Lesson 4-1, Video 5; Perpendicular Line 2
Summary
TLDRThis educational script guides viewers through finding the equation of a line perpendicular to a given line. It begins with a line in slope-intercept form, y = -1/7x + 7, and teaches how to derive the perpendicular line's slope, which is the opposite reciprocal of the original. Using the point-slope form, the script demonstrates how to plug in the slope and a given point to find the new line's equation. The lesson then transitions to a unique case where the perpendicular line is to the x-axis, illustrating the concept with a visual example and explaining that vertical lines are represented by x-values, leading to the equation x = 4 for the line passing through (4, -2).
Takeaways
- 📐 The original line is given by the equation y = -1/7x + 7, and its slope is identified as -1/7.
- 🔄 To find a line perpendicular to the original, use the opposite reciprocal of the original slope, resulting in a slope of 7 for the perpendicular line.
- 📍 The perpendicular line must pass through the point (-6, 6), which is provided in the script.
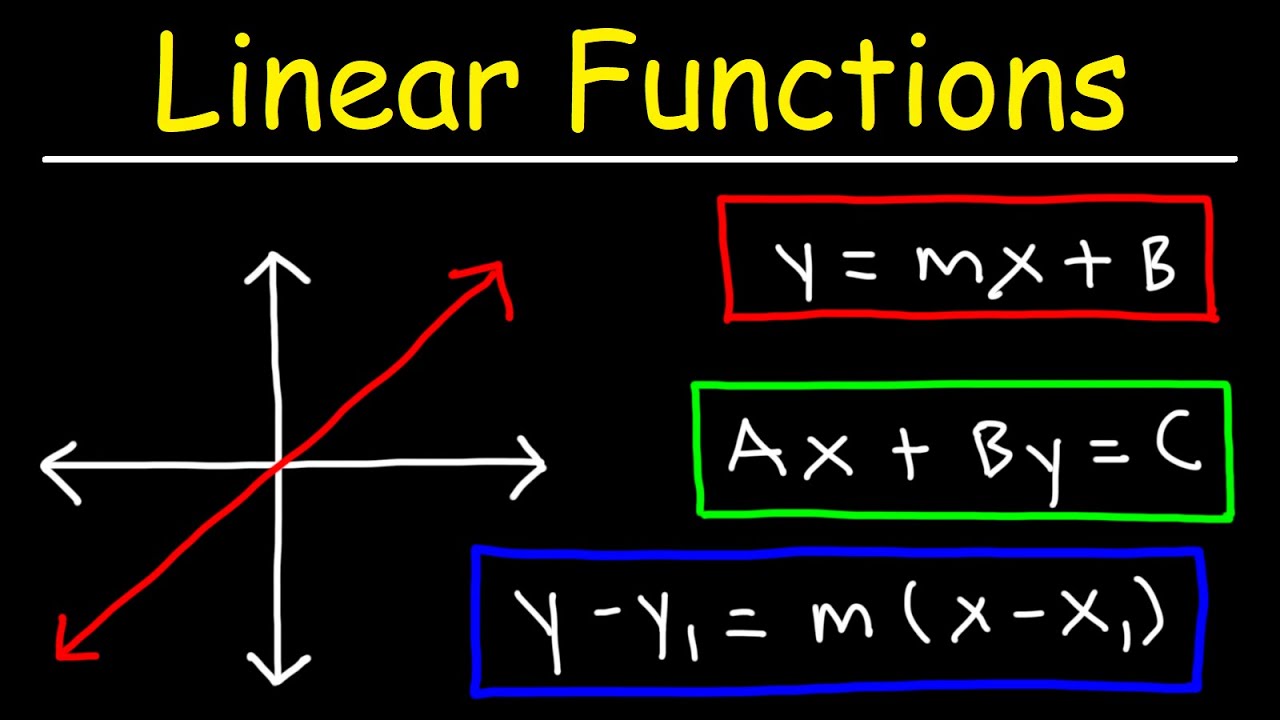
- 📘 The point-slope form of the equation of a line is used, which is y - y1 = m(x - x1), where m is the slope and (x1, y1) is a point on the line.
- 🔢 Plugging in the values for the perpendicular line gives the equation y - 6 = 7(x + 6).
- ✏️ Simplifying the equation from the point-slope form results in the final equation of the perpendicular line.
- 📏 For the second example, a line perpendicular to the x-axis is sought, which means it must be a vertical line.
- 📍 The vertical line should pass through the point (4, -2), as specified in the script.
- 📑 Vertical lines are represented by equations of the form x = constant, using the x-coordinate of the given point.
- 🔑 The final equation for the vertical line is x = 4, which is derived from the x-coordinate of the point (4, -2).
Q & A
What is the slope of the line given by the equation y = -1/7x + 7?
-The slope of the line is -1/7.
How do you find the slope of a line perpendicular to a given line?
-The slope of a line perpendicular to a given line is the opposite reciprocal of the original line's slope.
What is the slope of the line perpendicular to y = -1/7x + 7?
-The slope of the perpendicular line is the opposite reciprocal of -1/7, which is 7.
What is the point-slope form of a line?
-The point-slope form of a line is given by the equation y - y1 = m(x - x1), where m is the slope and (x1, y1) is a point on the line.
What is the point-slope form of the line perpendicular to y = -1/7x + 7 that passes through (-6, 6)?
-The point-slope form of the line is y - 6 = 7(x + 6).
What is the slope of a line perpendicular to the x-axis?
-A line perpendicular to the x-axis is vertical, and its slope is undefined because it has an infinite slope.
How can you represent a vertical line in a coordinate plane?
-A vertical line is represented by an equation of the form x = a, where 'a' is the x-coordinate of the line.
What is the equation of the line that is perpendicular to the x-axis and passes through the point (4, -2)?
-The equation of the line is x = 4, as it is a vertical line passing through the x-coordinate 4.
Why do horizontal and vertical lines form a 90-degree angle?
-Horizontal and vertical lines form a 90-degree angle because they are perpendicular to each other, intersecting at a right angle.
How can you determine if two lines are perpendicular without using slopes?
-You can determine if two lines are perpendicular by checking if they intersect at a 90-degree angle, or by visual inspection on a graph.
What is the significance of the opposite reciprocal in finding the slope of a perpendicular line?
-The opposite reciprocal is significant because it ensures that the product of the slopes of two perpendicular lines is -1, which is a requirement for perpendicularity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)