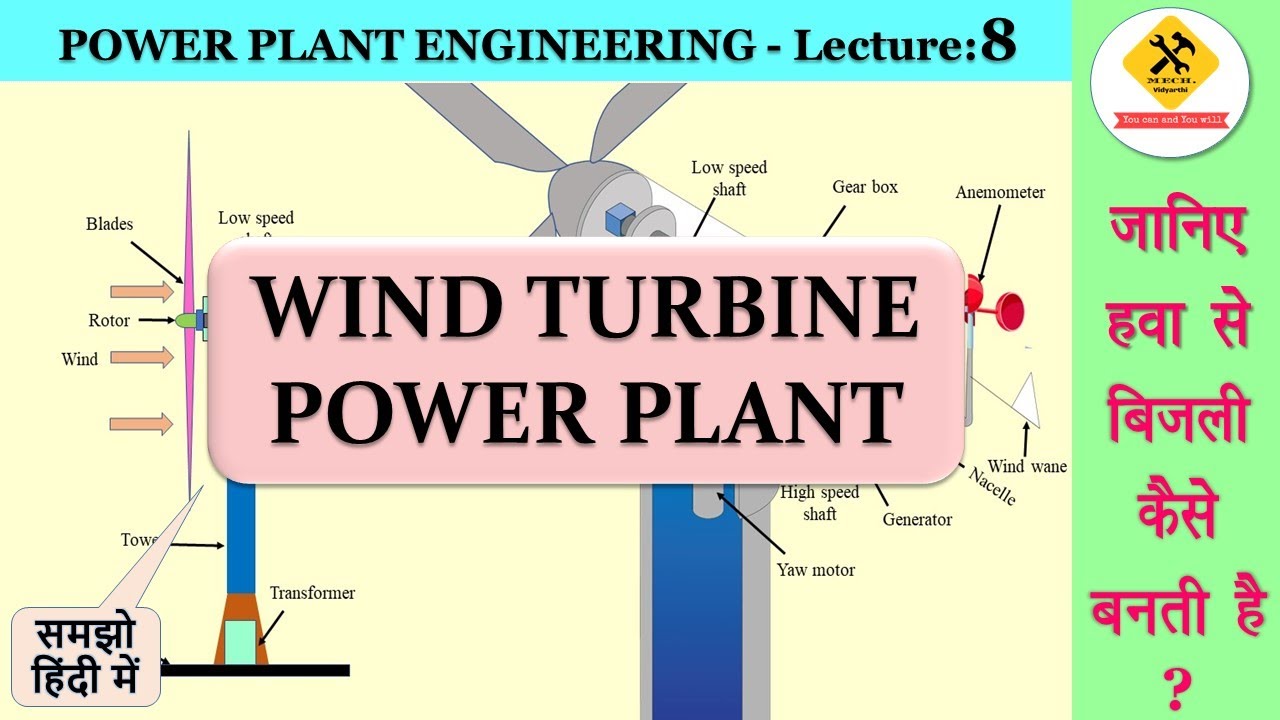
How Wind Turbines Really Work: The Hidden Secrets
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the mechanics of wind turbines and how they generate electricity. It covers the basic principles, from converting wind's kinetic energy into electrical power, to the key components of a turbine such as the blades, generator, and gearbox. The design considerations, like the number of blades and blade angles, are also discussed to optimize power generation. The video further explores the differences between small and large turbines, offshore vs. onshore installations, and the engineering complexities involved in maintaining efficient energy production. Additionally, it promotes learning about electrical engineering through Brilliant courses.
Takeaways
- 😀 Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy, which is then turned into electrical energy to power homes and towns.
- 😀 The size and height of wind turbine blades help capture more wind energy, and larger turbines are often placed at sea to avoid space limitations on land.
- 😀 The speed of the wind is the most important factor in power generation for wind turbines; higher wind speeds lead to more electricity production.
- 😀 Small wind turbines often have a tail fin to help align them with the wind, while large turbines use a wind vane and motors to adjust their position for optimal wind capture.
- 😀 A wind turbine's blades are designed with an aerodynamic shape, often twisted along their length, to optimize lift and minimize drag for efficient energy generation.
- 😀 Wind turbines with three blades are most efficient for large turbines as they balance wind capture and structural stability, while more blades can generate higher drag.
- 😀 The mechanical components inside a wind turbine, such as the gearbox and generator, convert the slow rotation of the blades into high-speed electrical output.
- 😀 The doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) is the most common generator for large wind turbines, helping convert variable rotor speeds into consistent electrical output at 50 or 60 Hz.
- 😀 Wind turbines use a pitch control system to adjust the angle of the blades, optimizing lift while preventing damage at high wind speeds by reducing rotational speed.
- 😀 The engineering of wind turbines involves complex systems, including gearboxes, generators, and controllers, which work together to harness wind energy efficiently and safely.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a wind turbine?
-The primary function of a wind turbine is to convert the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy to power homes, industries, or even entire towns.
Why are wind turbines placed at great heights?
-Wind turbines are placed at great heights to capture stronger, more consistent winds that are typically found at higher altitudes. The wind speed increases with height, and the air is also less turbulent, which helps optimize energy generation.
How do the size and number of blades impact a wind turbine's performance?
-The size of the blades directly influences the amount of wind energy that can be captured. Larger blades capture more energy, but they also need to be higher off the ground. The number of blades affects stability and efficiency; three blades are the most common because they provide a balance of performance, cost, and stability.
What is the role of the tail fin on smaller wind turbines?
-The tail fin on smaller wind turbines helps to align the blades with the wind direction. Without it, the turbine may turn away from the wind, reducing its efficiency. This feature is crucial for smaller turbines installed in areas with less consistent wind.
How does the wind turbine's gearbox work?
-The gearbox in a wind turbine increases the speed of the rotor shaft. It converts low-speed, high-torque rotational energy from the blades into high-speed, low-torque energy that is needed to generate the proper frequency for the electrical grid, typically 50 or 60 Hz.
What is the function of the wind vane and anemometer in a wind turbine?
-The wind vane detects the wind's direction, ensuring the turbine is always facing into the wind. The anemometer measures wind speed, helping the system adjust the blade pitch to control power output and ensure the turbine operates within safe limits.
Why do large wind turbines not use tail fins like smaller ones?
-Large wind turbines do not use tail fins because the turbines would need to be extremely large to be effective. Instead, large turbines use a computer-controlled system that adjusts the orientation of the turbine's nacelle to keep it facing into the wind.
What happens if the wind speed becomes too fast for a wind turbine?
-If the wind speed becomes too fast, the wind turbine will reach its 'cutout speed,' at which point it will stop generating electricity. The blades may tilt to reduce the power generated, and brakes are applied to prevent damage to the system.
What materials are used to construct wind turbine blades and why?
-Wind turbine blades are typically made from reinforced fiberglass because it is strong, lightweight, and resistant to fatigue. These materials allow for longer blades, which can capture more wind energy, while avoiding the weight and potential failures that heavier materials like metal or wood might cause.
What is the difference between direct drive and geared systems in wind turbines?
-Direct drive systems in small wind turbines use permanent magnet generators to convert rotational energy directly into electricity. In contrast, larger turbines use geared systems, where a gearbox increases the rotational speed of the rotor to match the required generator speed and produce the correct electrical frequency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)