Lineaire formules (VWO wiskunde B)
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the concept of linear equations, illustrating their definition, properties, and application through an example. It introduces the general form of a linear equation, 'y = mx + b', where 'm' is the slope indicating the line's steepness, and 'b' is the y-intercept. The script guides viewers through deriving the equation of a line parallel to another, using a given point on the line, emphasizing the importance of step-by-step problem-solving to ensure understanding and success in similar tasks.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video is about linear equations, explaining what they are, their properties, and how to apply this knowledge with an example.
- 📈 Linear equations are associated with graphs that represent straight lines, and each straight line has a corresponding linear equation.
- 🔍 The general form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where 'm' is the slope and 'b' is the y-intercept.
- 📉 The slope ('m') indicates the steepness of the line; a positive slope means the line rises as it moves to the right, while a negative slope indicates a downward movement.
- 📍 The y-intercept ('b') is the point where the line crosses the y-axis, representing the starting point of the line on the y-axis.
- 🔄 The concept of parallel lines is discussed, emphasizing that parallel lines have the same slope, indicating they are equally steep.
- 📝 The process of deriving the equation of a line involves using the general form y = mx + b, identifying the slope ('m'), and finding the y-intercept ('b').
- 🔢 To find the y-intercept, the video suggests using a known point on the line and solving for 'b' by substituting the point's coordinates into the equation.
- 📐 The video provides a step-by-step example of finding the equation of a line that passes through a given point and is parallel to another line.
- 👉 The importance of writing down the general form of the equation first is highlighted to demonstrate understanding and to systematically approach the problem.
- 📝 The conclusion of the video is to always write down the final equation as the answer to the question, ensuring that the problem is fully solved and the solution is clear.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is linear equations, explaining what they are, their properties, and how to apply this knowledge with an example.
What is the general form of a linear equation according to the video?
-The general form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
What does the slope (m) in a linear equation represent?
-The slope (m) represents the steepness of the line, indicating how much the line rises or falls for each unit moved along the x-axis.
What is the y-intercept (b) in a linear equation?
-The y-intercept (b) is the point where the line crosses the y-axis, which can be found as the value of b when x equals zero.
How can you determine if two lines are parallel according to the video?
-Two lines are parallel if they have the same slope, meaning their direction coefficients (m) are equal.
What is the example given in the video to illustrate a linear equation?
-The example given in the video is y = -x + 3, which is a linear equation representing a straight line on a graph.
How does the video suggest finding the y-intercept if it's not immediately clear?
-The video suggests using a known point on the line to find the y-intercept by substituting the x and y values of the point into the linear equation and solving for b.
What is the process for writing the equation of a line that passes through a given point and is parallel to another line?
-The process involves starting with the general form of a linear equation (y = mx + b), identifying the slope (m) from the parallel line, and then using a point on the new line to solve for the y-intercept (b).
What is the importance of writing down the general form of a linear equation when solving for a specific line?
-Writing down the general form of a linear equation demonstrates that you have the necessary knowledge to approach the problem and ensures you have a clear starting point for solving for the specific values of m and b.
How does the video emphasize the importance of step-by-step problem solving?
-The video emphasizes step-by-step problem solving by showing the process of determining the slope and y-intercept, and then writing the final equation, to ensure all parts of the problem are addressed and to avoid missing any steps.
What is the final step the video suggests after finding the values of m and b?
-The final step suggested by the video is to write down the conclusion, which is the complete linear equation with the found values of m and b, to answer the question posed by the problem.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

METODE NUMERIK P2 | METODE GAUSS UNTUK MENYELESAIKAN SPL

Funkcje w 6 minut
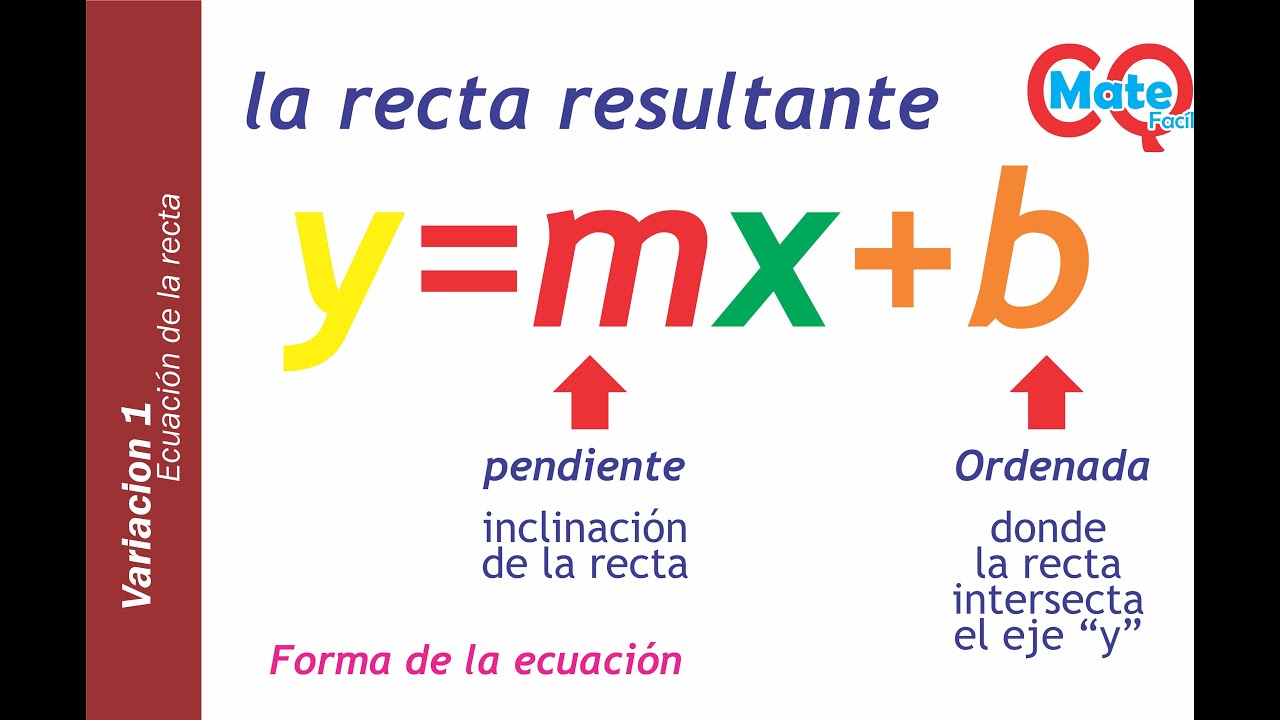
y=mx+b Ecuacíon de la recta, relación funcional

Matematika Kelas 9 Bab 1 Sistem Persamaan Linear Dua Variabel - hal. 2 - 6 - Kurikulum Merdeka

Recurrence Relation | Solution of Recurrence Relation | Discrete Mathematics by Gp sir

memahami konsep persamaan linear satu variabel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)