GCSE Chemistry - Acids and Bases #34
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the pH scale, which measures a solution's acidity or alkalinity from 0 to 14. It explains that a pH of 7 is neutral, while lower values are acidic and higher values are alkaline. Examples include stomach acid at pH 2 and bleach at pH 12. Measuring pH can be done with indicators or a pH probe for more precision. Acids are defined as substances with a pH less than 7, releasing hydrogen ions, while bases and alkalis (a subgroup of bases that are water-soluble) have a pH greater than 7, forming hydroxide ions. The video also covers neutralization reactions between acids and bases, resulting in salts and water, and highlights common acids and bases like hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The pH scale is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is, ranging from 0 to 14.
- 🍋 Low pH numbers indicate high acidity, with stomach acid being around pH 2.
- 🌧️ Acid rain has a pH of about 4, showing its acidic nature.
- 🧼 Alkaline substances like washing up liquid have a pH around 9, while bleach is around 12.
- 💧 Pure water is neutral with a pH of 7, neither acidic nor alkaline.
- 🌈 pH can be measured using indicators, which are chemical dyes that change color based on pH levels.
- 🔬 A more precise method to measure pH is by using a pH probe connected to a meter, providing a numerical reading.
- 🧪 Acids are substances that form aqueous solutions with a pH less than 7, releasing hydrogen ions.
- 🧴 Alkalis are a subgroup of bases that are soluble in water and form solutions with a pH greater than 7, releasing hydroxide ions.
- ⚖️ A neutralization reaction occurs when an acid and a base react, producing a salt and water, with a neutral pH of 7.
- 📚 Common acids include hydrochloric, sulfuric, and nitric acids, while common bases are often hydroxides or carbonates like sodium hydroxide or calcium carbonate.
Q & A
What is the pH scale and what does it measure?
-The pH scale is a measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is, ranging from 0 to 14. Low numbers indicate acidity, high numbers indicate alkalinity, and a pH of 7 is neutral, like pure water.
What is the pH level of stomach acid and acid rain?
-The pH level of stomach acid is around 2, which is highly acidic, and acid rain has a pH of about 4.
What is the pH of washing up liquid and bleach?
-Washing up liquid has a pH of around 9, and bleach has a pH of around 12, indicating they are alkaline.
How can pH be measured?
-pH can be measured using indicators, which are chemical dyes that change color depending on the pH, or by using a pH probe connected to a pH meter for more accurate electronic measurements.
What is the difference between a wide range indicator and a pH probe?
-A wide range indicator is a type of pH indicator that changes color across a wide range of pH values, while a pH probe provides a numerical reading and is more accurate and precise.
What is an acid and how is it defined in terms of pH?
-An acid is defined as any substance that forms aqueous solutions with a pH of less than seven, due to the release of hydrogen ions in water.
What are bases and alkalis, and how do they differ in terms of pH?
-Bases are substances with a pH greater than seven, while alkalis are a subgroup of bases that are soluble in water and form solutions with a pH greater than seven.
What happens when an acid and a base react together?
-When an acid and a base react, a neutralization reaction occurs, producing a salt and water. The pH of the products should be seven because they are neutral.
What are some common acids and bases mentioned in the script?
-Common acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid, while common bases are generally hydroxides or carbonates like sodium hydroxide or calcium carbonate.
Why is it important to know the pH of substances?
-Knowing the pH of substances is important for understanding their chemical properties, such as their reactivity and potential effects on the environment or biological systems.
How do hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions play a role in neutralization reactions?
-In neutralization reactions, hydrogen ions (H+) from the acid and hydroxide ions (OH-) from the base combine to form water (H2O), resulting in a neutral pH of seven.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What Is The pH Scale | Acids, Bases & Alkalis | Chemistry | FuseSchool
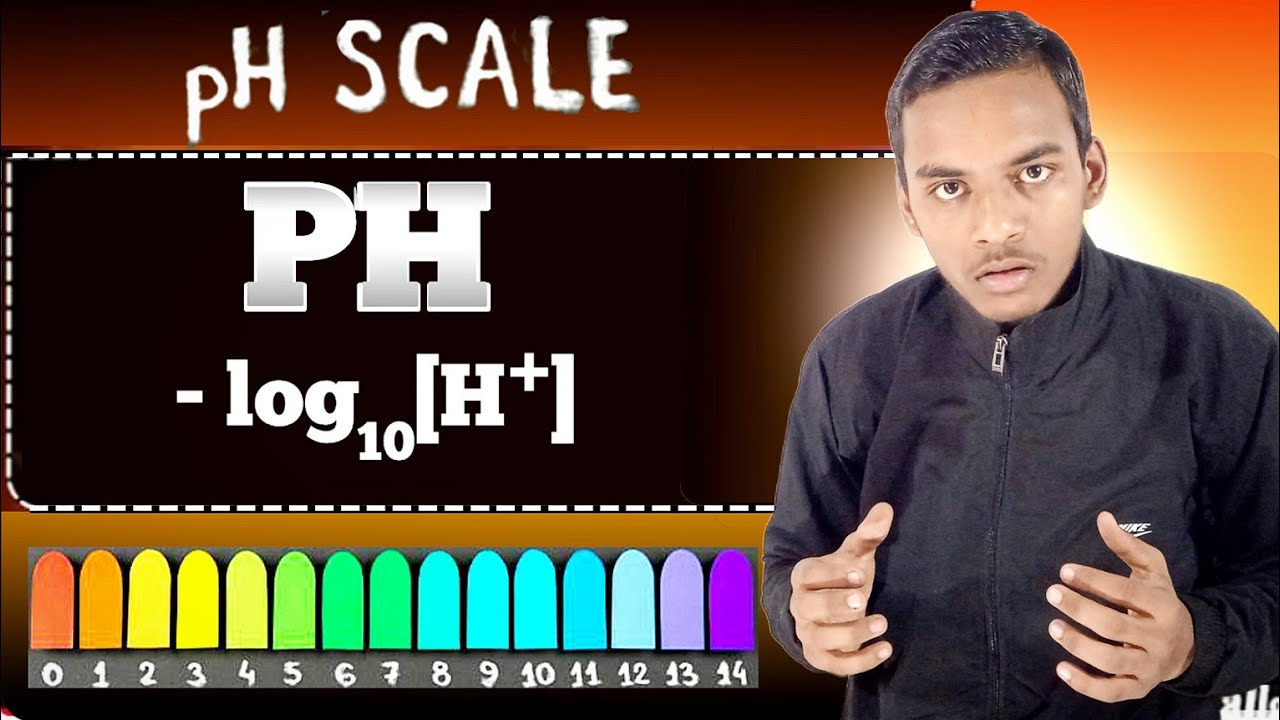
What is PH?🤔 PH क्या होता है ll How find it ll Chemistry ll importance in our daily life ll

What Are Indicators & How Do We Use Them? | Chemical Tests | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Introduction to pH | Biology foundations | High school biology | Khan Academy
Acid and Base | Acids, Bases & pH | Video for Kids
pH and pOH: Crash Course Chemistry #30
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)