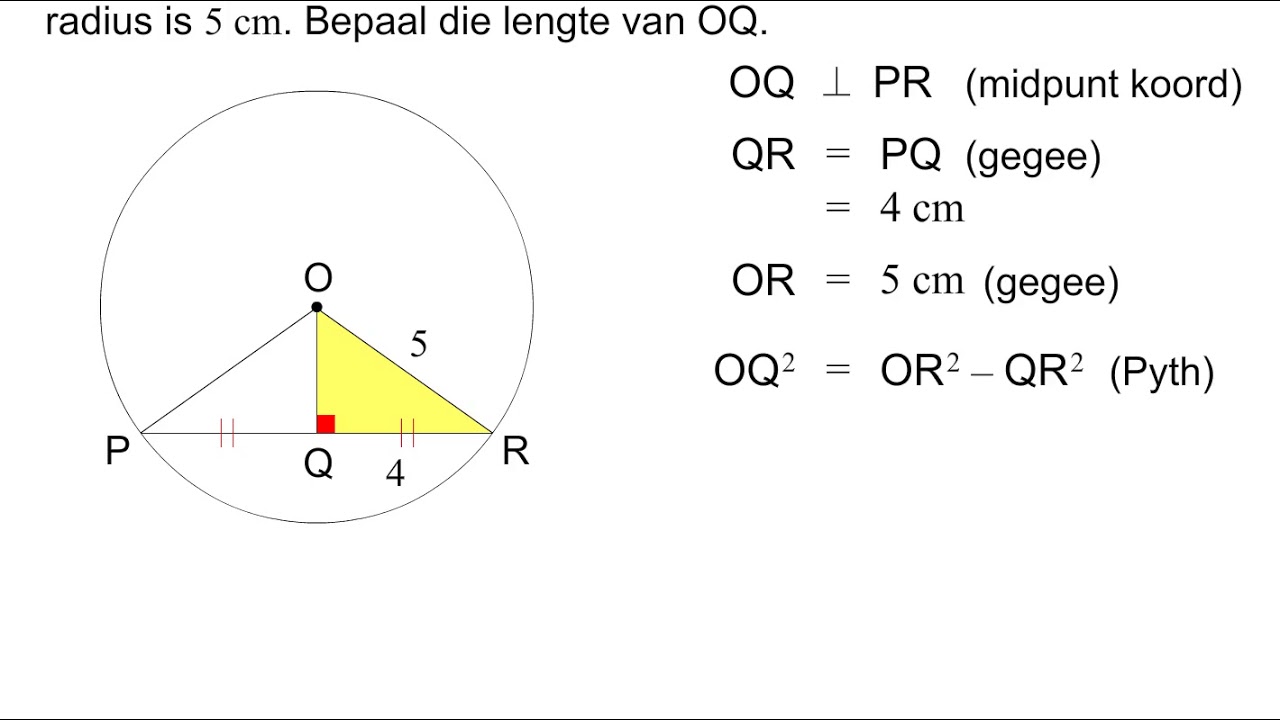
- 📐 The apothem is the perpendicular distance from the center of the circle to the midpoint of a chord, often used in calculating the area of a sector.
Q & A
What is a circle in the context of the video?
-A circle is a two-dimensional shape consisting of a set of points that form a curve and have the same length relative to their center point.
What is the term for the center point of a circle?
-The center point of a circle is called the 'center of the circle' or 'centroid'.
What is the radius of a circle and how is it represented?
-The radius of a circle is the distance from the center to any point on the circle, and it is typically represented by the lowercase letter 'r'.
What is the diameter of a circle and how does it relate to the radius?
-The diameter of a circle is a straight line that passes through the center and connects two points on the circle, and it is represented by the lowercase letter 'd'. It is twice the length of the radius.
What is a chord in a circle?
-A chord is a straight line that connects two points on the circle but does not pass through the center.
What is the term for the area enclosed by a circle?
-The area enclosed by a circle is called the 'area of the circle'.
What is the relationship between the central angle and the inscribed angle that subtends the same arc?
-The central angle is twice the measure of the inscribed angle that subtends the same arc.
What is an apothem in a circle?
-An apothem is the shortest distance between the center of the circle and a chord, typically perpendicular to the chord.
What is the term for the arc that forms a segment of the circle's circumference?
-The term for the arc that forms a segment of the circle's circumference is 'circular arc' or simply 'arc'.
How can the area of a sector be calculated if the radius and the central angle are known?
-The area of a sector can be calculated using the formula 'Area of sector = (central angle in degrees / 360) × π r^2', where r is the radius.
What is the relationship between the central angle and the inscribed angle when they subtend the same chord?
-The central angle and the inscribed angle subtending the same chord are equal.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)