Convex and Concave Lenses
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script explores the principles of image formation through convex and concave lenses. It uses a hands-on approach, with the presenter standing in for the object, to demonstrate how images are formed at different distances from the lenses. The script outlines the three key rules for ray diagrams with both types of lenses, explaining how these rules determine whether the image is real or virtual, magnified or diminished, and its position relative to the lens. The video aims to simplify a complex topic, making it accessible and engaging for viewers, and concludes with top questions to test understanding.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video discusses the image formation by convex and concave lenses, explaining where and how the image is formed when an object is placed in front of these lenses.
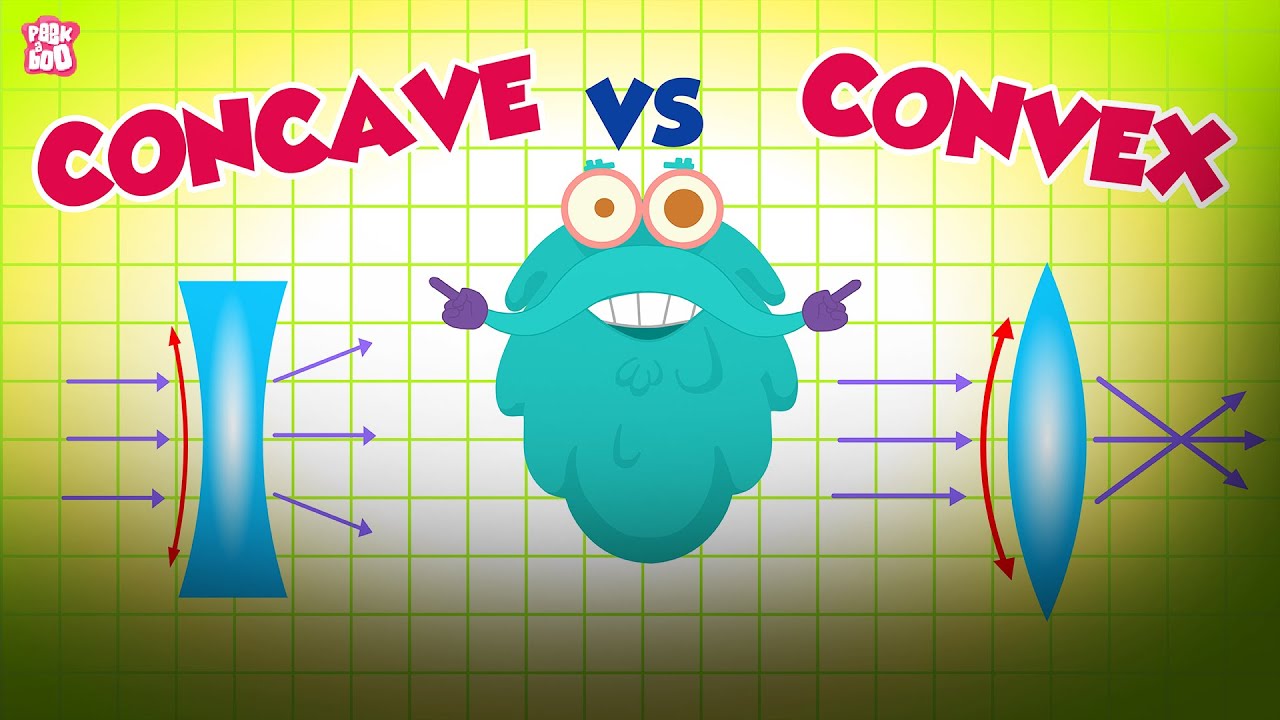
- 📏 For a convex lens, which is a converging lens, the video demonstrates how to draw it accurately by marking the principal axis, optical center, and principal foci.
- 🌟 Three light ray rules are introduced for convex lenses: (1) a parallel ray refracts through the focus, (2) a ray through the optical center continues undeviated, and (3) a ray through the focus refracts parallel to the principal axis.
- 👤 The presenter humorously uses themselves as the object to demonstrate image formation by standing at different positions relative to the lens.
- 🔄 The video explains that for a convex lens, the image properties (real/virtual, inverted/upright, magnified/diminished) and position depend on the object's distance from the lens.
- 🔍 In the case of a concave lens, which is a diverging lens, the video shows how to draw it by marking the principal axis and foci, noting that they are on opposite sides compared to a convex lens.
- 📋 Three light ray rules are also given for concave lenses, which are similar to those for convex lenses but with the refracted rays appearing to diverge from or converge to the focal points.
- 🔄 The video highlights that for a concave lens, the image is always virtual, upright, diminished, and formed between the object and the lens, regardless of the object's position.
- 🎓 The presenter encourages viewers to practice drawing ray diagrams and understanding the properties of images formed by lenses, which is crucial for mastering the topic.
- 📢 The video concludes with a call to action for viewers to try answering top three questions on the topic, engage in the comments, and subscribe to the presenter's educational platform for more content.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of the video?
-The primary purpose of the video is to simplify the concept of image formation for spherical lenses, specifically convex and concave lenses, by explaining the rules for image formation and demonstrating them with practical examples.
How does the presenter introduce the concept of image formation with a convex lens?
-The presenter introduces the concept by first explaining how to draw a convex lens accurately and then discussing the three light ray rules for image formation with a convex lens. The presenter also uses themselves as the object to demonstrate where the image would be formed in different scenarios.
What are the three light ray rules for a convex lens?
-The three light ray rules for a convex lens are: 1) A ray parallel to the principal axis after refraction passes through the focus on the other side of the lens. 2) A ray passing through the optical center of the lens goes straight, emerging without deviation. 3) A ray passing through the focus after refraction becomes parallel to the principal axis.
How does the presenter demonstrate the image formation with a convex lens?
-The presenter demonstrates the image formation by standing at different positions relative to the lens and applying the light ray rules to determine the position and properties of the image formed.
What are the properties of the image formed when the object is beyond 2F (twice the focal length) of a convex lens?
-When the object is beyond 2F of a convex lens, the image formed is real, inverted, diminished, and located between F and 2F.
What happens to the image when the presenter stands at the focal length (F) of the convex lens?
-When the presenter stands at the focal length (F) of the convex lens, the image formed is real, inverted, and highly magnified, and it appears to be at infinity.
How does the presenter explain the image formation with a concave lens?
-The presenter explains the image formation with a concave lens by drawing the lens accurately, stating the three light ray rules specific to concave lenses, and demonstrating how the image properties remain consistent regardless of the object's position.
What are the three light ray rules for a concave lens?
-The three light ray rules for a concave lens are: 1) A ray parallel to the principal axis after refraction appears to be coming from the focus. 2) A ray passing through the optical center of a concave lens goes straight through without being deviated. 3) A ray going towards the focus after refraction becomes parallel to the principal axis.
What are the properties of the image formed with a concave lens, regardless of the object's position?
-The image formed with a concave lens is always virtual, upright, diminished, and formed between the object and the lens.
What is the practical application of a convex lens when the object is very close to it?
-A practical application of a convex lens when the object is very close to it is as a magnifying glass, which produces a virtual, erect, and magnified image.
How does the presenter encourage interaction and further learning after the main content of the video?
-The presenter encourages interaction by posing top three questions related to the topic for the viewers to solve and share their answers in the comments. The presenter also invites viewers to explore more science and math videos on their website and subscribe to their YouTube channel for further learning.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CAHAYA DAN ALAT OPTIK (PART 3) : CERMIN CEMBUNG DAN LENSA CEKUNG IPA KELAS 8 SMP
Why Does Light Bend? | Concave & Convex Lenses | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz

Convex and concave Lenses - Physics - Eureka.in

Espelhos Planos, Côncavos e Convexos (Como as Imagens se Formam?)

Images Formed on Mirrors and Lenses | Grade 10 Science DepEd MELC Quarter 2 Module 4
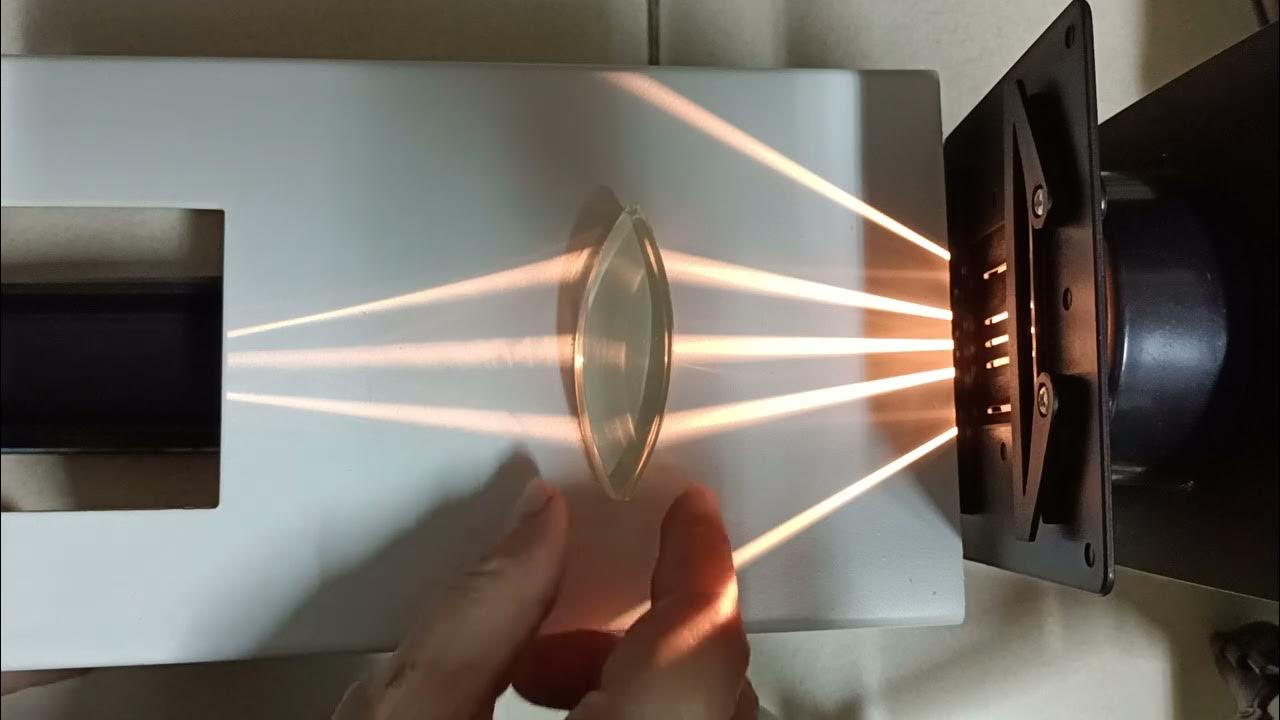

Pembiasan Cahaya Lensa Cembung dan Lensa Cekung
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)